Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for micro gps tracking device
In an increasingly interconnected world, sourcing effective micro GPS tracking devices has become paramount for businesses looking to secure their assets and ensure operational efficiency. As international B2B buyers navigate the complexities of the global market, they face the challenge of identifying the right solutions that fit their specific needs. This comprehensive guide delves into the diverse landscape of micro GPS tracking devices, exploring various types, applications, and key features that cater to industries ranging from logistics to personal safety.
Understanding the nuances of these devices is essential for businesses operating in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries such as Saudi Arabia and Nigeria. The guide equips buyers with actionable insights on supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and the latest technological advancements. By highlighting the importance of real-time tracking capabilities, battery life, and coverage across multiple regions, this resource empowers decision-makers to make informed purchasing choices that align with their operational goals.
With the right knowledge and strategies at their disposal, B2B buyers can confidently select micro GPS tracking devices that not only enhance security but also contribute to improved asset management and customer satisfaction. This guide serves as a vital tool in navigating the global market, ensuring that businesses can leverage GPS technology to stay ahead in a competitive landscape.
Table Of Contents
- Top 7 Micro Gps Tracking Device Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for micro gps tracking device
- Understanding micro gps tracking device Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of micro gps tracking device
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘micro gps tracking device’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for micro gps tracking device
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for micro gps tracking device
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘micro gps tracking device’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for micro gps tracking device Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing micro gps tracking device With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for micro gps tracking device
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the micro gps tracking device Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of micro gps tracking device
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for micro gps tracking device
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding micro gps tracking device Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mini GPS Tracker | Compact, versatile, real-time tracking, alerts, long battery life | Vehicle tracking, asset protection, personal safety | Pros: Discreet, easy to install; Cons: Limited range in some models. |
| Wearable GPS Tracker | Designed for personal use, often includes health monitoring | Tracking children, elderly care, employee safety | Pros: User-friendly, health insights; Cons: Battery life varies significantly. |
| Vehicle GPS Tracker | OBD-II integration, route history, geofencing capabilities | Fleet management, logistics, theft prevention | Pros: Detailed analytics, easy installation; Cons: May require ongoing subscriptions. |
| Asset GPS Tracker | Robust design, often weatherproof, suited for larger items | Shipping, construction equipment, high-value assets | Pros: Durable, long-range coverage; Cons: Bulkier than mini trackers. |
| Pet GPS Tracker | Lightweight, often waterproof, includes activity monitoring | Pet safety, tracking during travel | Pros: Tailored for pets, real-time alerts; Cons: Limited to pet use, may not suit other applications. |
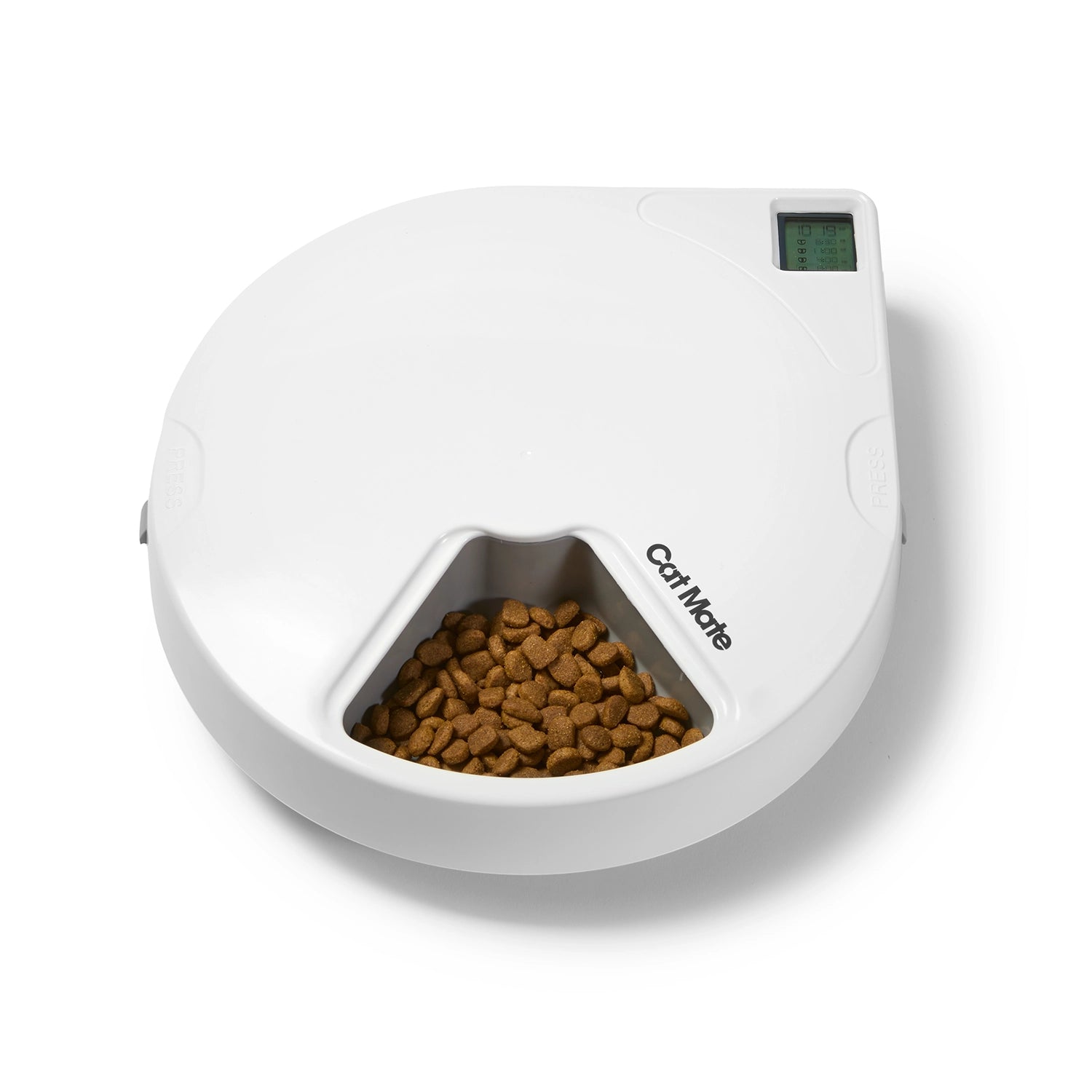
What are the Characteristics of Mini GPS Trackers?
