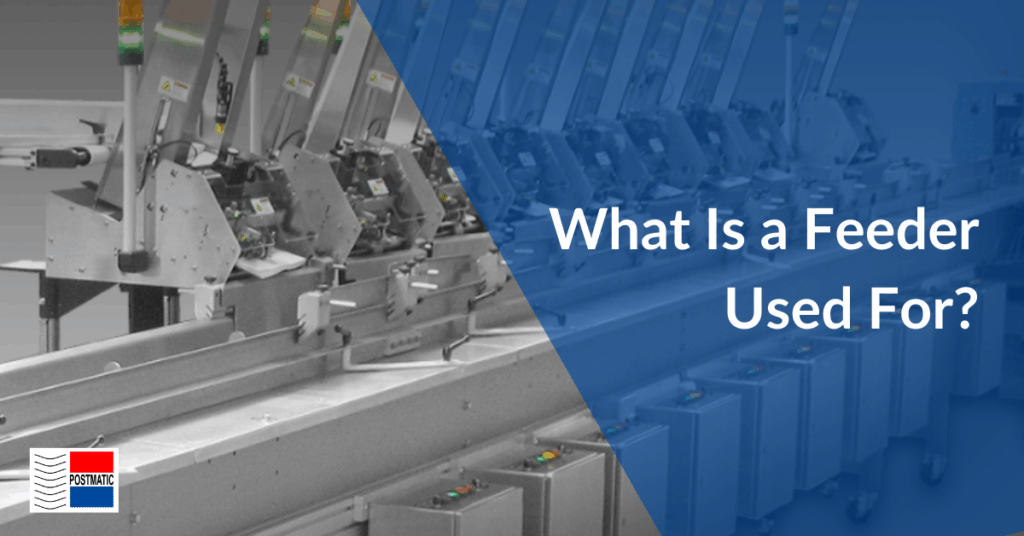
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for what feeder
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing the right feeder solutions can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers. With a myriad of options available, understanding the specific needs of your operations—whether in agriculture, animal husbandry, or industrial applications—is crucial. This guide to “what feeder” will illuminate the diverse types of feeders, their applications, and the nuances of selecting the best solutions tailored to your business context.
From livestock feeders that optimize feed efficiency to industrial feeders designed for material handling, this comprehensive resource covers it all. We delve into supplier vetting processes, helping you identify reliable partners who can meet your quality and compliance standards. Furthermore, we provide insights into cost considerations, ensuring that you can make informed financial decisions while maximizing your investment.
For B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Brazil and Saudi Arabia—this guide serves as a critical tool. It empowers you to navigate the complexities of the global feeder market with confidence, equipping you with the knowledge to enhance your supply chain and operational efficiency. With actionable insights and strategic recommendations, you’ll be well-prepared to make decisions that align with your business goals and foster long-term success.
Table Of Contents
- Top 4 What Feeder Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for what feeder
- Understanding what feeder Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of what feeder
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘what feeder’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for what feeder
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for what feeder
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘what feeder’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for what feeder Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing what feeder With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for what feeder
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the what feeder Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of what feeder
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for what feeder
