Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for tracker mode
In an increasingly interconnected world, sourcing the right tracker mode technology poses a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. Whether you’re managing logistics in the Middle East, monitoring assets in Africa, or ensuring compliance in Europe, the effectiveness of your tracking solutions can directly impact operational efficiency and security. This guide delves into the various types of tracker modes available, from ultra-sleep to active reporting, providing insights into their applications across different sectors.
We will explore critical factors such as supplier vetting, cost considerations, and the specific needs of diverse markets, including South America and Germany. By understanding the nuances of each mode—like how the transition from Ping to Lost mode can safeguard high-value assets—you will be better equipped to make informed purchasing decisions.
This comprehensive resource aims to empower you with the knowledge needed to navigate the global market for tracker mode technologies. By leveraging this guide, you can enhance your procurement strategies, ensuring that you select solutions that not only meet your operational requirements but also align with the dynamic demands of your industry.
Table Of Contents
- Top 9 Tracker Mode Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for tracker mode
- Understanding tracker mode Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of tracker mode
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘tracker mode’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for tracker mode
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for tracker mode
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘tracker mode’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for tracker mode Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing tracker mode With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for tracker mode
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the tracker mode Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of tracker mode
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for tracker mode
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding tracker mode Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Near Home | Ultra sleep mode, minimal power consumption, location updates every 10 seconds. | Pet tracking, personal safety devices | Pros: Long battery life (~2 years). Cons: Limited tracking frequency. |
| Ping Mode | Responds to location requests on demand; no continuous tracking. | Asset tracking, logistics management | Pros: Efficient use of battery. Cons: No historical data unless requested. |
| Active Mode | Continuous tracking with updates every 7 minutes. | Fleet management, active pet tracking | Pros: Regular updates provide real-time data. Cons: Shorter battery life (3 weeks). |
| Lost Mode | High-frequency updates every 30 seconds for immediate tracking. | Emergency response, high-value asset protection | Pros: Ideal for critical situations. Cons: Drains battery quickly (20 hours). |
| Standard Mode | Updates based on set intervals; balances frequency with battery life. | General asset management, logistics | Pros: Flexible tracking intervals. Cons: May not provide real-time data. |
What Are the Characteristics of Near Home Tracker Mode?
The Near Home tracker mode is designed for low-power usage while maintaining a connection to the cloud. It operates in ultra sleep mode, making it ideal for applications such as pet tracking and personal safety devices. Buyers looking for a long-lasting solution will appreciate its battery life of approximately two years, but they should note that the tracking frequency is limited to every 10 seconds, which may not suffice for real-time monitoring needs.
How Does Ping Mode Benefit B2B Users?
Ping mode allows users to request location updates on demand, making it particularly useful for asset tracking and logistics management where constant tracking is not necessary. This mode is battery-efficient, lasting up to one year, which is advantageous for companies looking to minimize operational costs. However, it lacks continuous tracking and does not maintain a location history unless actively requested, which can be a drawback for businesses requiring consistent monitoring.
Why Choose Active Mode for Real-Time Tracking?
Active mode provides continuous updates every seven minutes, making it suitable for fleet management and active pet tracking. This mode strikes a balance between providing timely data and maintaining acceptable battery life, lasting around three weeks with regular use. However, buyers should consider that the frequent updates may lead to quicker battery depletion compared to more passive modes, necessitating frequent recharging or battery replacement.
When Is Lost Mode Essential for Businesses?
Lost mode is critical in emergency situations, offering high-frequency updates every 30 seconds. This mode is particularly beneficial for high-value asset protection and emergency response scenarios, ensuring that assets can be located quickly. While it provides the most immediate tracking, the trade-off is a significant drain on battery life, lasting only about 20 hours. Businesses should weigh the urgency of their tracking needs against the potential for rapid battery consumption.
How Does Standard Mode Offer Flexibility?
Standard mode allows businesses to set tracking intervals that balance frequency with battery life. This makes it suitable for general asset management and logistics, where real-time tracking is not always necessary. The flexibility in choosing update frequencies helps businesses optimize their tracking solutions based on specific operational needs. However, the potential for delayed updates may not be ideal for situations requiring immediate data, making it essential for buyers to assess their tracking priorities carefully.