Mini GPS trackers are compact devices that offer real-time tracking capabilities across various applications, from vehicle monitoring to personal safety. They typically feature long battery life, often lasting several days to weeks on standby, and provide alerts for unauthorized movement. For B2B buyers, the versatility of these trackers makes them ideal for protecting valuable assets, ensuring safety in logistics, and enhancing personal security for employees. When considering a purchase, buyers should evaluate the device’s coverage area and subscription costs, as these can affect overall operational efficiency.
Illustrative image related to micro gps tracking device
How Do Wearable GPS Trackers Differ from Other Types?
Wearable GPS trackers are specifically designed for personal use, often incorporating health monitoring features alongside location tracking. This type of tracker is particularly beneficial for businesses focusing on employee safety, child supervision, or elderly care. Their user-friendly interfaces and health insights can enhance the overall well-being of individuals being monitored. However, B2B buyers must consider the variability in battery life and the potential for added costs associated with health monitoring features when selecting these devices.
Why Choose Vehicle GPS Trackers for Fleet Management?
Vehicle GPS trackers are designed for integration with a vehicle’s onboard diagnostic (OBD-II) system, providing detailed analytics on driving behavior, route history, and geofencing capabilities. These features are essential for businesses managing fleets, as they enhance operational efficiency and reduce theft risks. While installation is generally straightforward, buyers should be aware of the ongoing subscription fees necessary for real-time tracking and data analysis, which can impact budget planning.
What Makes Asset GPS Trackers Ideal for High-Value Items?
Asset GPS trackers are built for durability and often have weatherproof designs, making them suitable for tracking larger items like shipping containers or construction equipment. Their robust features provide long-range coverage, ensuring that businesses can monitor high-value assets in various environments. B2B buyers should assess the tracker’s size and weight, as these factors can influence the ease of installation and portability, especially in industries with demanding tracking needs.
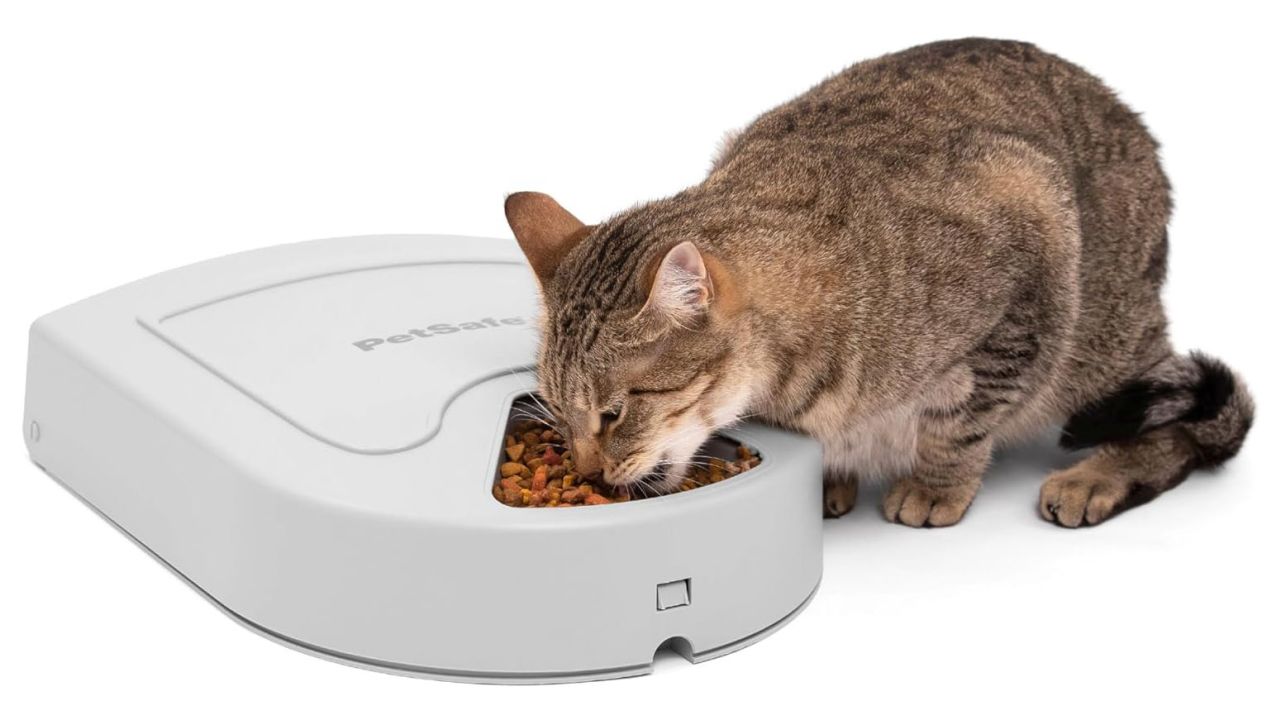
How Do Pet GPS Trackers Enhance Safety for Animals?
Pet GPS trackers are lightweight and often waterproof, designed specifically to monitor pets’ locations and activities. They offer real-time alerts to owners, making them an excellent choice for businesses in pet care or travel services. However, their specialized nature limits their use to pet tracking, which may not align with broader business applications. Buyers should consider the device’s features, such as activity monitoring and battery life, to ensure they meet the specific needs of their clientele.
Key Industrial Applications of micro gps tracking device
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of micro gps tracking device | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transportation & Logistics | Real-time tracking of fleet vehicles | Enhanced route optimization and reduced operational costs | Ensure global coverage, battery life, and integration with fleet management software. |
| Agriculture | Monitoring livestock and equipment location | Improved asset security and livestock management | Look for devices with long battery life and rugged design suitable for outdoor use. |
| Construction | Tracking heavy machinery and tools | Reduced theft and loss of expensive equipment | Consider durability, weather resistance, and real-time alert features. |
| Retail | Inventory tracking in warehouses | Increased efficiency in supply chain management | Assess compatibility with existing inventory management systems and data security features. |
| Personal Safety | Monitoring vulnerable individuals (e.g., children, elderly) | Enhanced security and peace of mind for families | Focus on user-friendly interfaces, emergency alerts, and subscription costs. |
How is Micro GPS Tracking Used in Transportation and Logistics?