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding what feeder Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Livestock Feeders | Designed for bulk feeding of animals; includes troughs and bins. | Agriculture, livestock management | Pros: Efficient feeding, reduces labor costs. Cons: High initial investment. |
| Bird Feeders | Various designs for attracting specific bird species; often decorative. | Wildlife conservation, landscaping | Pros: Promotes biodiversity, enhances aesthetics. Cons: Maintenance required, can attract pests. |
| Automatic Feeders | Mechanically dispense feed at set intervals; programmable settings. | Aquaculture, poultry farming | Pros: Reduces waste, ensures consistent feeding. Cons: Potential mechanical failures. |
| Feeder Roads | Infrastructure that connects smaller roads to major highways; facilitates transport. | Logistics, transportation planning | Pros: Increases accessibility, supports economic growth. Cons: High construction and maintenance costs. |
| Electric Feeders | Utilizes electric systems to distribute feed; often used in automated farms. | High-tech agriculture, dairy farms | Pros: Automation increases efficiency, reduces labor. Cons: Dependence on electricity, higher upfront costs. |
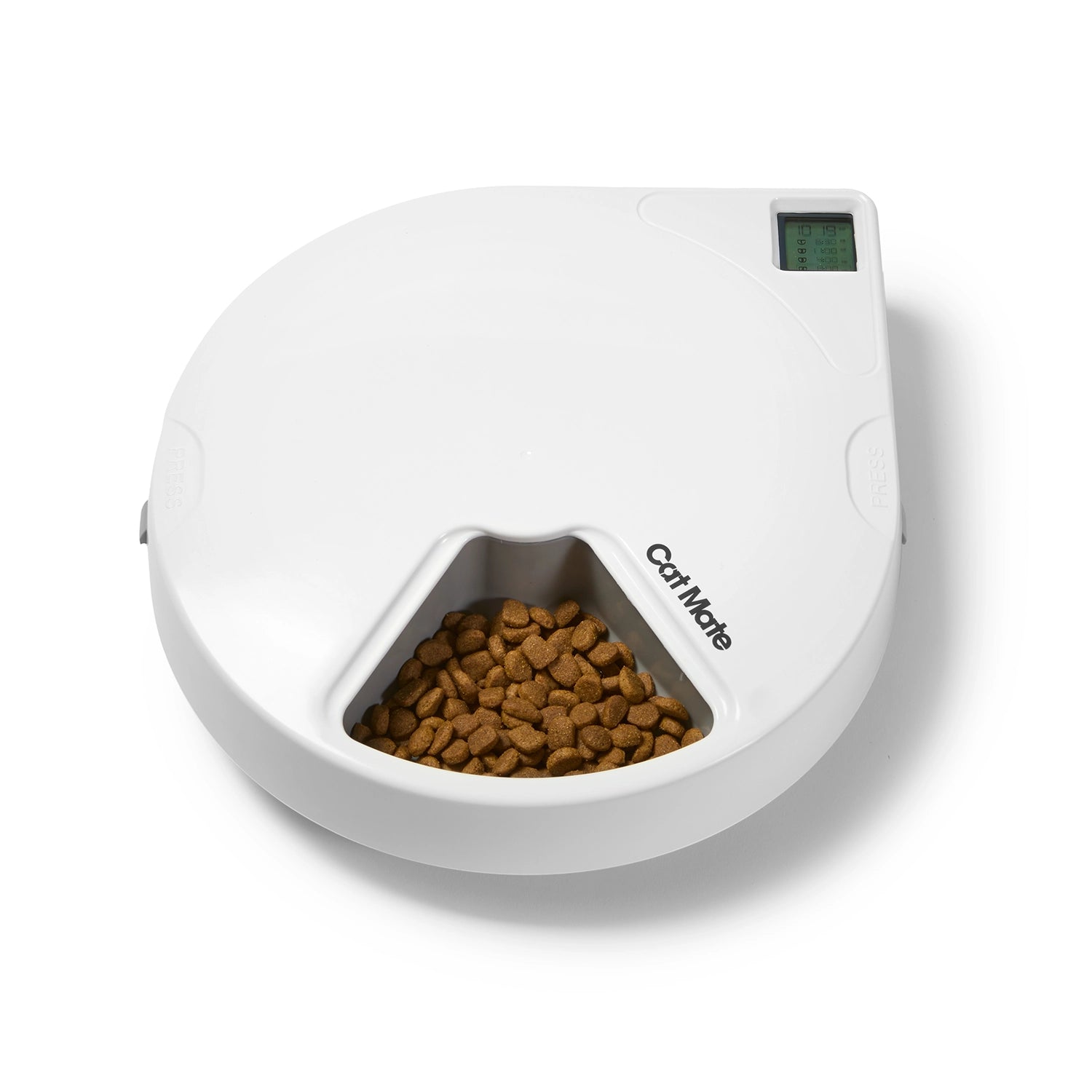
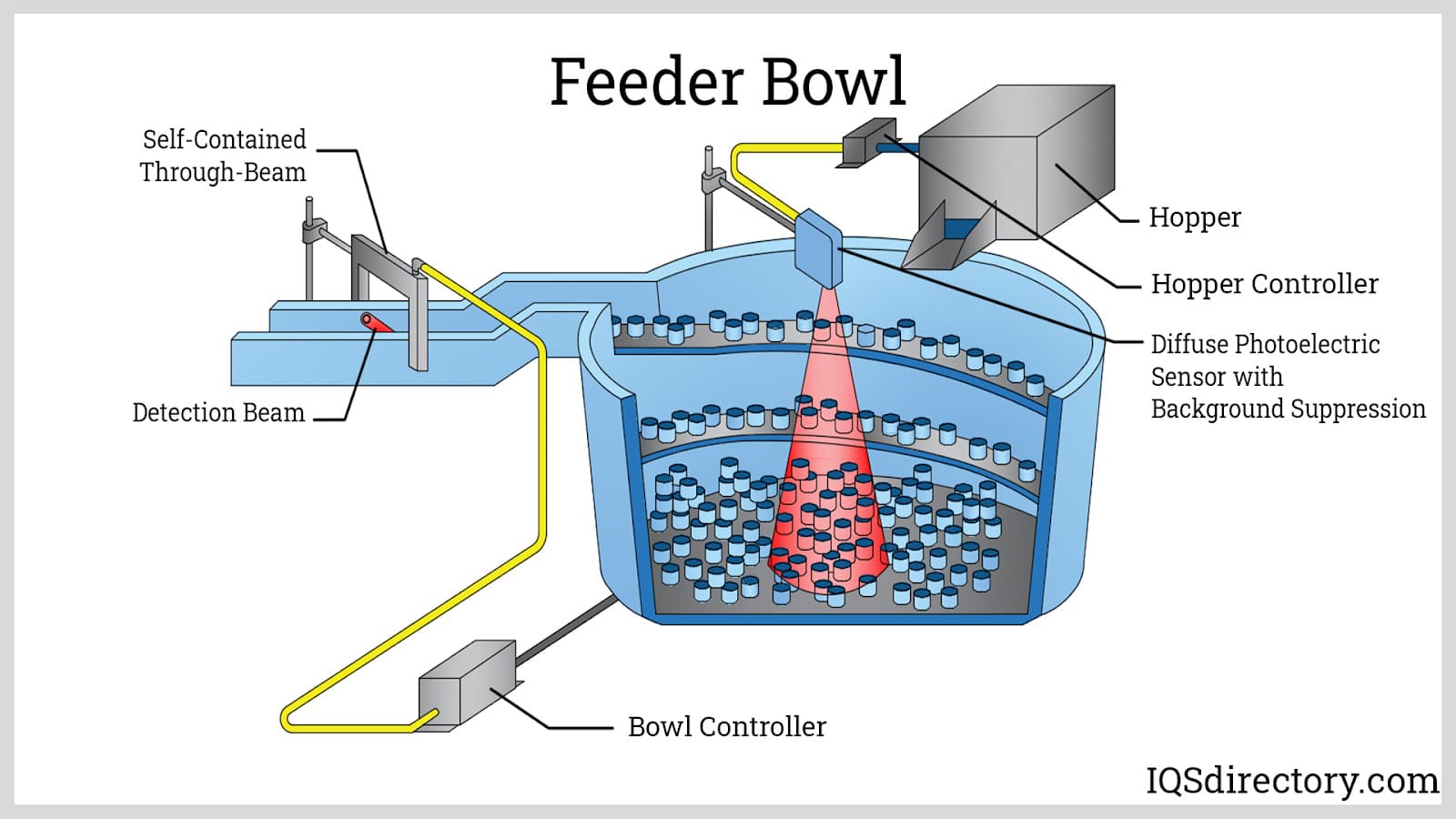
What Are Livestock Feeders and Their B2B Relevance?
Livestock feeders are essential devices designed for bulk feeding of farm animals, often including troughs, bins, and hoppers. These feeders allow for efficient distribution of feed, minimizing waste and labor costs. B2B buyers in agriculture and livestock management should consider the type of livestock they manage, the volume of feed required, and the feeder’s durability. While the initial investment can be significant, the long-term savings in labor and feed efficiency can justify the cost.

Illustrative image related to what feeder
How Do Bird Feeders Serve Business Needs?
Bird feeders come in various designs aimed at attracting specific bird species and are often used for aesthetic purposes in landscaping and wildlife conservation. For businesses involved in environmental education or landscaping, bird feeders can enhance the appeal of a property while promoting biodiversity. Buyers should assess the feeder’s material, ease of maintenance, and the types of birds they wish to attract. While they can enhance a location’s beauty, ongoing maintenance and potential pest issues should be factored into purchasing decisions.