Key Industrial Applications of tracker mode
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of tracker mode | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Logistics & Supply Chain | Real-time asset tracking of shipments | Improved efficiency and reduced losses through theft or misplacement | Compatibility with existing logistics software and devices |
| Agriculture | Livestock tracking and monitoring | Enhanced management of livestock health and location, reducing losses | Durability and battery life suitable for outdoor use |
| Fitness & Health | Monitoring workout sessions in gyms | Enhanced user engagement and personalized training plans | Integration capabilities with fitness apps and devices |
| Security & Surveillance | Tracking of high-value assets | Improved security and reduced risk of theft or loss | Robustness in adverse conditions and real-time alerts |
| Automotive | Fleet management for vehicle tracking | Optimized routes, reduced fuel costs, and improved driver safety | Scalability and support for various vehicle types |
How is Tracker Mode Applied in Logistics and Supply Chain Management?
In logistics, tracker mode is employed to provide real-time tracking of shipments and assets. This application allows businesses to monitor the location of goods in transit, significantly reducing the risk of loss or theft. By leveraging tracker mode, companies can enhance operational efficiency and streamline supply chain processes. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, ensuring compatibility with existing logistics software and devices is crucial to achieve seamless integration.
What Role Does Tracker Mode Play in Agriculture?
In the agricultural sector, tracker mode is utilized for monitoring livestock. This capability allows farmers to keep track of animal movements and health status, ultimately reducing losses due to theft or wandering. The ability to receive real-time data on livestock can enhance decision-making regarding feeding and breeding. Buyers in this sector should prioritize devices with durability and extended battery life, given the often challenging outdoor environments in regions like the Middle East and rural areas of Europe.
How is Tracker Mode Enhancing the Fitness and Health Industry?
In the fitness sector, tracker mode is pivotal for monitoring workout sessions, allowing users to track their performance in real time. This functionality enables fitness centers to provide personalized training plans based on user data, thereby enhancing customer engagement and satisfaction. For B2B buyers, particularly gym owners and fitness app developers, it’s essential to consider the integration capabilities of tracker mode with existing fitness applications and devices to maximize user experience.
Illustrative image related to tracker mode
How is Tracker Mode Used in Security and Surveillance?
Tracker mode serves a critical function in the security sector by enabling the tracking of high-value assets such as electronics or vehicles. This application enhances security measures, allowing businesses to receive real-time alerts in the event of theft or unauthorized movement. For international buyers, sourcing devices that demonstrate robustness in adverse conditions and provide reliable real-time alerts is essential to ensuring asset protection in various environments.
What Benefits Does Tracker Mode Offer in Fleet Management?
In the automotive sector, tracker mode is essential for effective fleet management. It allows companies to monitor vehicle locations, optimize routes, and improve driver safety, ultimately leading to reduced fuel costs and enhanced operational efficiency. Buyers should consider the scalability of tracking solutions to accommodate various vehicle types and the ability to integrate with existing fleet management systems, particularly in regions with growing logistics demands such as Europe and the Middle East.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘tracker mode’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty Balancing Tracking Frequency and Battery Life
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face the challenge of selecting the right tracking mode that balances the need for frequent location updates with the limitations of battery life. For instance, logistics companies may require real-time tracking of their fleet but struggle with devices that quickly drain their batteries, leading to potential downtime and loss of tracking capabilities. This can be particularly critical in regions with limited access to charging infrastructure, such as remote areas in Africa or South America, where fleet operations are essential for business continuity.
Illustrative image related to tracker mode
The Solution: To effectively address this issue, B2B buyers should assess their specific tracking needs and choose devices that offer customizable tracking modes. For instance, opting for a device that allows switching between modes like Active Mode for frequent updates during peak operations and Standard Mode for more extended periods can conserve battery life. Additionally, buyers should consider implementing a scheduling system for their tracking devices, where they can program the device to use higher frequency modes only during crucial operational hours. This not only optimizes battery consumption but also ensures that businesses maintain visibility of their assets when it matters most. Regularly reviewing and analyzing battery performance data can also inform better decisions about when to switch modes, ensuring that the tracking system is both efficient and effective.