In the transportation and logistics sector, micro GPS tracking devices are instrumental in real-time fleet management. Businesses can monitor vehicle locations, optimize routes, and reduce fuel costs by analyzing travel patterns. This technology addresses challenges such as delays and inefficiencies. International buyers should prioritize devices that provide global coverage and integrate seamlessly with existing fleet management systems, ensuring that they can track assets across borders without connectivity issues.
Illustrative image related to micro gps tracking device
What Role Does Micro GPS Tracking Play in Agriculture?
Agriculture professionals utilize micro GPS tracking devices to monitor livestock and equipment. By keeping tabs on the location of animals and machinery, farmers can enhance security and manage resources more effectively. This application helps prevent theft and ensures that livestock are where they should be, addressing common challenges in rural areas. Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should seek devices with robust battery life and durability, as agricultural environments can be harsh and unpredictable.
How Does Micro GPS Tracking Enhance Construction Operations?
In the construction industry, micro GPS tracking devices are vital for safeguarding heavy machinery and tools. These devices help minimize theft and loss, which are significant concerns in large construction projects. By providing real-time alerts and location data, businesses can quickly respond to unauthorized movements. Buyers should consider the ruggedness and weather resistance of the devices, as well as their ability to function in diverse environments, particularly in remote construction sites.
Why is Micro GPS Tracking Important for Retail Inventory Management?
Retailers are increasingly turning to micro GPS tracking devices for inventory management in warehouses. These devices facilitate real-time tracking of goods, leading to improved accuracy in stock levels and reduced shrinkage. By integrating GPS tracking with inventory management systems, businesses can streamline operations and enhance supply chain efficiency. International buyers should evaluate the compatibility of tracking devices with existing systems and ensure that data security measures are in place to protect sensitive information.
How Can Micro GPS Tracking Ensure Personal Safety?
Micro GPS tracking devices are also employed for personal safety, especially for monitoring vulnerable individuals such as children or the elderly. These devices provide peace of mind for families by enabling them to track loved ones’ locations in real-time. In regions with varying safety concerns, such as parts of the Middle East and Africa, buyers should focus on user-friendly designs, emergency alert features, and subscription models that fit their budget while ensuring reliable connectivity.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘micro gps tracking device’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Ensuring Asset Security During Transit
The Problem: B2B buyers, particularly in logistics and transportation, often face significant challenges in securing their assets during transit. In regions like Africa and South America, where theft and loss of goods can be prevalent, the inability to monitor the exact location of valuable shipments can lead to financial losses and operational disruptions. Companies may struggle with tracking shipments across borders and ensuring that their goods arrive safely at their destinations.
Illustrative image related to micro gps tracking device
The Solution: To address this issue, B2B buyers should invest in a micro GPS tracking device that offers real-time tracking capabilities and extensive coverage. Selecting a device with global connectivity, such as those supporting 4G technology, allows for seamless tracking across more than 100 countries. Additionally, implementing geo-fencing features can notify businesses when shipments enter or exit predetermined areas, providing an extra layer of security. It’s crucial to choose a device that is compact and discreet, enabling it to be concealed easily within shipments. Regular training for staff on how to utilize tracking applications effectively will ensure that they can respond promptly to any alerts about potential theft or deviations from the planned route.
Scenario 2: Managing Fleet Efficiency and Safety
The Problem: Fleet managers often grapple with the challenge of optimizing routes and ensuring the safety of drivers. In regions such as the Middle East and Europe, where fuel costs and road conditions can vary significantly, the lack of real-time data on vehicle locations can hinder effective decision-making. Furthermore, without proper tracking, companies may face difficulties in monitoring driver behavior, leading to increased risks of accidents and higher insurance premiums.
The Solution: Investing in micro GPS tracking devices specifically designed for fleet management can transform how businesses operate. These devices should provide real-time location data, allowing fleet managers to analyze routes and adjust them to minimize fuel consumption and improve delivery times. Look for devices that also offer driving behavior monitoring features, such as speed alerts and harsh braking notifications, to enhance safety. Additionally, integrating the tracking system with fleet management software can provide comprehensive insights into vehicle utilization and performance metrics. This data-driven approach will not only improve operational efficiency but also contribute to a safer driving environment for employees.
Scenario 3: Tracking Personal Safety for Vulnerable Populations
The Problem: Organizations that provide services to vulnerable populations, such as children, the elderly, or employees in high-risk jobs, often face challenges in ensuring their safety. In countries like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia, where personal safety can be a concern, the inability to monitor the whereabouts of these individuals can lead to serious security risks. The emotional toll on families and organizations relying on these individuals for care or support can be substantial.
The Solution: To mitigate these risks, B2B buyers should consider micro GPS tracking devices tailored for personal safety applications. Devices designed for this purpose typically come with features like emergency alerts, two-way communication, and location history. When selecting a device, prioritize those with long battery life and ease of use, ensuring that they can be easily carried or worn by the individual. It’s also essential to establish a protocol for monitoring and responding to alerts, which may include training staff on how to use the tracking system and maintain communication with families. By integrating these devices into their safety protocols, organizations can provide peace of mind to families and enhance the overall safety of vulnerable individuals.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for micro gps tracking device
What Are the Key Materials Used in Micro GPS Tracking Devices?
When selecting materials for micro GPS tracking devices, it is essential to consider properties that affect performance, durability, and compliance with international standards. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the manufacturing of these devices, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
How Does Plastic Contribute to Micro GPS Tracking Devices?
Key Properties: Plastics, particularly ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) and polycarbonate, offer excellent impact resistance and flexibility. They are lightweight and can withstand a wide range of temperatures, typically from -20°C to 80°C.