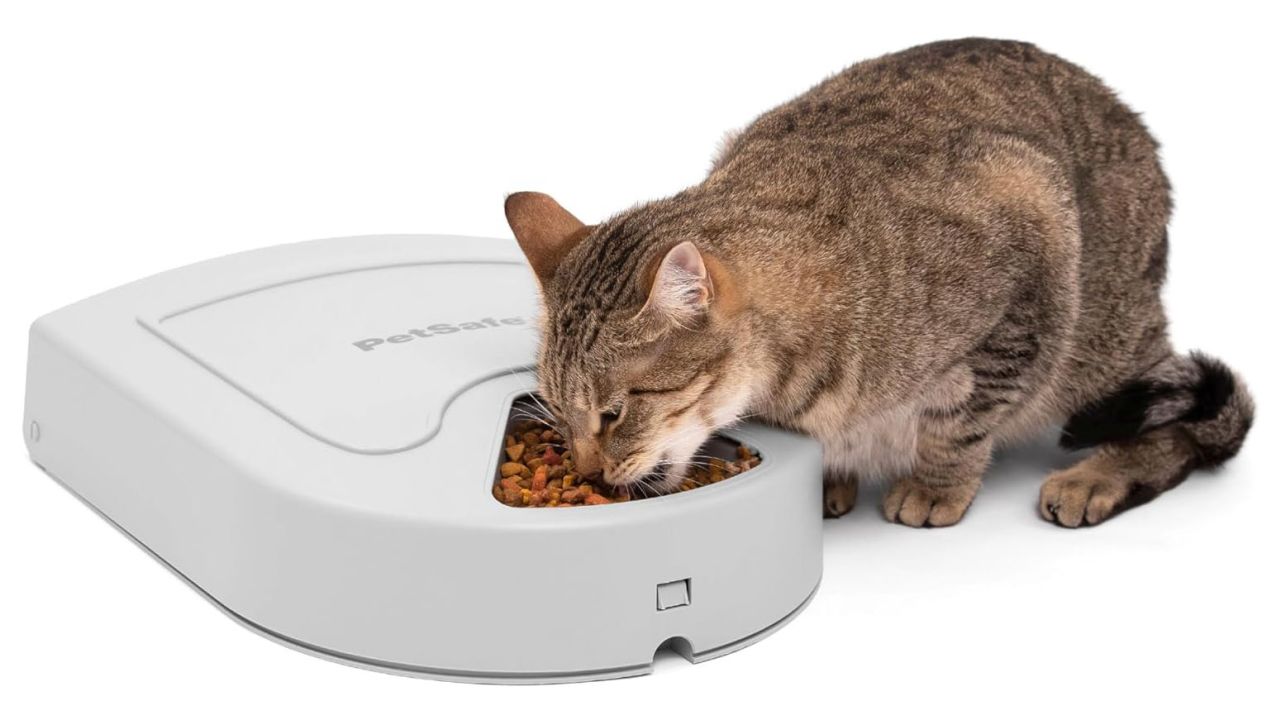
What Advantages Do Automatic Feeders Offer?
Automatic feeders are designed to dispense feed at predetermined intervals, making them ideal for aquaculture and poultry farming. These devices ensure that livestock receive a consistent amount of feed, which can reduce waste and improve growth rates. B2B buyers should consider the capacity, programming options, and reliability of these feeders. While they can lead to significant operational efficiencies, potential mechanical failures and the need for regular maintenance are critical considerations.
Why Are Feeder Roads Important in Logistics?
Feeder roads are smaller roads that connect rural areas to major highways, playing a crucial role in logistics and transportation planning. For businesses in logistics, these roads improve access to markets and resources, supporting economic growth. When evaluating feeder roads, buyers should consider construction costs, maintenance requirements, and their impact on traffic flow. While these roads can enhance operational efficiency, the initial investment and ongoing maintenance can be substantial.
What Are Electric Feeders and Their Benefits?
Electric feeders utilize automated systems to distribute feed, commonly used in high-tech agriculture and dairy operations. These feeders enhance efficiency by ensuring that livestock receive the appropriate amount of feed without manual intervention. B2B buyers should evaluate the feeder’s energy requirements, maintenance needs, and overall reliability. Although electric feeders can significantly reduce labor costs and improve feeding accuracy, their dependence on electricity and higher upfront costs are important factors to consider.
Key Industrial Applications of what feeder
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of what feeder | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | Livestock Feeders | Ensures efficient feeding and weight gain in livestock. | Quality of materials, capacity, and durability. |
| Manufacturing | Material Feeders in Production Lines | Streamlines production processes and minimizes waste. | Compatibility with existing machinery and maintenance support. |
| Food Processing | Ingredient Feeders for Automated Systems | Enhances accuracy in ingredient measurement and reduces labor costs. | Precision and reliability of the feeder system. |
| Energy & Utilities | Fuel Feeders for Power Generation | Optimizes fuel delivery and improves energy efficiency. | Compliance with safety standards and operational capacity. |
| Construction & Mining | Aggregate Feeders for Material Handling | Facilitates efficient movement of materials on-site. | Load capacity, adaptability to site conditions, and supplier reliability. |
How is ‘what feeder’ Used in Agriculture?
In the agriculture sector, livestock feeders play a crucial role in ensuring that animals receive the right amount of feed for optimal growth. These feeders are designed to minimize waste and maximize feed efficiency, which is essential for farmers looking to improve their profit margins. International buyers, especially from regions like Africa and South America, should consider factors such as feeder capacity, material durability, and ease of cleaning to ensure they meet local agricultural standards and practices.