Scenario 2: Inadequate Real-time Tracking During Critical Situations
The Problem: In emergency scenarios, businesses often require immediate and precise location data for high-value assets or personnel. For example, security companies monitoring high-risk areas may find that standard tracking modes do not provide the necessary update frequency, leading to delays in response times. This lack of real-time data can jeopardize safety and operational efficiency, especially in regions experiencing political instability or civil unrest.
The Solution: To mitigate this risk, B2B buyers should prioritize devices that offer an Emergency Mode with rapid location updates, typically every minute or less. When sourcing tracking solutions, it is crucial to inquire about the capabilities of the device in emergency situations and assess whether they can seamlessly switch to Emergency Mode at the push of a button. Furthermore, integrating real-time alerts and notifications into the tracking system can enhance situational awareness, allowing businesses to respond promptly. Training staff on how to quickly activate these emergency features and ensuring that devices are regularly maintained can further enhance reliability during critical operations, particularly in high-risk environments.
Scenario 3: Managing Data Overload and Reporting Complexity
The Problem: As businesses implement tracker modes, they often encounter a flood of data that can overwhelm their operational processes. For instance, companies in logistics may find it challenging to sift through vast amounts of location data generated by their tracking devices. This can lead to inefficiencies in decision-making, as teams struggle to identify actionable insights from the data. In regions with diverse operational landscapes, such as Europe with its varied urban and rural environments, this complexity can be even more pronounced.
The Solution: To streamline data management, B2B buyers should look for tracking solutions that include advanced reporting and analytics features. This allows businesses to filter and visualize data effectively, making it easier to extract meaningful insights. Implementing a centralized dashboard that aggregates data from various tracking modes can help teams focus on the most relevant information. Additionally, investing in training for staff on data interpretation and the use of analytical tools can empower them to leverage tracking data for strategic decision-making. Collaborating with software providers to customize reporting features according to specific business needs can also enhance the overall utility of the tracking system, ensuring that organizations can manage data without becoming overwhelmed.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for tracker mode
What Materials Are Best for Tracker Mode Devices?
When selecting materials for tracker mode devices, it is essential to consider their properties, performance, and suitability for various applications. Below, we analyze four common materials used in tracker mode devices, focusing on their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
1. Polycarbonate (PC)
Key Properties:
Polycarbonate is known for its high impact resistance and optical clarity. It can withstand temperatures up to 120°C and has excellent dimensional stability. Its inherent UV resistance makes it suitable for outdoor applications.
Pros & Cons:
The durability of polycarbonate makes it ideal for rugged environments, but it can be more expensive than other plastics. Manufacturing complexity is moderate, as it requires specialized molding techniques. While it is suitable for housings and covers, it may not provide the best chemical resistance.
Impact on Application:
Polycarbonate is compatible with a range of environmental conditions, making it suitable for outdoor tracker devices. However, exposure to certain solvents can lead to degradation.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in regions such as Europe and the Middle East should ensure compliance with RoHS and REACH regulations. In contrast, buyers from Africa and South America may prioritize cost-effectiveness and local availability.
2. Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance and can withstand high temperatures (up to 870°C). It has high tensile strength and is suitable for harsh environments.
Pros & Cons:
While stainless steel is incredibly durable, it is heavier and more expensive than plastics. Manufacturing processes can also be complex, requiring specialized equipment for cutting and shaping. Its robustness makes it ideal for applications where longevity is critical.
Illustrative image related to tracker mode
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel is particularly beneficial for tracker devices used in marine or industrial applications where exposure to corrosive elements is prevalent.
Considerations for International Buyers:
International buyers should be aware of standards such as ASTM A240 for stainless steel grades. Compliance with local regulations regarding material sourcing and environmental impact is also crucial.
3. ABS Plastic
Key Properties:
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a thermoplastic known for its toughness and impact resistance. It operates effectively within a temperature range of -20°C to 80°C.
Illustrative image related to tracker mode
Pros & Cons:
ABS is cost-effective and easy to mold, making it suitable for mass production. However, it has lower chemical resistance compared to polycarbonate and may not perform well in extreme temperatures.