Pros & Cons: The durability of plastics is generally good, but they can be susceptible to UV degradation if not treated. They are cost-effective and easy to mold, allowing for complex designs. However, their lower heat resistance compared to metals can limit their application in high-temperature environments.
Impact on Application: Plastics are suitable for external casings of GPS devices, providing a lightweight and protective shell. However, they may not be ideal for environments with extreme temperatures or exposure to harsh chemicals.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and the Middle East should ensure that the plastics used comply with local environmental regulations, such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances). Understanding the specific grades of plastics that meet ASTM or DIN standards is crucial for ensuring product reliability.
What Role Does Metal Play in Micro GPS Tracking Devices?
Key Properties: Metals such as aluminum and stainless steel provide excellent strength and corrosion resistance. They can endure high temperatures and pressures, making them suitable for rugged applications.
Pros & Cons: While metals offer superior durability and a premium feel, they are heavier and can increase the overall weight of the device. Manufacturing complexity is higher due to the need for machining and welding processes, which can also drive up costs.
Impact on Application: Metals are often used in internal components or casings where strength and heat dissipation are critical. They can enhance the device’s performance in extreme conditions, but their weight may be a drawback for portable applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ISO 9001 for quality management is essential. Buyers in Europe may also need to consider REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulations concerning metal components.
How Do Ceramics Enhance Micro GPS Tracking Devices?
Key Properties: Ceramics are known for their high-temperature resistance and electrical insulation properties. They can withstand harsh environments, including high humidity and corrosive substances.
Illustrative image related to micro gps tracking device
Pros & Cons: The durability of ceramics is exceptional, but they can be brittle and may not withstand physical shocks well. Their manufacturing process is complex and often more expensive than plastics or metals.
Impact on Application: Ceramics are ideal for components that require insulation or protection from extreme temperatures, such as in sensors. However, their fragility can limit their use in high-impact applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that ceramic materials meet specific industry standards for thermal and electrical properties. In regions with high humidity, such as parts of South America, ceramics can be particularly advantageous due to their moisture resistance.
What Benefits Do Composites Offer for Micro GPS Tracking Devices?
Key Properties: Composite materials combine the strengths of different materials, offering improved strength-to-weight ratios and resistance to environmental factors. Common composites include fiberglass and carbon fiber.
Pros & Cons: Composites are lightweight and can be tailored for specific applications, but they are often more expensive and can require specialized manufacturing techniques.
Impact on Application: Composites are well-suited for high-performance applications where weight savings are critical, such as in wearable GPS devices. Their versatility allows for innovative designs, but the cost may be a barrier for some buyers.
Considerations for International Buyers: Understanding local manufacturing capabilities is crucial, as not all regions may have the technology to produce or work with advanced composites. Compliance with international standards for material safety and performance is also vital.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Micro GPS Tracking Devices
| Material | Typical Use Case for micro gps tracking device | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plastic | External casings and lightweight components | Cost-effective and easy to mold | Susceptible to UV degradation | Low |
| Metal | Internal components and rugged casings | High strength and corrosion resistance | Increased weight and cost | Medium |
| Ceramic | Insulation and high-temperature applications | Excellent thermal and electrical properties | Brittle and complex manufacturing | High |
| Composite | High-performance, lightweight applications | Tailored properties and lightweight | Higher cost and specialized manufacturing | High |
This analysis provides valuable insights for B2B buyers considering the strategic selection of materials for micro GPS tracking devices, ensuring that they meet performance, durability, and compliance requirements in diverse international markets.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for micro gps tracking device
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Micro GPS Tracking Devices?
The manufacturing process for micro GPS tracking devices involves several critical stages, each ensuring that the final product meets the stringent demands of accuracy, reliability, and durability. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers assess suppliers more effectively.
1. Material Preparation: What Raw Materials Are Used?
The first stage involves sourcing high-quality materials essential for the performance and longevity of GPS tracking devices. Common materials include:
- Circuit Boards: Typically made from FR-4 (a flame-retardant material), these boards serve as the backbone for electronic components.
- Microprocessors and Chips: These are integral for processing GPS signals and data transmission. Suppliers should use reputable brands to ensure reliability.
- Casing Materials: Lightweight yet durable plastics or metals are used to protect internal components while maintaining portability.
Once materials are sourced, they undergo a thorough inspection to verify quality before proceeding to the next stage.
2. Forming: How Are Components Shaped and Prepared?
Forming is the process where raw materials are transformed into usable components. This stage includes:
Illustrative image related to micro gps tracking device
- PCB Fabrication: Circuit boards are manufactured using techniques like photolithography, etching, and layering. Precision is key, as even minor defects can lead to device malfunction.
- Injection Molding: For the casing, materials are injected into molds to form the outer shell of the device. This process allows for the creation of intricate designs that facilitate functionality and aesthetics.
At this point, manufacturers often conduct preliminary tests on individual components to ensure they meet specified tolerances and performance metrics.
3. Assembly: What Techniques Are Used to Bring Components Together?
The assembly stage combines all prepared components into a fully functional device. This process includes:
- Soldering: Components are soldered onto the PCB using automated machines or manual techniques, ensuring solid connections.
- Integration of Modules: GPS, GSM, and battery modules are integrated into the device, requiring precise alignment and secure connections.
- Quality Control Checkpoints: During assembly, manufacturers typically implement in-process quality checks (IPQC) to catch defects early.
B2B buyers should inquire about the assembly methods used, as automated processes often yield higher precision compared to manual assembly.
4. Finishing: How Is the Device Finalized for Market Readiness?
The finishing stage focuses on preparing the GPS tracking device for distribution. This includes:
- Surface Treatment: Casing may undergo treatments like painting or coating for aesthetic appeal and increased durability.
- Testing: Each device is subjected to rigorous testing, including functionality tests, environmental resistance (temperature, humidity), and battery life assessments.
Manufacturers must ensure that the devices comply with relevant certifications before shipping, which leads us to the next critical aspect: Quality Assurance.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for Micro GPS Tracking Devices?
Quality assurance (QA) is vital in the manufacturing of micro GPS tracking devices, ensuring that products meet international standards and customer expectations.