Illustrative image related to what feeder
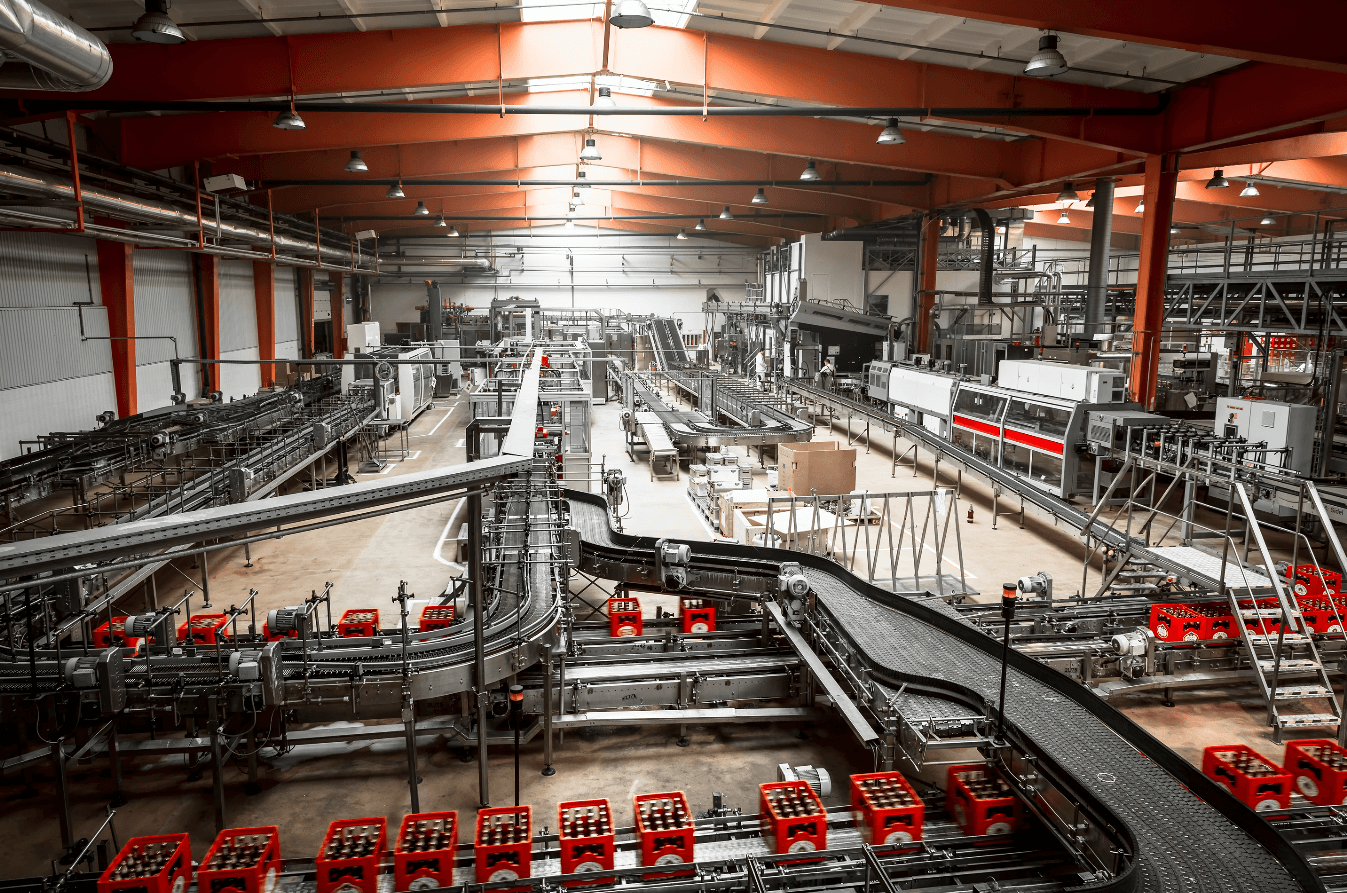
What Role Do Material Feeders Play in Manufacturing?
Material feeders are integral in manufacturing environments, where they automate the delivery of raw materials to production lines. By reducing manual handling, these feeders enhance operational efficiency and minimize the risk of human error. For B2B buyers, particularly in Europe and the Middle East, sourcing feeders that are compatible with existing machinery and offer robust maintenance support is vital to ensure uninterrupted production processes and lower downtime.
How Do Ingredient Feeders Benefit Food Processing?
In the food processing industry, ingredient feeders are utilized in automated systems to deliver precise amounts of ingredients for various products. This automation reduces labor costs and increases accuracy, which is critical for maintaining product quality. Buyers from emerging markets should prioritize precision and reliability in these systems, ensuring that the feeders can handle the specific ingredients used in local recipes and comply with food safety regulations.
Why Are Fuel Feeders Important in Energy & Utilities?
Fuel feeders are essential in power generation facilities, where they optimize the delivery of fuel to combustion systems. Efficient fuel delivery enhances energy efficiency and can lead to significant cost savings. For B2B buyers in regions like Brazil and Saudi Arabia, it is crucial to ensure that the feeders comply with local safety standards and can handle the specific types of fuel used in their operations, whether renewable or fossil-based.
Illustrative image related to what feeder
How Do Aggregate Feeders Assist in Construction & Mining?
In construction and mining, aggregate feeders facilitate the efficient movement of materials, such as sand and gravel, from storage to processing areas. These feeders help streamline operations and reduce material wastage. Buyers should consider load capacity and adaptability to varying site conditions when sourcing these feeders, ensuring they can withstand the rigors of the construction environment while maintaining reliability and performance.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘what feeder’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Ensuring Consistent Feed Quality for Livestock
The Problem: Many B2B buyers in the agricultural sector face challenges with inconsistent feed quality when sourcing feeders for livestock. This can lead to health issues in animals, decreased productivity, and ultimately financial losses. Variability in feed composition can occur due to supplier differences, seasonal variations, or inadequate storage conditions. Buyers often struggle to find reliable suppliers that can guarantee the nutritional value and quality of feed consistently.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing feeders from reputable suppliers that provide detailed nutritional information and quality certifications for their feed products. Conducting thorough due diligence on potential suppliers is essential. This includes checking for industry certifications, such as ISO or organic certifications, and requesting samples for analysis before committing to larger orders. Implementing a regular quality control process, including batch testing for key nutritional components, can also help ensure that the feed provided meets the required standards. Additionally, establishing long-term relationships with a few trusted suppliers can lead to more consistent supply and quality assurance.
Scenario 2: Optimizing Feed Delivery Logistics
The Problem: A frequent challenge for B2B buyers in the feeder market is the logistics of feed delivery. Delays in transportation can disrupt feeding schedules, impacting livestock health and growth rates. Buyers often deal with multiple suppliers, leading to confusion and inefficiencies in managing deliveries. This can be particularly problematic in regions where infrastructure may be lacking or during peak seasons when demand for feed surges.

Illustrative image related to what feeder
The Solution: To optimize feed delivery logistics, buyers should implement a centralized management system that tracks orders, deliveries, and inventory levels. Using technology like supply chain management software can help streamline operations by providing real-time data on feed availability and delivery schedules. Buyers should also consider working with logistics partners that specialize in agricultural supply chains to ensure timely and efficient delivery. Additionally, establishing a just-in-time inventory system can help maintain optimal feed levels, reducing the risk of shortages while minimizing storage costs.
Scenario 3: Adapting to Local Regulatory Standards
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter difficulties navigating the complex regulatory landscape regarding animal feed and feeders, especially in international markets. Different countries have varying regulations concerning feed composition, additives, and labeling, which can lead to compliance issues and potential fines. This situation is particularly challenging for buyers who operate in multiple regions with distinct regulatory requirements.
The Solution: To effectively navigate regulatory standards, buyers should invest in understanding the specific regulations of the regions in which they operate. This includes consulting with local agricultural authorities and industry experts to stay informed about changes in legislation. Developing a compliance checklist can help buyers ensure that all feed products meet local standards before purchasing. Additionally, collaborating with suppliers who have a strong understanding of local regulations can provide an added layer of assurance. Engaging legal counsel familiar with agricultural law can also be beneficial for ensuring compliance and avoiding costly penalties.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for what feeder
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Feeders, and What Are Their Key Properties?