Impact on Application:
ABS is suitable for indoor tracker devices or applications with limited exposure to harsh conditions. Its lightweight nature makes it ideal for portable devices.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should consider compliance with international standards such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems. In regions like Europe, ensuring that ABS is free from harmful substances is essential.
4. Silicone Rubber
Key Properties:
Silicone rubber is known for its flexibility, temperature resistance (from -60°C to 200°C), and excellent weatherability. It is also resistant to UV light and ozone.
Pros & Cons:
Silicone rubber is highly durable and provides excellent sealing properties, making it ideal for waterproof applications. However, it can be more expensive than conventional plastics and may require specialized manufacturing techniques.
Illustrative image related to tracker mode
Impact on Application:
Silicone is particularly useful for gaskets and seals in tracker devices, ensuring protection against moisture and dust ingress.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure that silicone materials comply with relevant food safety and environmental regulations, especially in regions such as the EU, where compliance with REACH is mandatory.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for tracker mode | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polycarbonate | Housings and covers | High impact resistance | Moderate chemical resistance | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Marine and industrial applications | Excellent corrosion resistance | Heavier and more expensive | High |
| ABS Plastic | Indoor devices | Cost-effective and easy to mold | Lower chemical resistance | Low |
| Silicone Rubber | Seals and gaskets | Excellent sealing properties | More expensive and complex to mold | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides insights into the various materials suitable for tracker mode devices, helping B2B buyers make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and compliance considerations.
Illustrative image related to tracker mode
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for tracker mode
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Tracker Modes?
The manufacturing process for tracker modes involves several critical stages, each essential for ensuring the final product meets the required specifications for performance, durability, and reliability. Here’s a breakdown of the typical stages involved:
1. Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used in Tracker Manufacturing?
The first stage involves sourcing and preparing high-quality materials. Common materials used in tracker devices include:
- PCB (Printed Circuit Board): The backbone of electronic devices, PCBs are manufactured with precise specifications to accommodate the circuitry for GPS and communication modules.
- Enclosures: Made from durable plastics or metals, these housings protect the internal components from environmental factors. Depending on the intended application, materials may vary to ensure ruggedness.
- Batteries: Lithium-ion or lithium polymer batteries are often used for their lightweight and long-lasting power capabilities. Battery selection is crucial for optimizing the device’s operational modes.
2. Forming: How Are Tracker Components Assembled?
Once materials are prepared, the forming stage begins. This includes:
- Component Placement: Using automated pick-and-place machines, electronic components are precisely positioned on the PCB.
- Soldering: Components are soldered onto the PCB using techniques such as wave soldering or reflow soldering, ensuring robust electrical connections.
- Molding and Machining: For plastic enclosures, injection molding is employed, while metal components may undergo machining processes to achieve the desired shapes and tolerances.
3. Assembly: What Is Involved in the Final Assembly of Tracker Devices?
The assembly stage involves integrating all components into a final product. This includes:
- Integration of Electronics: The assembled PCBs are combined with sensors, antennas, and power sources within the protective enclosure.
- Firmware Installation: The device’s firmware is uploaded, allowing it to operate in various modes such as Near Home, Ping, Active, and Lost modes.
- Final Assembly Testing: Before sealing the enclosure, functional tests are conducted to ensure that all components work as intended and that the device meets performance benchmarks.
4. Finishing: What Finishing Techniques Are Applied to Tracker Devices?
Finishing touches enhance both the aesthetics and functionality of tracker devices. This includes:
- Surface Treatments: Coatings may be applied to improve resistance to water, dust, and scratches, enhancing durability.
- Labeling and Packaging: Devices are labeled with necessary information, and packaging is designed to protect the product during shipping and storage.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Tracker Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in ensuring that tracker devices are reliable and meet international standards. Here’s how QA is typically structured:
Relevant International Standards: What Certifications Should Buyers Look For?
Manufacturers of tracker devices often adhere to several international quality standards, including:
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems, ensuring consistent quality in products and services.
- CE Marking: Required for products sold in the European Economic Area, this marking indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: Particularly relevant for devices used in logistics or transportation, these standards ensure that products meet specific industry requirements.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints During Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are established throughout the manufacturing process to catch defects early. Key checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, various tests are conducted at different stages to monitor quality. This may include functional tests and inspections of assembly processes.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the device is fully assembled, a comprehensive evaluation is performed, including functionality tests across all operating modes, battery performance assessments, and environmental tests.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Tracker Device Production?
