Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for can microchips be tracked
In an increasingly interconnected world, the ability to determine whether microchips can be tracked presents both a challenge and an opportunity for international B2B buyers. Understanding the nuances of microchip technology, including its applications and limitations, is crucial for businesses looking to enhance their operational efficiency and security. This guide delves into the intricacies of microchip tracking, covering various types of microchips, their applications across different industries, and the factors that influence supplier selection and cost.
B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries like Saudi Arabia and Brazil, will find actionable insights tailored to their unique market conditions. The guide not only clarifies the functionalities of microchips—highlighting the distinction between RFID technology and GPS tracking—but also provides a framework for evaluating potential suppliers. By addressing common concerns and offering strategic recommendations, this comprehensive resource empowers decision-makers to make informed purchasing choices that align with their business objectives.
As the global market evolves, equipping your organization with the right knowledge about microchip tracking can significantly impact your supply chain management, enhance product security, and improve customer trust.
Table Of Contents
- Top 4 Can Microchips Be Tracked Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for can microchips be tracked
- Understanding can microchips be tracked Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of can microchips be tracked
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘can microchips be tracked’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for can microchips be tracked
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for can microchips be tracked
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘can microchips be tracked’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for can microchips be tracked Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing can microchips be tracked With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for can microchips be tracked
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the can microchips be tracked Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of can microchips be tracked
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for can microchips be tracked
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding can microchips be tracked Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| RFID Microchips | Utilizes Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) technology. | Pet identification, inventory tracking | Pros: Cost-effective, passive scanning. Cons: No real-time tracking, limited range. |
| GPS-Enabled Microchips | Combines microchip technology with GPS for location tracking. | Asset tracking, personal safety | Pros: Real-time location data. Cons: Higher cost, requires power source. |
| Biometric Microchips | Incorporates biometric data for enhanced security. | Secure access control, identity verification | Pros: High security, unique identification. Cons: More complex and expensive. |
| Smart Microchips | Connects to mobile devices for notifications and updates. | Pet recovery, asset management | Pros: Immediate alerts, user-friendly. Cons: Requires smartphone compatibility. |
| Hybrid Microchips | Merges RFID and GPS technologies for comprehensive tracking. | Logistics, supply chain management | Pros: Versatile, extensive tracking capabilities. Cons: Higher costs and complexity. |
What Are RFID Microchips and Their B2B Relevance?
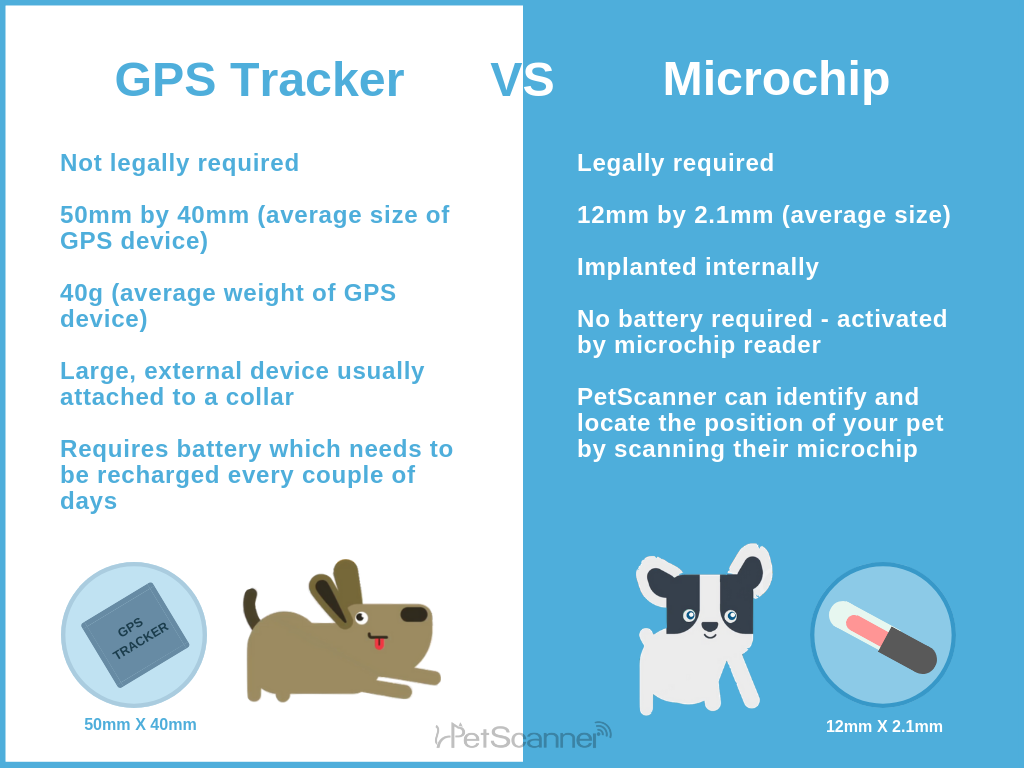
RFID microchips are small devices that utilize radio-frequency identification technology for identification purposes. They are commonly used in pet microchipping and inventory management. For B2B buyers, RFID microchips offer a cost-effective solution for tracking assets and ensuring efficient inventory control. However, they do not provide real-time location data, which may limit their effectiveness in scenarios requiring immediate tracking.
How Do GPS-Enabled Microchips Function in the B2B Space?
GPS-enabled microchips integrate traditional microchip technology with GPS capabilities, allowing for real-time tracking of assets or individuals. This technology is particularly valuable in sectors such as logistics and personal safety. B2B buyers should consider the higher initial costs and ongoing power requirements, but the advantage of real-time location updates can significantly enhance operational efficiency and security.

Illustrative image related to can microchips be tracked
What Are Biometric Microchips and Their Applications?
Biometric microchips are advanced devices that incorporate biometric data, such as fingerprints or retinal scans, to provide enhanced security measures. These microchips are increasingly used in secure access control systems and identity verification processes. For businesses, investing in biometric microchips can bolster security protocols. However, the complexity and higher costs associated with these systems may require careful consideration of ROI.
How Do Smart Microchips Improve User Experience for Businesses?