When selecting materials for feeders, especially in international B2B contexts, it is essential to understand the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material. This knowledge not only influences the performance of the feeder but also ensures compliance with local standards and preferences.
What Are the Key Properties of Stainless Steel for Feeders?
Stainless steel is a popular choice for feeders due to its excellent corrosion resistance and mechanical strength. It typically has a high-temperature rating, making it suitable for various environments. Stainless steel is also easy to clean, which is crucial in maintaining hygiene in applications involving food or animal feed.

Illustrative image related to what feeder
Pros: Its durability and resistance to rust and staining make it ideal for long-term use. Stainless steel is also relatively easy to fabricate, which can streamline the manufacturing process.
Cons: The primary disadvantage is its cost, as stainless steel can be more expensive than other materials. Additionally, while it is resistant to corrosion, it is not immune to certain acids or chlorides, which may limit its application in specific environments.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including water, oils, and various feed types. However, it may not be suitable for highly acidic or alkaline substances.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A240 for stainless steel is crucial. Buyers in regions like Europe and the Middle East often prefer grades like 304 or 316, which offer enhanced corrosion resistance.
How Does Plastic Compare as a Material for Feeders?
Plastic, particularly high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and polypropylene, is another common material for feeders. These plastics are lightweight and resistant to many chemicals, making them versatile for various applications.
Pros: Plastics are generally more affordable than metals and can be produced in various colors and shapes. They are also resistant to corrosion and do not rust, which is advantageous in humid environments.
Cons: The main drawback is that plastics may not withstand high temperatures or pressures as well as metals. They can also become brittle over time, especially when exposed to UV light.
Impact on Application: Plastic feeders are suitable for dry feed and some liquid applications but may not be ideal for high-temperature or high-pressure scenarios.

Illustrative image related to what feeder
Considerations for International Buyers: International buyers should ensure that the plastic materials comply with food safety regulations, such as FDA standards in the U.S. or EU regulations in Europe.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Feeder Construction?
Aluminum is often used in feeder construction due to its lightweight nature and good corrosion resistance. It is particularly useful in applications where weight is a concern, such as in mobile or portable feeders.
Pros: Aluminum is relatively inexpensive and easy to work with, allowing for efficient manufacturing processes. Its resistance to corrosion makes it suitable for outdoor applications.
Cons: While aluminum is durable, it is softer than steel and may not withstand heavy impacts or abrasive materials as well. Additionally, it can be prone to oxidation, which may affect its appearance and performance over time.
Impact on Application: Aluminum feeders are suitable for a variety of media, but care must be taken with abrasive materials that could wear down the surface.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should check for compliance with relevant standards such as ASTM B221 for aluminum extrusions. In regions like Africa and South America, local sourcing may also influence material choice.
How Does Composite Material Enhance Feeder Performance?
Composite materials, which combine plastic and fiberglass, offer unique advantages for feeder applications. They provide strength while remaining lightweight and resistant to various environmental factors.
Pros: Composites are highly durable and resistant to corrosion, making them suitable for harsh environments. They also offer good thermal insulation properties.
Cons: The primary limitation is the cost, as composite materials can be more expensive than traditional plastics or metals. Additionally, the manufacturing process can be more complex, which may lead to longer lead times.

Illustrative image related to what feeder
Impact on Application: Composites are well-suited for both dry and liquid feed applications, particularly in environments with extreme temperatures or corrosive substances.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that composites meet local standards and regulations, particularly regarding food safety and environmental impact.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Feeders
| Material | Typical Use Case for what feeder | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Food and animal feed applications | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost | High |
| Plastic | Dry feed and liquid applications | Lightweight and cost-effective | Limited high-temperature use | Low |
| Aluminum | Portable and outdoor feeders | Lightweight and good corrosion resistance | Softer than steel | Medium |
| Composite | Harsh environments and extreme conditions | High durability and insulation | Higher manufacturing complexity | High |
This analysis provides B2B buyers with a comprehensive overview of material options for feeders, enabling informed decisions based on performance, cost, and compliance with local standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for what feeder
What Are the Typical Manufacturing Processes for a Feeder?
The manufacturing of feeders, whether for agricultural, industrial, or other applications, involves several critical stages. Understanding these processes allows B2B buyers to evaluate potential suppliers effectively.
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Feeders?
-
Material Preparation
– Selection of Raw Materials: The choice of materials varies based on the type of feeder. Common materials include stainless steel for durability and corrosion resistance, plastics for lightweight designs, and galvanized metals for cost-effective solutions.
– Material Treatment: This may include processes such as cutting, shearing, and surface treatment (e.g., galvanizing or powder coating) to enhance performance and lifespan. -
Forming
– Shaping Techniques: Forming involves bending, stamping, or molding the prepared materials into desired shapes. For instance, sheet metal feeders may be formed through hydraulic presses, while plastic components could be produced via injection molding.
– Precision Engineering: High precision is critical in forming to ensure that all parts fit together seamlessly, which is vital for the feeder’s functionality. -
Assembly
– Component Integration: This stage involves assembling various components, which may include hoppers, trays, and electronic controls, depending on the feeder’s complexity.
– Automation vs. Manual Assembly: Depending on production scale and complexity, assembly may be done manually or through automated processes. Automated lines enhance consistency and speed, while manual assembly can allow for more intricate designs. -
Finishing
– Surface Treatments: After assembly, feeders often undergo finishing processes, such as polishing, painting, or applying protective coatings, to enhance aesthetic appeal and resistance to environmental factors.
– Final Inspection: This stage ensures that all components meet quality standards before the product is packaged and shipped.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Feeder Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of feeder manufacturing, ensuring that products meet both industry standards and customer expectations.

Illustrative image related to what feeder
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Look For in Feeders?
-
ISO 9001 Certification
– This globally recognized standard focuses on quality management systems (QMS) and is essential for ensuring that suppliers maintain consistent quality in their manufacturing processes. -
Industry-Specific Certifications
– Depending on the feeder’s application, additional certifications may be relevant:- CE Marking: Indicates compliance with European safety, health, and environmental requirements.
- API Standards: Relevant for feeders used in the oil and gas industry, ensuring they meet specific operational and safety standards.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints During Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are essential for maintaining the integrity of the manufacturing process.