To verify the quality and reliability of tracker devices, manufacturers employ various testing methods:
- Functional Testing: Ensures that all features of the device operate as intended. This includes testing the GPS accuracy, battery life, and responsiveness in different modes.
- Environmental Testing: Devices are subjected to extreme conditions, such as temperature variations, humidity, and shock, to ensure they can withstand real-world scenarios.
- Battery Testing: Evaluates battery performance under different loads and conditions to confirm longevity and reliability.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
When sourcing tracker devices, B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify the quality control practices of potential suppliers:
- Audits: Conducting on-site audits of manufacturing facilities can provide insights into the production processes and adherence to quality standards.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed QC reports from suppliers can help assess their quality management systems and testing outcomes.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased evaluation of the manufacturing processes and final products.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
B2B buyers from different regions may encounter specific quality control nuances, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe:
Illustrative image related to tracker mode
- Regulatory Compliance: Understanding local regulations and compliance requirements is crucial, as these can vary significantly between regions.
- Cultural Considerations: Different cultural attitudes toward quality and manufacturing practices can impact supplier relationships. Establishing clear communication and expectations is vital.
- Supply Chain Logistics: Buyers should consider the logistics of sourcing, including lead times, shipping regulations, and potential customs issues that could affect the quality of the final product.
By understanding the intricacies of manufacturing processes and quality assurance for tracker modes, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they select suppliers that meet their quality and performance standards. This thorough approach not only mitigates risks but also fosters long-term partnerships built on reliability and excellence.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘tracker mode’
This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers interested in procuring tracker mode technology. By following these steps, you can ensure that you choose a solution that meets your operational needs and aligns with your business goals.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by clearly outlining what you need from the tracker mode technology. Consider factors such as tracking frequency, battery life, and the type of data you want to collect. For instance, if you require real-time tracking for high-value assets, look for solutions that offer high-frequency updates, such as every minute or two.
Step 2: Assess Your Target Market Needs
Understanding the unique requirements of your target market is essential. Different regions may have specific regulations or preferences regarding tracking technology. For example, buyers in the Middle East might prioritize security features, while European buyers may focus on compliance with GDPR. Tailoring your procurement strategy to these needs will enhance acceptance and usability.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, thoroughly vet potential suppliers. Request comprehensive company profiles, product case studies, and references from clients in similar industries. Pay attention to their experience in your target markets, as familiarity with local regulations and customer expectations can significantly impact the success of your implementation.
Illustrative image related to tracker mode
Step 4: Analyze Pricing Models
Different suppliers may offer various pricing structures, such as subscription-based or one-time purchase models. Ensure you understand what is included in the price, such as software updates and customer support. Compare these models across suppliers to find the best value for your budget while also considering the long-term costs associated with maintenance and upgrades.
Step 5: Verify Compliance and Security Standards
In an era of heightened data privacy concerns, ensuring that your chosen tracker mode technology complies with relevant regulations is crucial. Verify that the supplier adheres to international standards such as GDPR or local data protection laws. Additionally, inquire about their security protocols to protect sensitive data from breaches.
Step 6: Conduct a Pilot Test
Before full-scale implementation, conduct a pilot test of the tracker mode technology. This trial will allow you to evaluate its performance in real-world conditions and identify any potential issues. Gather feedback from users during this phase to ensure the technology meets their needs and expectations.
Step 7: Plan for Integration and Support
Finally, consider how the tracker mode technology will integrate with your existing systems. Ensure that the supplier offers robust support for integration and ongoing maintenance. A reliable support system will help address any challenges quickly and minimize disruptions to your operations.
Illustrative image related to tracker mode
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing tracker mode technology, ultimately leading to improved operational efficiency and enhanced asset management.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for tracker mode Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Tracker Mode Sourcing?
Understanding the cost structure of tracker mode sourcing is essential for international B2B buyers aiming to optimize their procurement strategies. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margin.
-
Materials: The selection of components—such as GPS modules, batteries, and enclosures—significantly affects the overall cost. High-quality materials may increase initial expenses but can lead to better performance and longevity, reducing Total Cost of Ownership (TCO).