Smart microchips are designed to connect with mobile devices, providing users with notifications and updates regarding the status of the tracked item. This technology is particularly beneficial in pet recovery and asset management. B2B buyers should focus on the ease of use and immediate alert capabilities, though it is essential to ensure compatibility with existing mobile devices to maximize effectiveness.
What Are the Benefits of Hybrid Microchips for Supply Chain Management?
Hybrid microchips combine the functionalities of RFID and GPS technologies, offering comprehensive tracking solutions. They are especially useful in logistics and supply chain management, where both identification and real-time tracking are crucial. While hybrid microchips provide significant advantages in versatility and tracking capabilities, their complexity and higher costs necessitate a thorough evaluation of their integration into existing systems.
Key Industrial Applications of can microchips be tracked
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of can microchips be tracked | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Logistics and Supply Chain | Asset tracking and inventory management | Reduces loss, improves inventory accuracy, and enhances efficiency | Compatibility with existing systems, range of tracking, and data security measures |
| Agriculture | Livestock identification and monitoring | Enhances herd management, improves biosecurity, and aids in disease control | Durability in harsh environments, ease of integration, and regulatory compliance |
| Healthcare | Patient identification and medication tracking | Minimizes errors in patient care, enhances security, and streamlines processes | Compliance with health regulations, data privacy, and interoperability with health systems |
| Retail | Anti-theft measures and customer tracking | Reduces theft, enhances customer experience, and improves inventory turnover | Cost-effectiveness, ease of installation, and integration with point-of-sale systems |
| Pet Services | Reuniting lost pets with owners | Increases pet recovery rates, enhances customer satisfaction, and builds brand loyalty | Registration processes, international compatibility, and support for multiple chip types |
How is ‘can microchips be tracked’ utilized in Logistics and Supply Chain Management?
In the logistics and supply chain sector, microchips are pivotal for asset tracking and inventory management. Businesses can embed microchips in high-value items to monitor their location and status throughout the supply chain. This technology addresses the challenges of asset loss and inventory discrepancies, which can lead to financial losses. For international buyers, it’s crucial to consider the compatibility of microchips with existing tracking systems, the range of the tracking technology, and robust data security measures to protect sensitive information.
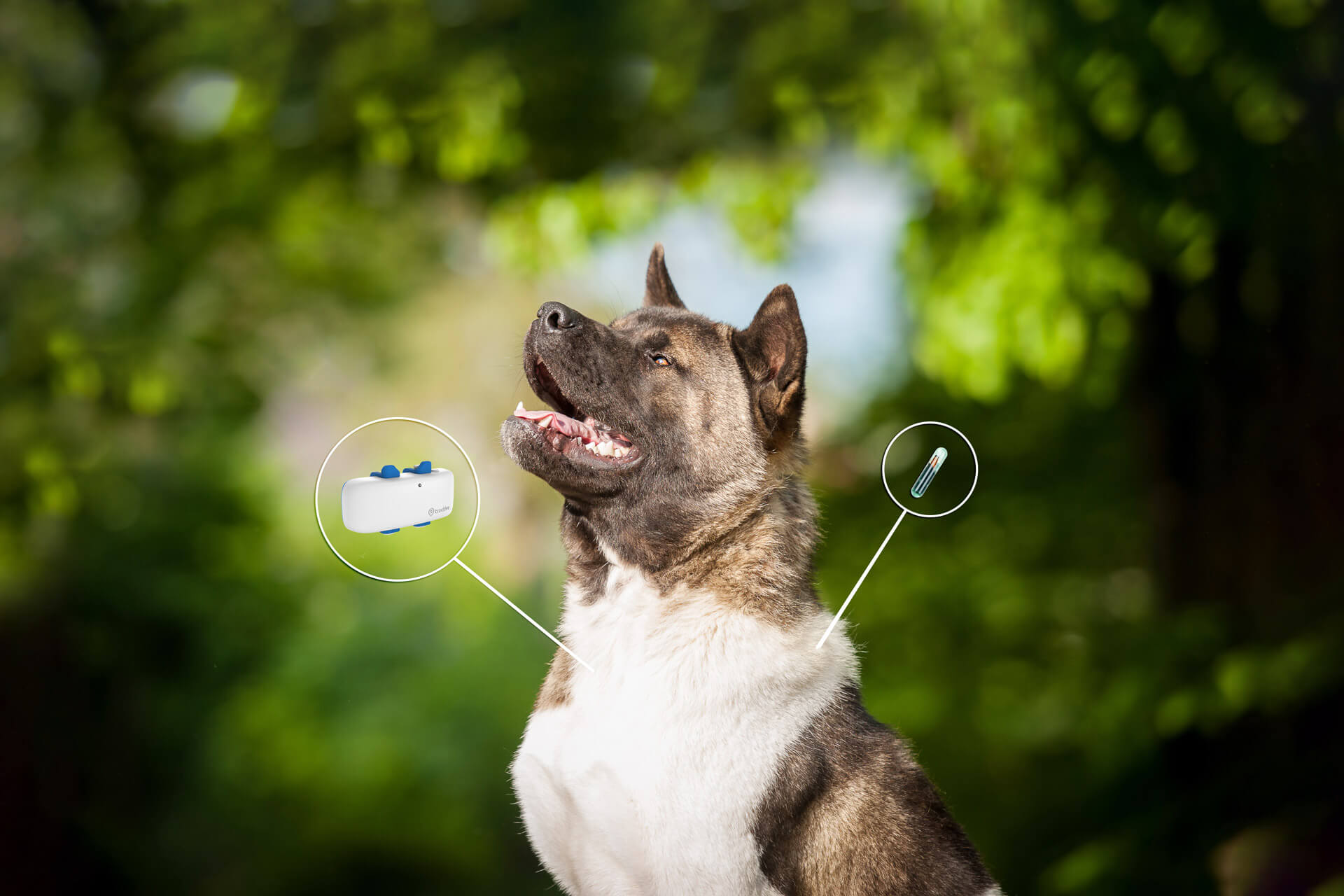

Illustrative image related to can microchips be tracked
What role do microchips play in Agriculture for Livestock Management?