International Standards: Which Certifications Should Buyers Look For?
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines the criteria for a quality management system, emphasizing customer satisfaction and continuous improvement. Suppliers with ISO 9001 certification demonstrate a commitment to quality processes.
- CE Marking: Required for products sold in the European Economic Area, CE marking indicates compliance with safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For devices used in specific industries (e.g., automotive), adherence to API standards can be crucial.
B2B buyers should verify that their suppliers possess these certifications, as they indicate a commitment to quality and regulatory compliance.
Illustrative image related to micro gps tracking device
How Are Quality Control Checkpoints Implemented Throughout the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control checkpoints are essential for ensuring the integrity of the manufacturing process. Here are the main checkpoints:
1. Incoming Quality Control (IQC)
Before production begins, incoming materials are subjected to IQC. This involves:
- Material Inspection: Raw materials are checked against specifications to ensure they are free from defects.
- Supplier Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can ensure that they maintain high-quality standards.
2. In-Process Quality Control (IPQC)
During the manufacturing process, IPQC is implemented to monitor and verify quality at various stages. This includes:
- Component Testing: Individual components are tested for functionality and performance as they are assembled.
- Assembly Checks: Regular checks during assembly can catch issues early, reducing waste and rework.
3. Final Quality Control (FQC)
Once the devices are fully assembled, FQC involves:
- Comprehensive Testing: Each device undergoes thorough testing for GPS functionality, battery performance, and communication capabilities.
- Certification Verification: Final checks ensure that all necessary certifications are in place before shipment.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Quality Assurance for GPS Devices?
Several testing methods ensure that micro GPS tracking devices meet required standards:
- Functional Testing: Verifies that the device performs its intended functions, such as accurate GPS tracking and data transmission.
- Environmental Testing: Devices are subjected to extreme conditions (temperature, humidity) to assess durability.
- Battery Life Testing: Evaluates how long the device can operate under various conditions, ensuring it meets user expectations.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers must take proactive steps to ensure that suppliers adhere to quality control standards. Here are some strategies:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits can provide insights into a supplier’s quality control processes and adherence to standards.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should be able to provide detailed quality reports that outline testing methods, results, and compliance with international standards.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can offer an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality assurance processes.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International B2B Buyers?
For buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, specific nuances exist:
- Regulatory Compliance: Different regions have varying regulatory requirements, and suppliers must be aware of these to ensure compliance.
- Cultural Considerations: Understanding cultural practices in quality assurance can aid in selecting reliable suppliers.
- Logistics and Supply Chain Challenges: Buyers should consider the impact of logistics on quality, particularly when shipping internationally. Delays or improper handling can compromise product integrity.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers for micro GPS tracking devices, ensuring they receive high-quality products that meet international standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘micro gps tracking device’
Introduction
This guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers seeking to procure micro GPS tracking devices. As demand for asset security and real-time monitoring increases, understanding the critical steps in sourcing these devices is essential for making informed decisions. This checklist will ensure you evaluate the necessary specifications, suppliers, and operational needs effectively.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outlining your technical requirements is crucial to ensure the GPS device meets your operational needs. Consider factors such as tracking accuracy, battery life, coverage area, and integration capabilities with existing systems. For example, if you require devices for a fleet in multiple countries, prioritize models with robust international coverage and long battery life.
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Regulations
Stay informed about the latest trends in GPS tracking technology and any regulatory requirements specific to your region. Regulations may vary significantly across markets such as Africa, South America, and Europe, affecting how you deploy and use these devices. Understanding these elements can help you avoid legal complications and ensure compliance with local laws.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, vet suppliers thoroughly to ensure they can deliver reliable products. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions. Pay attention to customer reviews and testimonials, as they can provide insight into product performance and supplier reliability.
- Supplier Certifications: Verify that the supplier holds relevant certifications, such as ISO or CE, which indicate adherence to quality standards.
- After-Sales Support: Assess the level of support offered post-purchase, including warranty terms and customer service availability.
Step 4: Assess Product Features and Usability
Analyze the features of potential devices to determine which ones align best with your needs. Key features to look for include live tracking capabilities, historical route data, geofencing options, and alert systems. A user-friendly interface is also essential to ensure that your team can easily utilize the tracking system without extensive training.
Step 5: Determine Subscription and Operating Costs
Understand the total cost of ownership, which includes not just the initial device cost but also any ongoing subscription fees for data services. Different models may have varying subscription plans, so it’s important to choose one that aligns with your budget and usage requirements. Also, consider any potential hidden costs related to international usage.
Step 6: Request Samples and Conduct Trials
Before finalizing your order, request samples or conduct trials of the GPS tracking devices. This hands-on experience allows you to assess the practicality and reliability of the devices in real-world conditions. Pay attention to the ease of installation and the responsiveness of the tracking software during the trial period.
Step 7: Finalize the Purchase and Review Terms
Once you have selected a supplier and product, finalize the purchase by reviewing the terms of sale carefully. Ensure that all agreed-upon features, support, and delivery timelines are clearly documented. Establish clear communication channels with your supplier to facilitate a smooth procurement process.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing micro GPS tracking devices effectively, ensuring they make informed and strategic purchasing decisions.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for micro gps tracking device Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Micro GPS Tracking Devices?
When sourcing micro GPS tracking devices, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The quality and type of components, such as GPS modules, batteries, and casings, significantly influence the overall cost. Sourcing high-quality, durable materials can lead to higher initial costs but may reduce long-term expenses related to warranty claims and replacements.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and can affect the final pricing of the devices. In countries with higher labor costs, such as those in Europe, the manufacturing expenses will be reflected in the price. Conversely, sourcing from regions with lower labor costs can lead to significant savings.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to utilities, equipment maintenance, and factory management. Efficient operations can help minimize these costs, but they are still a significant factor in the pricing equation.