-
Labor: Labor costs vary based on the geographical location of the manufacturing facility. Regions with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing, but buyers should consider the trade-off with quality and production efficiency.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility management. Efficient production processes can help minimize these expenses, impacting the final price.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs can be substantial, especially for custom designs. These costs are amortized over production volume, making larger orders more cost-effective per unit.
-
Quality Control (QC): Investing in robust QC processes ensures product reliability and compliance with international standards. While this adds to upfront costs, it can mitigate risks associated with defects and recalls.
-
Logistics: Transportation, warehousing, and customs duties must be factored into the overall cost. Choosing efficient logistics partners and optimal shipping methods can minimize delays and additional costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing. Understanding industry standards for margins can aid buyers in assessing fair pricing.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Tracker Mode Sourcing?
Several factors influence the pricing of tracker mode devices, which can be critical for buyers in diverse markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Illustrative image related to tracker mode
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) can significantly affect pricing. Larger orders typically result in lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their demand forecasts.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom features can lead to higher costs. Buyers should clearly define requirements to avoid unnecessary expenses while ensuring that essential functionalities are included.
-
Materials: The choice between standard and premium materials will influence both the cost and performance of the tracker. Buyers should evaluate the long-term benefits of higher-quality materials against their budget constraints.
-
Quality/Certifications: Products that comply with international standards or possess certifications (e.g., CE, FCC) may carry a premium. However, these certifications can enhance trust and reduce liability in international markets.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, production capacity, and reliability can influence pricing. Building long-term relationships with trusted suppliers can lead to better pricing negotiations and service.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms affects the responsibility for logistics costs and risks. Understanding these terms can help buyers negotiate better shipping terms and manage costs effectively.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in Tracker Mode Sourcing?
-
Negotiate Wisely: Leverage your purchasing power by negotiating prices based on volume and long-term contracts. Be transparent about your needs to foster a cooperative relationship.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but also maintenance, warranty, and operational costs. This comprehensive approach can lead to more informed purchasing decisions.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Transactions: Be aware of exchange rates, tariffs, and local regulations that may impact pricing. This is particularly relevant for buyers from diverse regions, such as Europe and the Middle East.
-
Request Samples: Before finalizing orders, request samples to assess quality and performance. This can help avoid costly mistakes down the line.
-
Stay Informed on Market Trends: Keeping abreast of technological advancements and market shifts can provide leverage in negotiations and sourcing strategies.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of the cost structure, pricing influences, and strategic negotiation can empower international B2B buyers to make informed decisions in tracker mode sourcing, maximizing value while minimizing costs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing tracker mode With Other Solutions
In the rapidly evolving landscape of tracking solutions, businesses are presented with a variety of options to monitor assets, pets, or personnel. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of different methods is critical for B2B buyers seeking the most effective tracking solution for their specific needs. Here, we compare the traditional ‘tracker mode’ with two viable alternatives: GPS tracking systems and RFID technology.
| Comparison Aspect | Tracker Mode | GPS Tracking Systems | RFID Technology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High frequency updates in lost mode, energy-efficient in other modes. | Real-time tracking with high accuracy; performance can vary based on signal availability. | Limited range (typically a few meters); not suitable for real-time tracking over long distances. |
| Cost | Generally low cost; includes hardware and subscription fees. | Moderate to high costs depending on the device and service plan. | Low hardware costs but may require significant investment in infrastructure. |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple app-based control with minimal setup required. | Can require complex installation and configuration, especially for fleet management. | Requires specialized readers and tags, making initial setup more complex. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; battery life varies by mode. | Moderate maintenance; devices may require regular updates and charging. | Low maintenance; passive RFID tags do not require batteries. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for personal tracking (pets) and casual use. | Best suited for logistics and fleet management where real-time tracking is essential. | Effective for inventory management and asset tracking in confined environments. |
What are the Key Advantages and Disadvantages of GPS Tracking Systems?