In agriculture, particularly in livestock management, microchips serve as an essential tool for identification and monitoring. Farmers can track the health and movements of their animals, which enhances herd management and biosecurity. The ability to monitor livestock helps in disease control and improves overall productivity. Buyers in this sector should prioritize microchips that are durable enough to withstand harsh outdoor conditions, ensure ease of integration with existing farm management systems, and comply with local agricultural regulations.
How can Healthcare benefit from tracking microchips?
In the healthcare industry, microchips can be used for patient identification and medication tracking, significantly reducing the risk of errors in patient care. By embedding microchips in wristbands or medical devices, healthcare providers can streamline processes and enhance security. This technology is particularly beneficial in large hospitals where patient data must be accurately matched with treatments. Buyers must ensure that the microchips comply with health regulations, maintain data privacy standards, and offer interoperability with existing healthcare systems to maximize efficiency.
What advantages do Retailers gain from using microchips for Anti-theft?
Retailers leverage microchips for anti-theft measures and customer tracking. By embedding microchips in products, businesses can significantly reduce theft and improve inventory turnover. Additionally, tracking customer interactions can enhance the shopping experience and inform marketing strategies. When sourcing microchips for retail applications, businesses should consider the cost-effectiveness of the technology, ease of installation, and seamless integration with point-of-sale systems to ensure a smooth operational workflow.
How do microchips assist Pet Services in Reuniting Lost Pets?
In the pet services industry, microchips are a vital tool for reuniting lost pets with their owners. When a lost pet is found, shelters and veterinary clinics can scan the microchip to access the owner’s contact information, significantly increasing recovery rates. This technology not only enhances customer satisfaction but also builds brand loyalty among pet owners. For international buyers, it’s essential to navigate the registration processes for microchips, ensure compatibility across different countries, and support various chip types to facilitate effective pet recovery services.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘can microchips be tracked’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Misconceptions About Microchip Tracking Capabilities
The Problem:
B2B buyers, particularly those in the pet industry, often grapple with the misconception that microchips function like GPS trackers. This misunderstanding can lead to poor purchasing decisions, as many businesses may invest in microchips expecting real-time location tracking of pets or assets, only to find that microchips primarily serve as identification tools. This gap in understanding can create frustration and lost opportunities, particularly in sectors where asset recovery or pet reuniting is critical.
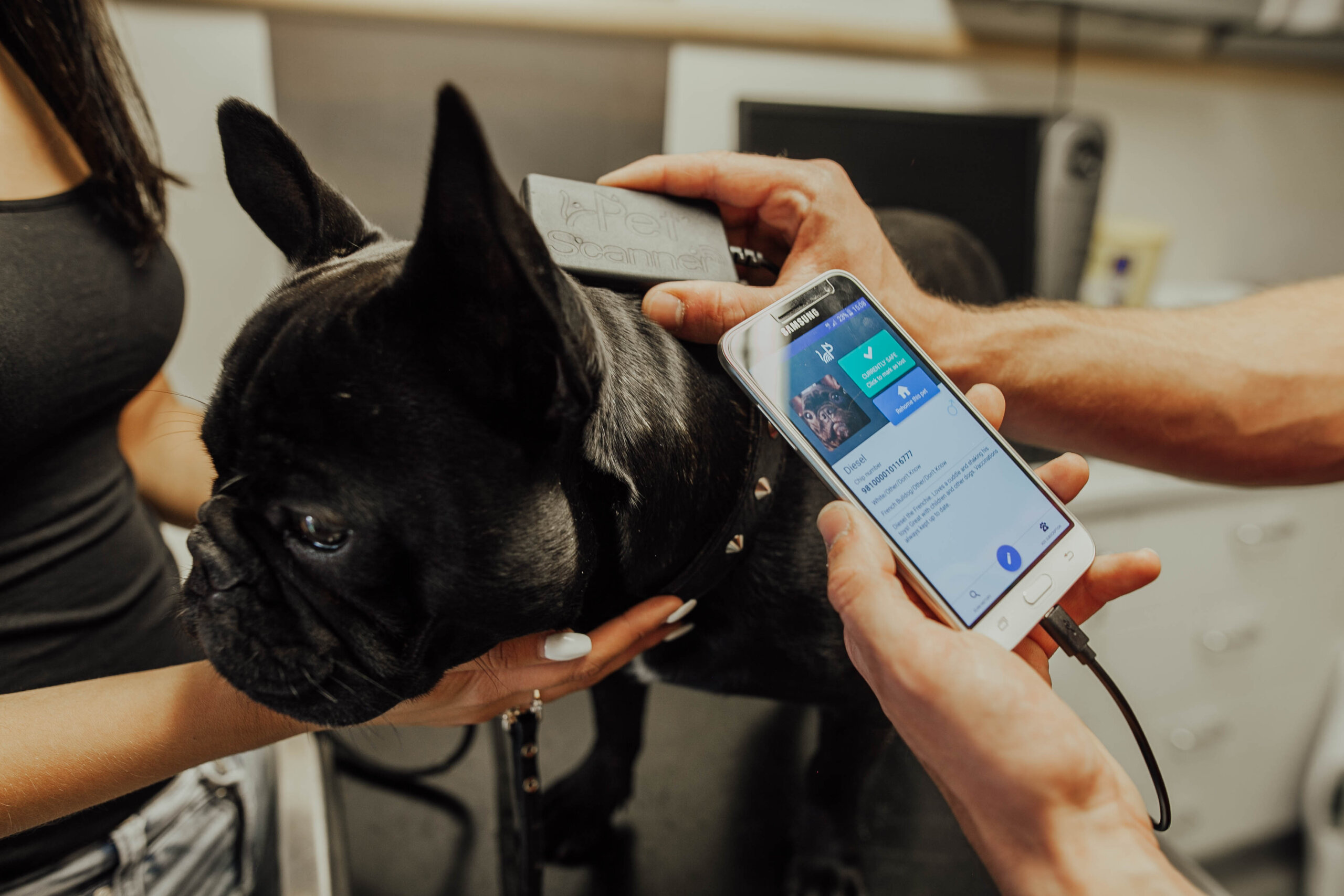

Illustrative image related to can microchips be tracked
The Solution:
To overcome this challenge, businesses should prioritize education on the distinct functionalities of microchips versus GPS technology. When sourcing microchips, ensure that product descriptions clearly outline that microchips utilize RFID technology for identification and cannot provide real-time tracking. Consider partnering with manufacturers who offer comprehensive training materials, including webinars or informational brochures, to educate staff and customers alike. Additionally, businesses should explore complementary GPS tracking solutions for those needing real-time location data. Investing in a dual-approach strategy that combines microchipping for permanent identification and GPS technology for live tracking can significantly enhance customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
Scenario 2: Lack of Registration and Update Protocols
The Problem:
A common pain point arises when businesses fail to emphasize the importance of registering microchips and keeping contact information updated. In cases where a lost pet is found, the inability to trace the owner can lead to heart-wrenching situations and financial losses for veterinary clinics and shelters that rely on microchip data to reunite pets with their families. Without a robust protocol for registration and updates, businesses face a significant risk of decreased effectiveness in their microchip services.