-
Tooling: The cost of tools and molds necessary for manufacturing can be substantial, especially for customized devices. These costs are typically amortized over the production volume, impacting the unit price.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC processes is essential for ensuring product reliability and customer satisfaction. However, this adds to the overall cost structure. Buyers should weigh the benefits of investing in quality assurance against potential future costs from defects.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs, including freight and insurance, can vary widely depending on the location of the supplier and the buyer. International shipping may involve customs duties and taxes, further complicating logistics costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically add a profit margin to cover their operational costs and ensure profitability. This margin can vary based on market competition and the supplier’s positioning.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Micro GPS Tracking Device Sourcing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of micro GPS tracking devices:
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in bulk can lead to significant discounts. Suppliers often have minimum order quantities (MOQ) that can affect pricing, so negotiating for larger orders can yield better unit prices.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features, such as enhanced battery life or specialized tracking capabilities, can increase costs. Clearly defining requirements upfront can help manage expenses.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications (like CE, FCC) can increase costs but may be necessary for compliance in certain markets. Understanding the market requirements can help buyers make informed decisions.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record, while newer suppliers might offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: The terms of delivery (such as FOB or CIF) can impact the total landed cost of the products. Buyers must understand these terms to avoid unexpected expenses during shipping.
What Buyer Tips Can Help in Negotiating Costs for Micro GPS Tracking Devices?
To optimize sourcing strategies, buyers should consider the following tips:
-
Negotiate Terms: Don’t hesitate to negotiate pricing, especially for bulk orders. Suppliers may have flexibility in their pricing structures that can lead to cost savings.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Assess not just the initial purchase price but also long-term costs, including maintenance, warranties, and potential replacements. This holistic view can reveal more cost-effective options.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, international taxes, and tariffs that can affect the final cost. Establishing relationships with suppliers familiar with the target regions can also ease the sourcing process.
-
Conduct Market Research: Stay informed about market trends and competitor pricing to ensure you are negotiating from an informed position. This knowledge can aid in discussions with suppliers.
In conclusion, navigating the cost and pricing landscape for micro GPS tracking devices requires careful consideration of various components and influencing factors. By leveraging these insights, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their strategic objectives and budget constraints.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing micro gps tracking device With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Micro GPS Tracking Devices
In the realm of asset tracking, micro GPS tracking devices offer robust solutions for real-time location monitoring. However, businesses may also consider alternative technologies and methods that serve similar purposes. This section compares micro GPS tracking devices against geofencing software and RFID tracking systems, providing B2B buyers with insights into their respective advantages and limitations.
| Comparison Aspect | Micro GPS Tracking Device | Geofencing Software | RFID Tracking System |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High accuracy; real-time tracking in over 100 countries | Accurate within designated areas; relies on GPS and cellular data | High accuracy within short distances; excellent for inventory management |
| Cost | Moderate initial cost plus subscription fees | Variable pricing based on software and usage | High initial setup cost; low ongoing costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple installation; requires subscription setup | Requires software installation and configuration | Complex setup; needs infrastructure (readers, tags) |
| Maintenance | Regular software updates; battery management needed | Continuous software support; minimal hardware maintenance | Low maintenance; tags have long lifespan but may need replacement |
| Best Use Case | Personal tracking, fleet management, asset protection | Monitoring movement in defined areas; marketing | Inventory tracking, logistics, asset management |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Geofencing Software?
Geofencing software utilizes GPS or RFID technology to create virtual boundaries. When assets enter or leave these boundaries, alerts are sent to users.
Pros:
– Cost-effective for businesses with specific area monitoring needs, such as retail locations or delivery routes.
– Provides a comprehensive overview of asset movement within designated areas, enhancing operational efficiency.
Cons:
– Limited to areas where GPS and cellular signals are strong, which may not be reliable in remote locations.
– Requires a solid understanding of software to set up and maintain effectively.
How Does RFID Tracking System Compare?
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) tracking systems consist of tags and readers that communicate wirelessly to track items in close proximity.
Pros:
– Highly effective for inventory management and logistics, enabling rapid scanning and tracking of multiple items simultaneously.
– Low ongoing costs once the initial setup is complete, making it suitable for businesses with high volumes of assets.
Illustrative image related to micro gps tracking device
Cons:
– High initial investment in infrastructure, including readers and tags.
– Limited range; best suited for environments where assets are kept in close quarters, such as warehouses or retail spaces.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Business Needs
When selecting the appropriate tracking solution, B2B buyers should consider their specific needs, including the nature of the assets being tracked, the environment in which they operate, and budget constraints. Micro GPS tracking devices offer flexibility and global coverage, making them ideal for personal tracking and fleet management. Geofencing software is suitable for businesses focusing on specific locations, while RFID systems excel in environments with dense inventory. By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each option, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and enhance asset security.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for micro gps tracking device
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Micro GPS Tracking Devices?
Understanding the essential technical properties of micro GPS tracking devices is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly those operating in logistics, security, and asset management. Here are some critical specifications that you should consider:
-
Battery Life
– Definition: This refers to the duration a GPS tracker can operate before needing a recharge. Battery life can vary significantly based on usage mode—whether in standby or active tracking.
– B2B Importance: Longer battery life means less frequent recharging, reducing operational downtime and maintenance costs. For businesses that rely on continuous tracking, such as logistics companies, devices with extended battery life can enhance efficiency. -
Coverage Area
– Definition: This specifies the geographical range within which the GPS tracker can provide accurate location data, often measured in countries or regions.
– B2B Importance: A tracker with global coverage is essential for international shipping and logistics, allowing companies to monitor their assets in real time, regardless of their location. This feature is especially beneficial for businesses operating across multiple continents, such as in Africa or South America. -
Real-Time Tracking Capability
– Definition: This indicates the ability of the GPS device to provide instantaneous location updates, typically through a mobile or web application.
– B2B Importance: Real-time tracking is critical for businesses that need immediate access to location data for decision-making, such as fleet management and security services. It allows for prompt responses to emergencies or logistical challenges. -
Size and Weight
– Definition: The physical dimensions and weight of the GPS device, often measured in grams or centimeters.
– B2B Importance: Smaller, lightweight devices are easier to conceal and transport, making them ideal for personal tracking or covert applications. This is particularly relevant for businesses in security sectors, where discretion is paramount. -
Data Security Features
– Definition: This refers to the measures in place to protect the data transmitted by the GPS device, including encryption and secure data transmission protocols.