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC)
– Raw Material Inspection: Before materials enter the production line, they should be inspected for quality and compliance with specifications. This may include checking for material grades and certifications. -
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC)
– Monitoring During Production: Regular checks during manufacturing help identify defects early. This can involve measuring dimensions, testing for proper assembly, and ensuring that manufacturing processes are followed correctly. -
Final Quality Control (FQC)
– End-of-Line Testing: Completed feeders undergo final inspections and tests to verify functionality, safety, and compliance with relevant standards. This may include load testing and functionality assessments.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, especially those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, ensuring the quality of feeders involves several strategies:
-
Supplier Audits
– Conducting regular audits of potential suppliers can reveal their adherence to quality standards and manufacturing processes. Buyers should look for suppliers with a history of successful audits and certifications. -
Quality Assurance Reports
– Requesting detailed QA reports from suppliers can provide insights into their QC processes, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC stages. These reports should be comprehensive and available upon request. -
Third-Party Inspections
– Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality practices. These inspections can be conducted at various stages of the manufacturing process, ensuring that standards are upheld throughout.
What Are the Common Testing Methods Used in Quality Control?
Understanding common testing methods can help buyers assess the reliability of feeders:
-
Mechanical Testing
– This includes tensile, compression, and impact testing to evaluate the strength and durability of materials used in the feeder. -
Functional Testing
– Feeders should be tested under operational conditions to ensure they perform as expected. This may involve simulating the feeder’s working environment to assess performance. -
Environmental Testing
– For feeders exposed to harsh conditions, environmental tests (e.g., salt spray tests for corrosion resistance) are crucial to validate long-term performance.
What Nuances Should International Buyers Be Aware of Regarding Quality Control?
B2B buyers from diverse regions must be aware of specific nuances in quality assurance:
- Cultural and Regulatory Differences: Understanding local regulations and cultural practices related to quality control can affect supplier selection and compliance.
- Language Barriers: Clear communication is vital; therefore, buyers should ensure that all documentation, including quality standards and test results, is available in a language they understand.
- Logistical Considerations: International shipping can introduce variability in product quality. Buyers should discuss how suppliers handle logistics and any steps taken to maintain quality during transportation.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers for feeders, ensuring reliability and compliance with international standards.

Illustrative image related to what feeder
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘what feeder’
To assist international B2B buyers in sourcing the appropriate feeder, this guide provides a practical checklist to streamline the procurement process. Whether you’re looking for animal feeders, material feeders, or other types, following these steps will help ensure you make informed and effective purchasing decisions.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is crucial for narrowing down your options. Consider the type of feeder you need—whether it’s for livestock, poultry, or industrial applications. Detail the capacity, materials, and any specific features that are essential for your operations, such as durability or automation capabilities.
- Capacity Requirements: Determine the volume of feed or materials the feeder must accommodate.
- Material Specifications: Identify if you require stainless steel, plastic, or other materials based on your operational environment.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers that specialize in the type of feeder you need. Utilize online platforms, industry directories, and trade shows to gather a list of potential vendors.
- Industry Reputation: Look for suppliers with a strong track record in your specific sector.
- Local vs. International: Consider the benefits of local suppliers who understand regional requirements and international suppliers who may offer advanced technologies.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications and Compliance
Before proceeding with a supplier, verify their certifications and compliance with international standards. This is particularly important in industries where safety and quality are paramount.

Illustrative image related to what feeder
- Quality Assurance Certifications: Check for ISO certifications or other relevant quality standards.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that the supplier adheres to local regulations regarding materials and safety.
Step 4: Request Product Samples
Requesting samples is an effective way to assess the quality and functionality of the feeder. This step allows you to evaluate whether the product meets your specifications and expectations.
- Functional Testing: Use the samples in your operational environment to test their performance.
- Material Quality Assessment: Check the durability and construction quality of the samples provided.
Step 5: Analyze Pricing and Payment Terms
Once you have identified a few potential suppliers, analyze their pricing structures and payment terms. Ensure that you consider the total cost of ownership, including shipping, installation, and maintenance.
- Comparative Cost Analysis: Create a spreadsheet to compare prices, features, and terms from different suppliers.
- Payment Flexibility: Look for suppliers who offer flexible payment options that suit your cash flow needs.
Step 6: Check References and Reviews
Before making a final decision, check references and customer reviews. Engaging with previous clients can provide insights into the supplier’s reliability and product performance.
- Client Testimonials: Seek feedback from customers in similar industries or regions.
- Case Studies: Request case studies that demonstrate the supplier’s ability to meet specific needs.
Step 7: Finalize the Contract
Once you’ve selected a supplier, it’s time to finalize the contract. Ensure that all agreed-upon terms are documented clearly, including delivery schedules, warranties, and support services.
- Clear Terms: Make sure all aspects, from pricing to service level agreements, are clearly outlined.
- Legal Review: Consider having a legal expert review the contract to protect your interests.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing feeders more efficiently, ensuring they select the right products and suppliers to meet their operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for what feeder Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing ‘What Feeder’?
When sourcing feeders, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The type and quality of materials significantly impact the overall cost. For example, high-grade plastics or metals may incur higher upfront costs but can enhance durability and performance.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary depending on the region and the complexity of the manufacturing process. Skilled labor may be required for more intricate designs, influencing the total cost.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs such as utilities, rent, and administrative expenses associated with production facilities. Efficient operations can help mitigate these costs.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling is often necessary for specialized feeders, which can add to initial costs but may reduce per-unit costs in larger production runs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes ensures product reliability and compliance with industry standards, but it also adds to the cost.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary based on distance, mode of transport, and Incoterms. Buyers should consider these factors, particularly when sourcing internationally.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically apply a margin to cover costs and generate profit. This margin can fluctuate based on competitive pressures and market demand.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Feeder Sourcing?
Several factors influence pricing in the feeder market, particularly for international buyers:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) can lead to significant cost savings. Bulk purchasing often allows buyers to negotiate lower per-unit prices.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized feeders tailored to specific needs may incur higher costs due to additional design and manufacturing efforts. Buyers should evaluate the necessity of these custom features against their budget.
-
Materials: The choice of materials directly impacts both the cost and the quality of the feeders. Sustainable or premium materials can enhance product value but may also increase initial expenditures.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that meet international quality standards or possess certifications may command higher prices. Buyers should weigh the importance of these certifications against their application requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reliability, experience, and reputation can influence pricing. Established suppliers may offer higher prices but provide assurances of quality and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is essential for managing logistics costs and responsibilities. Different terms can lead to variations in total landed costs.
What Buyer Tips Can Help Optimize Feeder Sourcing Costs?
B2B buyers can adopt several strategies to enhance their sourcing efficiency:
-
Negotiation: Engaging suppliers in discussions about pricing can yield favorable terms. Highlighting long-term relationships or potential volume increases can be advantageous.