The Solution:
To mitigate this issue, businesses should establish and communicate clear protocols for microchip registration during the sale or implantation process. This includes creating easy-to-follow guides for pet owners on how to register their microchip and regularly check that their information is current. Consider implementing automated reminders through email or SMS to prompt pet owners to verify their contact details periodically. Additionally, integrating a feature into your service offerings that allows for seamless updates directly from your platform can encourage compliance. By fostering a culture of proactive communication, businesses can enhance the reliability of microchip technology and improve outcomes for pets and their owners.
Scenario 3: Limited Awareness of Microchip Recovery Processes
The Problem:
Many businesses in the pet care and veterinary sectors encounter difficulties due to a lack of awareness among clients regarding the proper steps to take if a microchipped pet goes missing. This situation can result in prolonged searches, increased stress for pet owners, and decreased trust in the microchipping service provided. For B2B buyers, the reputational risk associated with these scenarios can impact customer loyalty and satisfaction.
The Solution:
To address this issue, B2B companies should invest in creating and disseminating educational resources about the recovery process for lost microchipped pets. This could take the form of informative brochures, engaging videos, or online webinars that detail steps such as checking local shelters, contacting microchip registries, and using social media for wider outreach. Additionally, businesses can enhance their offerings by providing a follow-up service, where they assist clients with the recovery process after a pet goes missing. Establishing partnerships with local shelters and veterinarians to create a network for reporting and recovering lost pets can also improve outcomes. By proactively educating clients and providing support, businesses can reinforce the value of microchipping and ensure higher rates of successful reunions.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for can microchips be tracked
What Materials Are Commonly Used for Microchips and Their Tracking Capabilities?
When considering the materials used in microchips, especially in the context of tracking, several common options are evaluated. Each material has unique properties, advantages, and limitations that can significantly impact performance and suitability for various applications. This analysis focuses on silicon, polymers, ceramics, and metals.
How Does Silicon Perform in Microchip Applications?
Silicon is the most widely used material for microchips due to its excellent electrical properties and thermal stability. It has a high melting point of around 1,414°C, making it suitable for high-temperature applications. Silicon microchips are resistant to oxidation, which enhances their durability in various environments.
Pros: Silicon is relatively inexpensive and widely available, which lowers manufacturing costs. It also allows for the integration of complex circuits, making it ideal for advanced tracking applications.
Cons: While silicon is durable, it can be brittle under mechanical stress. Additionally, its performance can degrade in extreme environmental conditions, such as high humidity or corrosive atmospheres.
Impact on Application: Silicon microchips are compatible with various electronic devices, making them versatile for tracking applications in pets, assets, and vehicles.
Illustrative image related to can microchips be tracked
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local electronic standards, such as IEC and ISO, to avoid issues in product deployment.
What Role Do Polymers Play in Microchip Design?
Polymers are increasingly used in microchip packaging due to their lightweight and flexible properties. They can withstand a temperature range from -40°C to 85°C, making them suitable for various environments.
Pros: Polymers are cost-effective and can be molded into complex shapes, allowing for innovative design solutions. They also provide excellent insulation properties.
Cons: Their thermal stability is lower than that of silicon or ceramics, which may limit their use in high-temperature applications. Additionally, polymers can be susceptible to environmental degradation over time.
Impact on Application: Polymers can enhance the durability of microchips in consumer electronics, but their limitations may affect long-term tracking reliability in harsh conditions.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the availability of specific polymer grades that meet local environmental regulations, especially in regions with strict waste management laws.
How Do Ceramics Enhance Microchip Performance?
Ceramics are known for their exceptional thermal and chemical resistance, making them ideal for high-performance microchips. They can operate effectively in extreme temperatures, up to 1,600°C, and are resistant to corrosion.
Pros: Ceramics provide excellent durability and longevity, making them suitable for tracking applications in challenging environments, such as industrial settings.

Illustrative image related to can microchips be tracked
Cons: The cost of ceramics is typically higher than that of silicon or polymers, which can increase overall manufacturing expenses. Additionally, their brittleness can pose challenges during handling and installation.
Impact on Application: Ceramics are particularly beneficial for microchips used in high-stakes tracking applications, such as in aerospace or military contexts, where reliability is paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must be aware of compliance with international ceramic standards, such as ASTM and DIN, to ensure product quality and reliability.
Illustrative image related to can microchips be tracked
What Advantages Do Metals Offer in Microchip Applications?
Metals, such as gold and copper, are often used in microchip connections due to their excellent conductivity. They can withstand high temperatures and provide robust mechanical support.
Pros: Metals offer superior electrical performance and durability, making them ideal for high-frequency applications. They can also be recycled, which adds an environmental benefit.
Cons: The cost of metals can be high, particularly for precious metals like gold. Furthermore, they may corrode in certain environments, necessitating protective coatings.