– B2B Importance: In industries dealing with sensitive information, such as transportation of valuable goods or personal tracking, robust data security is essential. It mitigates risks associated with data breaches and enhances customer trust. -
Subscription Model
– Definition: This outlines the payment structure for utilizing the GPS tracking service, often involving monthly or annual fees based on usage.
– B2B Importance: Understanding the subscription model is vital for budgeting purposes. Businesses must assess the cost-effectiveness of the service in relation to their operational needs, particularly for those tracking multiple assets.
What Are the Common Trade Terminology and Jargon in the Micro GPS Tracking Industry?
Familiarity with industry-specific terminology can greatly enhance communication and negotiations between B2B buyers and suppliers. Here are some essential terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Relevance: Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for buyers looking to customize GPS devices or integrate them into larger systems. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Relevance: Knowing the MOQ helps businesses plan their purchases according to budget and inventory needs, particularly when considering bulk orders. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for a specific quantity of goods or services.
– Relevance: RFQs are vital for obtaining competitive pricing and understanding the financial implications of procurement decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in international transactions.
– Relevance: Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for understanding shipping costs, insurance, and liability, which can impact the total cost of ownership for GPS tracking devices. -
GPS (Global Positioning System)
– Definition: A satellite-based navigation system that provides location and time information.
– Relevance: Understanding GPS technology is fundamental for evaluating the performance and reliability of tracking devices, as it directly affects accuracy and functionality. -
API (Application Programming Interface)
– Definition: A set of protocols for building software and applications that allow different systems to communicate.
– Relevance: APIs are important for businesses looking to integrate GPS tracking systems with other software solutions, enhancing operational efficiency and data management.
These technical specifications and industry terms will empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions regarding micro GPS tracking devices, ensuring they select solutions that align with their operational needs and strategic goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the micro gps tracking device Sector
What are the Key Drivers and Trends in the Micro GPS Tracking Device Market?
The micro GPS tracking device market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for asset security and real-time location tracking across various industries. Internationally, sectors such as logistics, transportation, and personal safety are pushing the adoption of these devices. In regions like Africa and South America, the rise of e-commerce and delivery services has heightened the need for reliable tracking solutions, while in the Middle East and Europe, regulatory frameworks for logistics and transport safety are further propelling market growth.
Emerging technologies, such as 5G connectivity and IoT integration, are also reshaping the landscape, enabling more sophisticated tracking capabilities. Features like geofencing, which alerts users when assets move in and out of designated areas, are becoming standard. Additionally, the miniaturization of technology has led to the development of smaller, more discreet devices that can be integrated into various applications, from personal items to vehicle tracking.
Illustrative image related to micro gps tracking device
B2B buyers should be aware of the competitive landscape, which includes both established brands and innovative startups. Buyers should consider factors such as device compatibility, subscription models, and customer support when sourcing from international suppliers. As market dynamics continue to evolve, staying informed about these trends will be critical for making strategic procurement decisions.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact Your B2B Strategy for Micro GPS Tracking Devices?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are increasingly crucial in the micro GPS tracking device market. As global awareness of environmental issues grows, buyers are seeking suppliers that prioritize sustainability in their production processes. This includes using eco-friendly materials and minimizing waste throughout the supply chain.
Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and adherence to RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) standards can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability. Additionally, manufacturers that implement circular economy practices—such as recycling components or offering take-back programs—are more appealing to environmentally-conscious businesses.
For B2B buyers, emphasizing sustainability can enhance brand reputation and customer loyalty, particularly in markets where consumers are increasingly valuing corporate responsibility. It also aligns with governmental regulations aimed at reducing environmental impact, particularly in regions like Europe where compliance is strictly enforced. Therefore, buyers should prioritize partnerships with suppliers who demonstrate a clear commitment to ethical practices and sustainable sourcing.
What is the Historical Context of Micro GPS Tracking Devices and Their Relevance Today?
The evolution of GPS tracking technology dates back to the late 20th century, initially developed for military applications. Over the years, the technology became more accessible, leading to the commercialization of GPS devices in the 1990s. With advancements in mobile technology and the internet, GPS tracking systems transitioned from bulky units to compact, user-friendly devices.
Illustrative image related to micro gps tracking device
Today, micro GPS tracking devices leverage cutting-edge technology, including cloud computing and mobile applications, to provide real-time tracking and data analytics. This evolution has made them indispensable tools for businesses looking to enhance security, improve operational efficiency, and optimize resource management.
In the current B2B landscape, understanding the historical context of these devices can provide valuable insights into their capabilities and applications, ensuring that buyers make informed decisions that align with their strategic objectives. As the market continues to evolve, staying abreast of technological advancements will be essential for leveraging the full potential of micro GPS tracking devices.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of micro gps tracking device
-
How do I ensure the reliability of a micro GPS tracking device supplier?
To ensure reliability, conduct thorough due diligence on potential suppliers. Request references and customer testimonials, and check their business history and reputation in the market. Verify certifications related to quality assurance, such as ISO standards, and assess their ability to provide after-sales support. Consider engaging in a pilot program to evaluate the product’s performance and the supplier’s responsiveness before committing to larger orders. -
What is the best micro GPS tracking device for logistics and fleet management?
For logistics and fleet management, look for devices that offer real-time tracking, geofencing capabilities, and robust battery life. The best options typically feature 4G connectivity for global coverage, alerts for unauthorized movement, and a user-friendly interface for easy monitoring. Brands that provide extensive reporting features, such as route history and usage analytics, will help you optimize operations and improve asset security. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) for micro GPS tracking devices?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly by supplier and region. Generally, MOQs for micro GPS tracking devices can range from 100 to 1,000 units, depending on the manufacturer’s production capabilities and the complexity of the device. It’s crucial to discuss your specific needs with suppliers and negotiate MOQs that align with your budget and market demand. -
What payment terms are common when purchasing micro GPS tracking devices internationally?