-
Cost Efficiency: Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) rather than just the purchase price. Consider factors like maintenance, operational costs, and expected lifespan when making decisions.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of currency fluctuations, tariffs, and import duties that may affect pricing. Collaborating with local experts can help navigate these challenges.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for feeders can vary widely based on the factors mentioned above. It is essential for buyers to conduct thorough research and request quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure they receive the best value for their investment.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing what feeder With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to ‘What Feeder’
In the dynamic landscape of B2B solutions, identifying the right tools and methods is crucial for operational efficiency. When evaluating ‘what feeder’—a device designed to supply food or resources—it’s essential to consider viable alternatives. Each alternative presents unique advantages and disadvantages, influencing the decision-making process for international buyers across diverse markets.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | ‘What Feeder’ | Alternative 1: Automated Conveyor System | Alternative 2: Manual Feeding Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency in food distribution | Very high throughput, suitable for bulk | Moderate efficiency, labor-dependent |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment | High initial investment, lower long-term costs | Low initial investment, high labor costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Relatively easy to install and integrate | Complex installation, requires skilled labor | Simple to implement, minimal training needed |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance requirements | Requires regular maintenance and monitoring | Minimal maintenance, but high labor reliance |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for consistent feeding applications | Best for high-volume production environments | Suitable for small-scale operations or artisanal setups |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternatives
Automated Conveyor System
Automated conveyor systems are designed for high-volume operations, providing rapid and efficient food distribution. They excel in environments where bulk feeding is essential, such as in large-scale livestock operations or food processing plants. The primary advantage of this system is its throughput; however, the initial investment is significantly higher than that of ‘what feeder.’ Additionally, while maintenance costs can be minimized with proper care, the complexity of the system requires skilled technicians for installation and upkeep.
Manual Feeding Method
The manual feeding method is the most straightforward alternative, relying on human labor for food distribution. This method is cost-effective, especially for small-scale operations where automation may not be justified. The simplicity of implementation allows for quick adaptation, making it attractive for artisanal producers or businesses in developing regions. However, this approach is labor-intensive and can lead to inefficiencies and inconsistent feeding, which may affect overall productivity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Business Needs
When choosing between ‘what feeder’ and its alternatives, it is essential for B2B buyers to assess their specific operational requirements. Consider factors such as the scale of production, budget constraints, and the level of automation desired. For businesses seeking efficiency and reliability, ‘what feeder’ may provide the ideal balance between performance and cost. However, for those in high-volume scenarios, an automated conveyor system could be more suitable. Conversely, smaller operations may benefit from the simplicity and low cost of manual feeding methods. Ultimately, aligning the chosen solution with the operational goals will lead to improved productivity and profitability.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for what feeder
What Are the Key Technical Properties of a Feeder in B2B Transactions?
When considering the purchase of feeders, several technical properties are crucial for ensuring optimal performance and compliance with industry standards. Understanding these specifications can greatly influence decision-making and procurement processes.
1. Material Grade
The material grade of a feeder is critical as it directly impacts durability and performance. Common materials include stainless steel, plastic, and aluminum, each offering different levels of resistance to corrosion, wear, and temperature variations. For instance, stainless steel is preferred for its strength and resistance to rust, making it ideal for environments with high moisture or exposure to chemicals. Buyers should assess their specific operational conditions to choose the right material grade.
2. Feed Rate
The feed rate refers to the speed at which the feeder can dispense materials. This metric is essential for optimizing production efficiency, especially in high-volume operations. A feeder with an adjustable feed rate allows for flexibility in production processes, accommodating varying material types and sizes. Understanding feed rate capabilities can help buyers match feeders with their operational needs, ensuring they maintain productivity levels.
3. Tolerance Levels
Tolerance levels define the acceptable limits of variation in the dimensions of the feeder components. High precision in these specifications is vital for ensuring that feeders operate smoothly and integrate well with other machinery. For example, tighter tolerances may be necessary in applications where the feeder interacts closely with other parts, preventing jams or misalignments. Buyers must prioritize tolerances that align with their operational requirements to avoid costly downtime.
4. Power Requirements
The power requirements of a feeder, including voltage and phase, are crucial for compatibility with existing systems. Understanding whether a feeder operates on single-phase or three-phase power can influence installation costs and operational efficiency. Buyers should ensure that the power specifications match their facility’s electrical infrastructure to avoid complications during installation.
5. Safety Features
Safety features such as emergency stop buttons, overload protection, and safety guards are essential for compliance with industry regulations and for protecting workers. These features not only enhance operational safety but can also minimize liability for businesses. Buyers should evaluate safety certifications and features when selecting feeders to ensure they meet local safety standards.
What Are the Common Trade Terms Related to Feeders?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some common terms that buyers should understand:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of feeders, understanding the OEM’s reputation and reliability can help buyers choose high-quality products that meet their specifications.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest amount of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is essential for budget planning and inventory management. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their operational needs without overcommitting financially.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services. This tool is crucial for comparing costs and ensuring that buyers receive competitive pricing for feeders. A well-structured RFQ can facilitate a smoother procurement process.

Illustrative image related to what feeder
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms helps buyers understand shipping costs, delivery responsibilities, and risk management, ultimately leading to more informed decision-making.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. Understanding lead times is essential for inventory management and production planning. Buyers should factor in lead times when coordinating their supply chain operations to avoid disruptions.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing feeders, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and profitability.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the what feeder Sector
What Are the Key Drivers Influencing the Global What Feeder Market?
The global market for ‘what feeder’ systems is witnessing significant growth driven by several key factors. Firstly, the increasing demand for efficient food supply systems in agriculture is pushing innovations in feeder technologies, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, where agricultural productivity is crucial. Additionally, the rise of precision agriculture and smart farming technologies is transforming traditional feeding systems into more automated and data-driven solutions. This trend is especially relevant in Europe and the Middle East, where there is a strong focus on optimizing resource use and improving yield outputs.
Moreover, the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technologies into feeder systems is emerging as a game-changer. IoT-enabled feeders allow for real-time monitoring and data collection, which helps farmers make informed decisions regarding feed management. As a result, international B2B buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who can provide advanced tech solutions that enhance operational efficiency and reduce waste.

Illustrative image related to what feeder
Another notable trend is the consolidation of supply chains, with buyers seeking reliable partners who can ensure the timely delivery of high-quality feeder systems. This is particularly important for buyers in regions like Brazil and Saudi Arabia, where logistics and supply chain efficiency are vital for maintaining competitiveness. Overall, the ‘what feeder’ sector is evolving rapidly, and international buyers need to stay abreast of these trends to make informed sourcing decisions.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shape the What Feeder Sector?
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of the ‘what feeder’ market, with an increasing emphasis on reducing environmental impact and fostering ethical supply chains. International buyers are now prioritizing suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices, such as using eco-friendly materials and minimizing waste during production. This shift is particularly relevant in regions like Europe and the Middle East, where regulatory frameworks increasingly demand compliance with environmental standards.