Impact on Application: Metals are essential for ensuring reliable connections in microchips, enhancing the overall performance of tracking systems.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the availability and cost of metals in their local markets, especially in regions with fluctuating commodity prices.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Microchips
| Material | Typical Use Case for can microchips be tracked | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silicon | Consumer electronics, pet tracking devices | Cost-effective, excellent electrical properties | Brittle under stress, performance degradation in extreme conditions | Low |
| Polymers | Packaging for microchips, flexible electronics | Lightweight, cost-effective, moldable | Lower thermal stability, environmental degradation | Low |
| Ceramics | High-performance applications, industrial tracking | Exceptional durability, high thermal resistance | Higher cost, brittle | High |
| Metals | Connections in microchips, high-frequency applications | Superior conductivity, robust support | High cost, potential for corrosion | Med |
This detailed analysis provides B2B buyers with actionable insights into material selection for microchips used in tracking applications, helping them make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for can microchips be tracked
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Microchips for Tracking?
The manufacturing of microchips designed for tracking involves several crucial stages, each contributing to the overall performance and reliability of the final product. Understanding these processes is essential for B2B buyers looking to ensure that their suppliers maintain high standards in quality and performance.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used in Microchip Production?
The first stage in manufacturing microchips involves the careful selection and preparation of materials. Commonly used materials include silicon wafers, which serve as the substrate for the microchips, and various metals for wiring and connections. Other materials may include polymers for packaging and insulation. The purity of these materials is critical, as impurities can lead to defects in the chips, affecting their functionality and longevity.
How Is Microchip Forming Achieved?
Once materials are prepared, the next step is forming the microchips. This process typically involves photolithography, where light-sensitive chemicals are applied to the silicon wafer. A mask is then used to expose specific areas to light, allowing for the selective etching of circuits. After photolithography, processes such as ion implantation and chemical vapor deposition are used to create the necessary electronic properties. These steps are vital for ensuring that the microchips can efficiently transmit and receive data.
What Does the Assembly Process Involve for Microchips?
Following the formation of the microchips, the assembly process begins. This involves attaching the microchip to its housing, which may include connecting it to antennas or other components necessary for tracking functionality. Advanced techniques, such as wire bonding or flip-chip bonding, are employed to ensure a robust connection. Proper assembly is crucial, as any faults can compromise the microchip’s ability to function in real-world applications.
How Is Finishing Conducted in Microchip Manufacturing?
The finishing stage encompasses various processes aimed at preparing the microchips for distribution. This includes encapsulation, where the microchips are coated with protective materials to prevent damage from environmental factors. Additionally, final tests are performed to ensure that each microchip meets the required specifications. This stage is essential for ensuring that the microchips can withstand the conditions they will encounter in the field.
What Quality Control Measures Are Essential in Microchip Production?
Quality control (QC) is a critical aspect of microchip manufacturing, particularly for those designed for tracking applications. Adhering to international standards and implementing rigorous QC checkpoints can significantly enhance the reliability of the products.
Which International Standards Should Microchip Manufacturers Adhere To?
ISO 9001 is one of the most recognized international standards for quality management systems. Compliance with ISO 9001 ensures that manufacturers follow best practices in quality assurance, which is particularly important for B2B buyers concerned with product reliability. Other industry-specific certifications, such as CE marking in Europe or API (American Petroleum Institute) standards for specific applications, may also be relevant depending on the intended use of the microchips.
Illustrative image related to can microchips be tracked
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Microchip Manufacturing?
Quality control in microchip manufacturing typically involves several key checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage ensures that all materials received from suppliers meet specified quality standards before they enter the manufacturing process.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, continuous monitoring is conducted to detect any defects or deviations from established parameters. This includes real-time testing of the microchip’s electrical properties.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once manufacturing is complete, final inspections are performed. This includes functional testing to verify that the microchips operate as intended and meet all performance criteria.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Quality Control for Microchips?
Several testing methods are employed to ensure that microchips meet quality standards. These include:
-
Electrical Testing: Verifies the microchip’s operational capabilities, ensuring it functions correctly under various conditions.
-
Environmental Testing: Assesses the durability of microchips under extreme temperatures, humidity, and other environmental factors.
-
Functional Testing: Confirms that the microchip performs its intended functions, such as data transmission for tracking.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, verifying the quality control processes of suppliers is essential to ensure they are receiving reliable products. Several strategies can be employed:
What Role Do Audits Play in Verifying Quality Control?
Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide valuable insights into their quality control processes. Audits help assess compliance with international standards and identify areas for improvement. Buyers should consider including audit clauses in their contracts to ensure ongoing adherence to quality standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Utilize Quality Control Reports?
Requesting detailed quality control reports from suppliers can help buyers evaluate the effectiveness of their QC processes. These reports should outline testing results, defect rates, and corrective actions taken to address any issues. This transparency is crucial for building trust between buyers and suppliers.
What Is the Importance of Third-Party Inspections in Quality Assurance?
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an objective assessment of a supplier’s quality control measures. These inspections can be particularly beneficial for international buyers, as they offer an additional layer of assurance regarding product quality. Third-party inspectors can verify compliance with relevant standards and provide recommendations for improvement.
What Are the Quality Control Considerations for International Buyers?
For B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control is critical. Different regions may have varying standards and practices, which can impact product reliability.
How Do Regional Standards Affect Quality Assurance?
Buyers should be aware of the specific standards applicable in their regions. For instance, CE marking is essential for products sold in Europe, while buyers in the Middle East may need to adhere to local regulations regarding electronics. Understanding these requirements can help ensure compliance and facilitate smoother transactions.
What Challenges Might International Buyers Face in Quality Control?
International buyers may encounter challenges such as language barriers, differing regulatory frameworks, and varying quality expectations. Building strong relationships with suppliers and maintaining clear communication can help mitigate these challenges. Additionally, investing in local representatives or consultants can provide valuable insights into regional practices.

Illustrative image related to can microchips be tracked
By focusing on these manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing microchips for tracking applications, ensuring they receive high-quality, reliable products that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘can microchips be tracked’
The following practical sourcing guide is designed to assist B2B buyers in understanding and procuring microchips, particularly in the context of tracking capabilities and overall functionality. This checklist will help you navigate the complexities of microchip technology and make informed purchasing decisions.