Common payment terms for international purchases include a deposit (typically 30-50%) upfront, with the balance due prior to shipping or upon delivery. Some suppliers may offer letter of credit options or payment through escrow services for added security. Always clarify payment terms upfront to avoid misunderstandings and ensure a smooth transaction process. -
How can I customize micro GPS tracking devices to fit my business needs?
Customization options vary by supplier but often include alterations in software features, hardware specifications, and branding. Discuss your specific requirements with the supplier, including desired functionalities like enhanced battery life, additional sensors, or unique packaging. Be prepared to provide clear specifications and possibly engage in a development phase to ensure the final product meets your expectations. -
What quality assurance measures should I expect from a reputable GPS tracking device supplier?
A reputable supplier should implement rigorous quality assurance measures, including testing devices for durability, accuracy, and performance under various conditions. Look for suppliers that provide detailed testing reports and certifications. Regular audits and adherence to international quality standards, such as ISO 9001, are also indicators of a supplier committed to maintaining high product quality. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing micro GPS tracking devices?
Consider factors such as shipping times, customs regulations, and potential tariffs when sourcing internationally. Ensure that the supplier has experience in navigating logistics in your target markets, especially in regions like Africa and South America, where customs processes can be complex. Clarify shipping terms (FOB, CIF, etc.) and ensure you have a clear plan for inventory management upon arrival. -
How do I handle warranty and support issues with my micro GPS tracking devices?
Ensure that your supplier provides a clear warranty policy that covers defects in materials and workmanship for a defined period, typically one year. Familiarize yourself with the process for reporting issues and obtaining replacements or repairs. A good supplier will offer responsive customer support and may also provide resources such as user manuals and troubleshooting guides to assist with common problems.
Top 7 Micro Gps Tracking Device Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Family1st – Free Delivery Service
Domain: family1st.io
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: This company, Family1st – Free Delivery Service, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
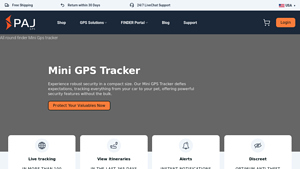
2. PAJ GPS – Mini GPS Tracker
Domain: paj-gps.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Mini GPS Tracker | PAJ GPS USA
– Experience robust security in a compact size.
– Live tracking in more than 100 countries.
– View itineraries in the last 365 days.
– Instant notifications and alerts.
– Discreet anti-theft protection.
– POWER Finder 4G: $39.99, battery up to 90 days on standby, applications include cars, motorhomes, boats, scooters, motorcycles, beekeeping, horseback riding, contai…
3. Pebblebee – Pebblebee Card
Domain: bestbuy.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: [{‘name’: ‘Pebblebee Card’, ‘model’: ‘PB-621-S’, ‘sku’: ‘6593433’, ‘rating’: ‘3.5 out of 5 stars’, ‘reviews’: ’20 reviews’, ‘description’: ‘Rechargeable item tracker for wallets, bags, or narrow spaces. Works with Android Find My Device or Apple Find My. Features bright LED and loud sound for easy locating.’}, {‘name’: ‘Pebblebee Clip’, ‘model’: ‘PB-531-S’, ‘sku’: ‘6593435’, ‘rating’: ‘3.9 out of …
4. Tracki – Best Overall GPS Tracker
Domain: gpstracker247.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: [{“name”:”Tracki GPS Tracker”,”type”:”Best Overall”,”cost”:”$28.88 + $9.95–$19.95/mo”,”key_features”:”Global tracking with multiple network fallback, 14-day battery with real-time 4G, waterproof magnetic case, works where cellular fails, two-way speakerphone, super detailed tracking, 2-month battery, waterproof, ultra-compact, strong magnet”,”size”:”1.74″ x 1.5″ x 0.6″”,”weight”:”1.26 Oz”,”battery…
5. Mini GPS Tracker – Ultra Compact Design
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Smallest GPS tracker needed to fit into a tube with an inside diameter of .200 inches. The user is looking for a GPS tracker that is smaller than existing models, which are typically around 30mm x 40mm. Suggestions include custom designs and the use of thin batteries and circuits. Other users mention alternatives like AirTags for tracking bags or pets, and the need for a tracker that can be attach…
6. Lightbug – Key GPS Tracking Products
Domain: lightbug.io
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: Lightbug offers a range of GPS tracking technologies characterized by ultra-long battery life, small size, and low total cost of ownership (TCO). Key products include: 1. Lightbug Pro: An industrial-grade tracker with a battery life of up to 15 years, optional magnetic mount. 2. Lightbug Zero: One of the smallest GPS tracking devices globally. 3. Lightbug RH2 RTK Handset: Provides ultra-high accur…
7. SpyCentre – Waterproof Miniature GPS Tracker
Domain: spycentre.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”: “Waterproof Miniature GPS Tracker”, “SKU”: “9094”, “Sale Price”: “$89.99”, “Regular Price”: “$159.99”, “Weight”: “5.80 ounces”, “Dimensions”: “3.5 inches”, “Features”: [{“Real-Time Tracking”: “30-second updates when in motion”}, {“Waterproof”: “IP67 weatherized case”}, {“Battery Life”: “Up to 22 days standby time with 2 hours active reporting per day”}, {“Data Storage”: “Saves up …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for micro gps tracking device
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Micro GPS Tracking Device Procurement?
In the competitive landscape of micro GPS tracking devices, strategic sourcing emerges as a crucial factor for B2B buyers looking to maximize value. By prioritizing suppliers that offer innovative solutions, such as real-time tracking capabilities, extended battery life, and extensive global coverage, businesses can enhance their operational efficiency and security measures. Understanding the diverse applications of these devices—from asset protection to personal tracking—enables companies to tailor their purchasing decisions effectively.
For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, leveraging strategic sourcing can lead to significant cost savings and improved service quality. Engaging with manufacturers that prioritize transparency, support, and competitive pricing can facilitate smoother logistics and better customer satisfaction.
Illustrative image related to micro gps tracking device
As the demand for micro GPS tracking devices continues to grow, now is the time to evaluate your sourcing strategy. Embrace innovation, assess supplier capabilities, and stay ahead of the curve. The future of asset management and personal security is at your fingertips—take action today to secure the best solutions for your business needs.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.