One critical aspect of this trend is the adoption of green certifications, which signal a supplier’s commitment to sustainable practices. Buyers are encouraged to seek out products that carry certifications such as the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) or Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS), ensuring that their sourcing choices align with their sustainability goals. Furthermore, the use of recyclable materials in the production of feeders is gaining traction, allowing buyers to mitigate their environmental footprint.
Ethical sourcing practices also play a significant role in shaping buyer preferences. Companies that can demonstrate transparency in their supply chains and fair labor practices will likely gain a competitive edge. As global consumers become more conscious of sustainability, B2B buyers must align their sourcing strategies with these values to meet market expectations and enhance their brand reputation.

Illustrative image related to what feeder
What Historical Developments Have Influenced the What Feeder Market?
The evolution of the ‘what feeder’ market can be traced back to the early developments in agricultural practices. Initially, feeding systems were rudimentary, relying on manual processes that limited efficiency and scalability. However, as agricultural demands grew, particularly in the 20th century, innovations in feeder design and technology began to emerge. The introduction of mechanized feeders revolutionized livestock management, allowing for more efficient feeding processes and better resource management.
In recent decades, the focus has shifted towards automation and smart technologies, with the rise of IoT and data analytics transforming how feeders are utilized in modern agriculture. This evolution reflects a broader trend towards precision agriculture, where data-driven decisions are crucial for optimizing productivity and sustainability. As the market continues to evolve, understanding this historical context provides valuable insights for B2B buyers looking to navigate current and future trends in the ‘what feeder’ sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of what feeder
-
How do I choose the right feeder for my business needs?
Choosing the right feeder involves assessing your specific requirements, including the type of feed you need to dispense, the volume, and the feeding mechanism. Consider the size of your operations and the species of animals being fed. Evaluate materials for durability and hygiene, especially if you’re in regions with specific environmental conditions. Engage with suppliers to discuss customization options that can better meet your operational needs, ensuring efficiency and reliability in feed distribution. -
What are the key features to look for in a feeder?
Key features include adjustable dispensing mechanisms, ease of cleaning, and materials that are resistant to wear and tear. Look for feeders with robust designs that can withstand local weather conditions and animal behaviors. If you have multiple animal types, consider feeders that allow for different feed types. Additional features like anti-spill designs and integrated monitoring systems can enhance functionality and reduce waste, providing better value for your investment. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) when sourcing feeders?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly between suppliers. Many manufacturers may require a MOQ to cover production costs, particularly for customized feeders. It’s essential to communicate your needs directly with potential suppliers to negotiate terms that suit your business model. Smaller orders may be available, but they could come with higher per-unit costs. Consider bulk purchasing to lower overall expenses if your demand justifies it. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing feeders internationally?
Payment terms typically vary by supplier and may include options such as upfront payment, net 30/60/90 days, or letters of credit. Many suppliers prefer partial payment upfront with the balance upon delivery to mitigate risks. It’s crucial to establish clear payment terms before finalizing an order to avoid potential disputes. Ensure that you understand currency exchange implications and international transaction fees that may affect total costs. -
How can I vet suppliers for quality and reliability?
Vetting suppliers involves researching their history, customer reviews, and industry reputation. Request samples to evaluate product quality firsthand and inquire about certifications that ensure compliance with international standards. Establish communication with current or previous clients to gather insights into their experiences. Consider visiting the supplier’s facility if feasible, or utilize third-party inspection services to verify production capabilities and quality assurance processes. -
What should I know about logistics and shipping for feeder procurement?
Logistics and shipping considerations include selecting reliable freight forwarders, understanding customs regulations, and calculating shipping costs. Assess the lead time required for manufacturing and shipping to ensure timely delivery. Be aware of import duties and taxes that may apply in your country. Establishing a clear logistics plan with your supplier can help mitigate delays and ensure that your feeders arrive safely and on schedule. -
Are there customization options available for feeders?
Many suppliers offer customization options to meet specific requirements. This may include size adjustments, material choices, and branding elements such as logos or colors. Discussing your specific needs with potential suppliers can lead to tailored solutions that enhance functionality and align with your operational goals. Customization may also involve modifying feeders for particular animal species or feeding methods, improving efficiency and animal welfare. -
What quality assurance measures should I expect from feeder manufacturers?
Quality assurance measures should include adherence to international manufacturing standards, regular quality checks during production, and thorough testing of final products. Reputable manufacturers will provide documentation of their quality control processes and certifications. It’s advisable to request information on warranty policies and after-sales support, ensuring that you have recourse in case of defects or operational issues after purchase.
Top 4 What Feeder Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Merriam-Webster – Feeder Definition
Domain: merriam-webster.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Feeder is a noun defined as: 1) one that feeds, such as a device or apparatus for supplying food; 2) an animal that eats or takes nourishment, especially one being fattened; 3) something that supplies, replenishes, or connects, including tributaries, heavy wire conductors in electric distribution systems, branch transportation lines, or roads providing access to major arteries. Examples include bi…
2. Reddit – Feeder Conductors
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Feeder: All circuit conductors between the service equipment, the source of a separately derived system, or other power supply source and the final branch circuit overcurrent device. Examples include the SER between the main disconnect and panel, and the cable between a generator and transfer switch or panel.
3. Urban Dictionary – Terminology Explained
Domain: urbandictionary.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: This company, Urban Dictionary – Terminology Explained, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
4. WAPA – Feeder Listings for Virgin Islands
Domain: viwapa.vi
Introduction: WAPA Feeder Listing for Virgin Islands, includes feeder listings for St. Croix district and St. Thomas/St. John district, updated June 2024. WAPA Alerts messaging system available for service updates.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for what feeder
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Feeder Supply Chain?
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of feeders presents a significant opportunity for international B2B buyers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By prioritizing supplier relationships and leveraging local market insights, companies can optimize their procurement processes, reduce costs, and enhance product quality. Understanding the diverse applications of feeders—whether in agriculture, logistics, or energy—allows businesses to tailor their sourcing strategies effectively.
Investing in a robust feeder supply chain not only ensures continuity and reliability but also fosters innovation through collaboration with suppliers who share similar values and sustainability goals. As markets continue to evolve, staying ahead of the competition necessitates a proactive approach to sourcing that embraces flexibility and adaptability.
Illustrative image related to what feeder
We encourage B2B buyers to engage actively with suppliers, assess their sourcing strategies, and explore new partnerships that can drive growth and efficiency. The future of feeder procurement is ripe with potential; seize the opportunity to transform your supply chain and position your business for success in an increasingly interconnected world.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.