Step 1: Identify Your Tracking Requirements
Understanding your specific tracking needs is essential before sourcing microchips. Determine whether you require real-time tracking, data logging, or passive identification. This will influence the type of microchip technology you should consider, such as RFID or GPS-enabled chips.
Step 2: Research Microchip Technologies
Familiarize yourself with the different types of microchip technologies available on the market. For instance, RFID microchips are commonly used for identification and can be scanned to retrieve stored information, while GPS-enabled devices provide real-time location data. Knowing these differences will help you choose the right technology for your application.
Illustrative image related to can microchips be tracked
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before engaging with potential suppliers, verify their certifications and compliance with international standards. Certifications such as ISO 9001 or ISO 13485 can indicate a supplier’s commitment to quality management. Ensure that the microchips meet regulatory requirements relevant to your industry or region, especially in markets like Africa, South America, and the Middle East.
Step 4: Analyze Cost vs. Value
When comparing suppliers, it’s crucial to assess the cost of microchips in relation to their value. Cheaper options may compromise on quality or features, while more expensive microchips could offer advanced functionalities that justify their price. Consider the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and potential upgrades.
Step 5: Review Supplier Track Record
Investigate the supplier’s history and reputation within the industry. Look for case studies, testimonials, or references from other businesses that have used their microchips. A supplier with a solid track record is more likely to provide reliable products and support.
Step 6: Inquire About Data Management Solutions
Data management is a critical aspect of using microchips for tracking. Ensure that the supplier offers robust data management solutions, including easy access to microchip information and integration with existing systems. This can streamline operations and enhance the overall efficiency of tracking processes.
Step 7: Assess Post-Purchase Support
Evaluate the post-purchase support offered by the supplier. Reliable customer service, warranty options, and technical support are vital for addressing any issues that may arise after procurement. Confirm that the supplier has a clear process for handling inquiries and providing assistance.

Illustrative image related to can microchips be tracked
By following these steps, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the procurement process for microchips, ensuring they select the most suitable technology and supplier for their specific needs. This thorough approach will facilitate informed decision-making and foster successful partnerships in the microchip sourcing landscape.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for can microchips be tracked Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Microchips?
When considering the sourcing of microchips, especially for tracking applications, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and margin.
-
Materials: The raw materials for microchips, such as silicon, metals for contacts, and packaging materials, form the foundation of the cost. Prices fluctuate based on global supply and demand dynamics. Buyers should be aware that sourcing from regions with lower raw material costs can reduce overall expenses.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly depending on the manufacturing location. For instance, countries in Southeast Asia may offer lower labor costs compared to Europe or North America. However, the skill level and expertise required for high-precision microchip manufacturing can impact this cost.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, maintenance, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize these overheads, influencing the final pricing.
-
Tooling: The design and setup of specialized equipment for microchip production can be costly. Tooling costs are often amortized over production volume, meaning higher minimum order quantities (MOQs) may lead to lower per-unit costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that microchips meet specific industry standards requires investment in QC processes and testing. High-quality certifications can add to costs but are essential for maintaining reliability and performance.
-
Logistics: The shipping and handling of microchips can add significant costs, especially for international transactions. Factors such as distance, freight methods, and customs duties must be considered when evaluating the total cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically apply a margin that reflects their operational costs and desired profit. Understanding the competitive landscape can help buyers negotiate better terms.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Microchip Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of microchips, particularly for international B2B buyers:
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in larger quantities often leads to lower per-unit costs. However, buyers must assess their demand forecasts to avoid excess inventory.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom-designed microchips tailored to specific applications typically incur higher costs due to the additional engineering and development time required.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials impacts both the durability and cost of microchips. Additionally, certifications such as ISO can increase costs but are vital for compliance and market acceptance.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and financial health of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their products, but this often comes with enhanced support and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: The terms of shipping and delivery (Incoterms) can greatly influence costs. Buyers should be aware of who bears the risk and costs at each stage of transportation, which can affect the overall price.
What Are the Best Practices for Negotiating Microchip Prices?
International B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should consider the following tips to enhance their negotiation strategies:

Illustrative image related to can microchips be tracked
-
Research and Benchmarking: Understand market rates and competitor pricing to leverage during negotiations. Knowledge of industry standards can help justify your price expectations.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Focus on TCO rather than just upfront costs. Consider long-term maintenance, reliability, and potential savings from higher-quality microchips.
-
Establish Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing, improved terms, and priority service.
-
Flexibility in Terms: Be open to discussing payment terms, delivery schedules, and other contractual elements that could lead to better pricing arrangements.
-
Be Prepared to Walk Away: If the terms do not meet your budgetary constraints, be ready to explore alternative suppliers. This not only strengthens your negotiating position but also opens the door to discovering better options.
Conclusion
While sourcing microchips for tracking applications, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and the various price influencers is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. By employing strategic negotiation techniques and being aware of the total cost of ownership, international B2B buyers can optimize their sourcing strategies, ensuring both cost-effectiveness and quality in their microchip procurement.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing can microchips be tracked With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Microchip Tracking: What Are Your Options?
In the realm of tracking solutions, microchips have emerged as a popular choice for pet and asset identification. However, they are not the only option available. Businesses and individuals looking for effective tracking solutions can explore alternatives such as GPS trackers and RFID tags. This section will compare the tracking capabilities of microchips against these alternatives to help B2B buyers make informed decisions.
| Comparison Aspect | Can Microchips Be Tracked | GPS Trackers | RFID Tags |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Limited to identification; requires scanning to retrieve data | Real-time location tracking with GPS satellites | Limited range; scans within close proximity |
| Cost | Generally low initial cost (typically $20-$50) | Higher upfront cost ($50-$300) + subscription fees | Low-cost (typically $1-$5 per tag) |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple procedure; requires registration | Requires installation and often a subscription | Easy to implement; minimal setup |
| Maintenance | Minimal; only requires registration updates | Regular charging/battery replacement and subscription | Very low; no maintenance required |
| Best Use Case | Permanent identification for lost pets/assets | Real-time tracking of pets/assets in transit | Inventory management and short-range asset tracking |
What Are the Pros and Cons of GPS Trackers?
GPS trackers provide real-time tracking capabilities, making them suitable for individuals who require immediate location data. They are particularly beneficial for active pets or valuable assets that frequently change locations. However, they come with higher costs, including initial purchase and monthly subscription fees. Additionally, GPS devices can be bulky and may require regular charging, which can be a downside for smaller pets.
How Do RFID Tags Compare as an Alternative?
RFID tags are another viable alternative for tracking purposes. They are often used in inventory management and can be extremely effective for short-range scanning. RFID tags are generally inexpensive, making them a cost-effective solution for businesses looking to manage assets. However, their limitations include a short range for scanning and the requirement of specialized readers, which may not be practical for all tracking needs.
Conclusion: Which Tracking Solution is Right for Your Business?
When evaluating tracking solutions, B2B buyers must consider their specific needs and circumstances. If real-time tracking is essential, GPS trackers may offer the best performance despite their higher costs. On the other hand, microchips serve as a reliable identification method, particularly for pets, where the goal is to reunite lost animals with their owners. RFID tags can be a cost-effective choice for businesses focused on inventory control but may not provide the same level of tracking versatility. Ultimately, the right choice will depend on factors such as budget, intended use, and the importance of real-time location data.

Illustrative image related to can microchips be tracked
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for can microchips be tracked
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Microchips Used for Tracking?
When considering microchips for tracking purposes, several technical properties are vital for ensuring effective functionality and reliability. Below are critical specifications that B2B buyers should focus on:
-
Material Composition
Microchips are typically made from biocompatible materials such as glass or silicone. The choice of material is crucial as it affects the chip’s longevity and integration with the host (e.g., pets or products). For B2B buyers, understanding the material can help gauge the chip’s durability and suitability for specific applications, such as animal tracking or product identification. -
Frequency Range
Microchips operate on specific radio frequencies, usually between 125 kHz and 134.2 kHz for RFID applications. The frequency affects the read range and compatibility with scanners. B2B buyers should consider the frequency when selecting microchips to ensure they meet industry standards and can be effectively scanned by available devices. -
Size and Form Factor
The size of microchips can vary, but they typically resemble a grain of rice. Smaller chips are preferable for applications involving pets or small items, as they are less invasive. Buyers must evaluate the form factor based on the intended use to ensure ease of implantation or integration into products. -
Read Range
The read range indicates how far away a scanner can detect the microchip. Standard RFID chips generally have a read range of up to several centimeters. Understanding the read range is critical for B2B buyers to ensure that the microchips will function effectively within their operational environments, particularly in logistics and inventory management. -
Registration and Data Management
Microchips require registration in databases to be effective. The process involves linking the microchip ID with the owner’s contact information. B2B buyers should prioritize microchips that offer user-friendly registration processes and robust data management features, ensuring they can maintain up-to-date information for effective tracking. -
Compliance with Standards
Microchips should comply with international standards, such as ISO 11784/11785, which govern the use of RFID technology. Compliance is essential for ensuring interoperability across different systems and enhancing the reliability of tracking solutions. Buyers should confirm that their chosen microchip meets these standards to facilitate global trade and usability.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Microchip Tracking?
Understanding industry jargon is essential for effective communication and decision-making in the B2B landscape. Here are some common terms related to microchip tracking:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce components that are used in another company’s products. In the context of microchips, B2B buyers may need to engage with OEMs to ensure compatibility and quality in their tracking solutions. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers, as understanding the MOQ can help in budgeting and inventory planning, especially when sourcing microchips in bulk. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting a price quote for specific products or services. B2B buyers should utilize RFQs to gather pricing information for microchips, ensuring they receive competitive offers and can make informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized terms used in international trade to define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers. Familiarity with Incoterms can aid B2B buyers in understanding shipping logistics, insurance, and risk management when importing microchips from different regions. -
RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification)
RFID is a technology that uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. B2B buyers should be well-versed in RFID technology, as it forms the basis for most tracking microchips and influences their selection process. -
Lifecycle Management
This term refers to the process of managing a product’s lifecycle from inception to disposal. For microchips, understanding lifecycle management helps B2B buyers anticipate upgrades, replacements, and environmental impacts, ensuring long-term sustainability in their tracking systems.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing microchips for tracking applications.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the can microchips be tracked Sector
What are the Key Market Dynamics Influencing Microchip Tracking Technology?
The microchip tracking market is evolving rapidly, driven by advancements in technology and increasing consumer demand for security and traceability. Key global drivers include the rising need for efficient pet recovery systems, growing awareness about animal welfare, and regulatory pressures to ensure responsible pet ownership. For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is crucial for making informed sourcing decisions.
Emerging trends indicate a shift towards integrating microchips with complementary technologies such as GPS and blockchain. While traditional microchips use RFID technology for identification, the future may see a convergence with GPS capabilities, enhancing tracking features. Blockchain can provide a secure and immutable record of ownership and movements, thereby increasing trust among buyers and sellers in the pet industry. Moreover, the demand for innovative products such as microchips that facilitate direct communication with pet owners via smartphone applications is on the rise. These developments present opportunities for B2B buyers to source advanced microchip solutions that meet evolving market needs.
How is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Microchip Industry?
Sustainability is becoming increasingly important in the microchip sector, as environmental concerns continue to grow among consumers and businesses alike. The production and disposal of microchips can have significant environmental impacts, particularly if hazardous materials are involved. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who adhere to sustainable manufacturing practices and use eco-friendly materials. This not only mitigates environmental risks but also enhances brand reputation among environmentally conscious consumers.
Furthermore, ethical sourcing is gaining traction as businesses recognize the importance of responsible supply chains. Buyers should look for suppliers that are transparent about their sourcing practices and can demonstrate compliance with international standards. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability. Embracing these practices not only aligns with corporate social responsibility goals but also appeals to a growing segment of the market that values ethical considerations in their purchasing decisions.
How Has the Microchip Technology Evolved Over Time?
The history of microchip technology can be traced back to the early 1980s when the first pet microchips were introduced as a means of permanent identification. Initially, these microchips were basic RFID devices, offering limited functionality primarily focused on providing pet owners with a way to reunite with lost animals. Over the decades, technological advancements have led to more sophisticated microchips that not only enhance the tracking process but also improve data security and management.
As consumer expectations evolve, the industry has seen innovations such as the integration of microchips with mobile applications and GPS technologies. These advancements have transformed microchips from simple identification tools to comprehensive tracking solutions that provide real-time information about a pet’s whereabouts. For B2B buyers, understanding this evolution is critical in selecting suppliers that offer cutting-edge technology that can adapt to the changing landscape of pet recovery and ownership management.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of can microchips be tracked
-
How do I determine if a microchip can be tracked?
Microchips, particularly those used for pets, do not have GPS capabilities and cannot be tracked in real-time. Instead, they utilize RFID technology that requires a scanner to read the microchip’s unique identification number. To ensure effective tracking, it’s crucial to register the microchip with up-to-date contact information in a recognized database. If you’re sourcing microchips for asset tracking or other applications, confirm with suppliers that the chips meet your specific tracking requirements and consider whether additional GPS solutions are needed. -
What is the best microchip solution for asset tracking?
For asset tracking, the best microchip solutions often incorporate RFID technology designed for specific environments and applications. Look for microchips that offer high read ranges, compatibility with existing systems, and robust durability. Suppliers should provide detailed specifications and case studies demonstrating successful implementations. Additionally, consider solutions that allow for seamless integration with software platforms to facilitate real-time monitoring and data analysis. -
How can I ensure the quality of microchips from international suppliers?
To ensure quality, vet suppliers by requesting certifications, quality assurance processes, and product samples. Check for compliance with international standards such as ISO and industry-specific regulations. Conduct audits if possible, and seek references from other B2B clients who have sourced from the same supplier. Establish clear quality criteria in your contracts and consider incorporating third-party testing to verify the performance of the microchips before large-scale procurement. -
What customization options are available for microchips?
Customization options for microchips can vary widely based on the supplier. Common customizations include unique identifiers, specific frequency ranges, and varying sizes or shapes tailored to fit particular applications. Some suppliers may also offer the ability to integrate additional features, such as tamper-proof designs or enhanced data storage capabilities. Discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to explore available options that meet your operational requirements. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for microchips?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for microchips can differ significantly depending on the manufacturer and the specific type of microchip. Generally, MOQs can range from a few hundred to thousands of units. Factors influencing MOQs include production costs, customization requirements, and market demand. When negotiating with suppliers, clarify your needs and explore whether they can accommodate smaller orders or offer flexible terms based on your project scale. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing microchips internationally?
Payment terms for international microchip sourcing can vary based on the supplier’s policies and your relationship with them. Common terms include upfront deposits, payment upon delivery, or letters of credit for larger orders. It’s essential to discuss and agree on terms that protect both parties, particularly in international transactions where risks can be higher. Ensure that all payment conditions are clearly outlined in the contract to avoid misunderstandings. -
What logistics considerations are important when importing microchips?
Logistics considerations when importing microchips include shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Choose reliable shipping partners familiar with electronics to ensure timely delivery. Verify that the microchips comply with the importing country’s regulations to avoid delays at customs. Additionally, consider the lead time for production and shipping to effectively plan your supply chain and avoid disruptions in your operations. -
How can I track the performance of microchips in my application?
To track the performance of microchips in your application, implement a monitoring system that records data such as read rates, failure rates, and integration with your existing software. Utilize analytics tools to analyze the data collected and identify trends or issues. Regularly review performance metrics with your team and the supplier to ensure that the microchips are meeting your operational needs and to make informed decisions about future purchases or adjustments.
Top 4 Can Microchips Be Tracked Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Dr. Phillips Animal Hospital – Pet Microchips
Domain: drphillipsanimalhospital.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Pet microchips do not have GPS technology; they use Radio-frequency identification (RFID) technology to store and transmit the pet owner’s contact information. Microchips are about the size of a grain of rice and are implanted under the pet’s skin, usually between the shoulder blades. They help reunite lost pets with their owners when scanned at veterinary clinics or animal shelters. It is essenti…
2. WikiHow – Microchip Identification for Pets
Domain: wikihow.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Microchips are small electronic devices implanted in pets, typically in the back of the neck, to store identification and contact information. They do not provide real-time tracking or location services, as they lack a battery and GPS functionality. Microchips function as a permanent ID, allowing vets and shelters to scan them to retrieve the owner’s contact information when a lost pet is found. R…
3. Facebook – Pet Microchip
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Microchip for pets; allows identification via scanner by vets, humane society, animal control, and some police officers; does not allow real-time tracking; important to update contact information; free microchipping event on September 21 at Fromm Family Foods Fromm Petfest; partnership with Friends of MADACC and Yutka Fence; reminder for pet owners to ensure microchip information is current.
4. PaoliVet – Save This Life™ Microchip
Domain: paolivet.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: $45 Save This Life™ Microchip; includes an aluminum, machine stamped ID tag with “Search this # to Find my Family”; links to a photo of the pet and a secure contact form; sends text, email, and Google map with pet’s location; coverage for up to $1,000 in emergency care for accidents while lost; ISO compliant, readable by universal scanners; coated to prevent migration; no registration fees, no ann…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for can microchips be tracked
In conclusion, while microchips play a crucial role in the identification and recovery of pets, they do not offer real-time tracking capabilities like GPS technology. For businesses involved in the pet care industry, understanding the distinction between microchips and GPS devices is essential for providing accurate information to customers. Emphasizing the importance of registration and maintaining updated contact information can significantly enhance the effectiveness of microchipping, ultimately leading to higher rates of successful reunifications.
Strategic sourcing in the microchip and pet technology sector should focus on partnerships with reliable microchip manufacturers and registries. This can help streamline operations and improve customer satisfaction by ensuring that all microchips are compliant and easily scannable. Additionally, exploring innovative solutions, such as those that combine microchip identification with mobile technology, can position your business as a leader in the market.
As international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, now is the time to invest in advanced pet identification solutions. By prioritizing strategic sourcing and staying informed about technological advancements, you can enhance your offerings and meet the evolving needs of your customers effectively.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.