GPS tracking systems provide high accuracy and real-time updates, making them suitable for applications such as fleet management and high-value asset tracking. However, their performance can be hindered by signal interference in urban areas or remote locations. Additionally, the costs associated with GPS devices and subscription services can be significant, making them less appealing for small businesses or personal use. The complexity of installation and configuration can also pose challenges for companies without dedicated IT support.
How Does RFID Technology Compare as a Tracking Solution?
RFID technology excels in environments where items are frequently scanned, such as in warehouses or retail settings. Its low maintenance and passive tags reduce the need for regular power sources. However, RFID is limited by its range and is not suitable for tracking moving assets over large distances. The initial setup cost can also be high due to the need for specialized readers and infrastructure. Thus, while RFID is effective for specific applications, it does not provide the same versatility as tracker modes or GPS systems.
Illustrative image related to tracker mode
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Tracking Solution?
When selecting a tracking solution, B2B buyers should consider their specific operational needs, budget constraints, and the environments in which they will be using the technology. For casual or personal tracking, ‘tracker mode’ offers an efficient and cost-effective solution with flexible battery usage. In contrast, businesses that require real-time tracking across vast distances may find GPS systems more beneficial, despite their higher costs and complexity. Conversely, RFID technology is optimal for inventory management in controlled environments but lacks the versatility needed for dynamic tracking scenarios. Ultimately, understanding these differences will empower buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their unique requirements.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for tracker mode
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Tracker Mode?
1. Battery Capacity
Battery capacity, typically measured in milliampere-hours (mAh), indicates how long a device can operate before needing a recharge. For instance, a tracker with a 350mAh battery can function in various modes for different durations. This specification is crucial for B2B buyers as it directly affects the operational lifespan of the device, influencing maintenance schedules and overall efficiency.
2. Current Consumption
Current consumption is expressed in microamperes (µA) and varies based on the device’s mode of operation. For example, a tracker in “At Home” mode may consume just 18µA, while “Lost Mode” could draw up to 15mA. Understanding these consumption rates helps businesses estimate battery life and operational costs, ensuring they choose a tracker that aligns with their usage needs.
3. Location Update Frequency
This specification refers to how often the tracker sends location data. Frequencies can range from every 30 seconds in “Lost Mode” to hourly in “Standard Mode.” For B2B operations, particularly in logistics or asset management, knowing the update frequency is essential for real-time tracking and effective resource allocation.
Illustrative image related to tracker mode
4. Operational Modes
Different operational modes (e.g., “Active,” “Ping,” “Lost”) define how the tracker functions under varying circumstances. Each mode is designed for specific use cases, such as active tracking during transport or conserving battery life when stationary. This versatility allows businesses to adapt the tracking solution to their specific needs, optimizing both performance and cost.
5. Environmental Tolerance
Environmental tolerance refers to the device’s ability to function under various conditions such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to dust or water. A rugged tracker suited for harsh conditions can significantly reduce failures and downtime, making it a critical property for industries such as construction, agriculture, or logistics.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Tracker Mode?
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is essential for B2B buyers as it affects product quality, warranty, and support structures. Buyers should seek OEMs with a strong reputation to ensure reliability in their tracking solutions.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is vital for B2B negotiations, as it can impact inventory management and cash flow. Buyers must clarify MOQs to ensure they can meet their operational needs without overcommitting financially.
Illustrative image related to tracker mode
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document requesting a price quotation from suppliers. It often includes specifications, quantities, and delivery timelines. This process allows buyers to compare offers and negotiate better terms, making it a crucial step in sourcing tracking devices.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms helps B2B buyers understand shipping costs, risk management, and delivery obligations, which are critical for global procurement of tracking technologies.
5. KPI (Key Performance Indicator)
KPIs are measurable values that demonstrate how effectively a company is achieving key business objectives. For businesses utilizing tracking modes, relevant KPIs may include the accuracy of location data, battery life performance, or operational efficiency. Setting and monitoring KPIs can guide decision-making and improve tracking solutions over time.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting tracker mode solutions that align with their operational needs and strategic goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the tracker mode Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics Influencing Tracker Mode Technology?
The tracker mode sector is witnessing significant growth driven by the increasing demand for real-time location tracking across various industries. As international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (notably Saudi Arabia and Germany) seek innovative solutions to enhance operational efficiency and asset management, several key trends are emerging. The proliferation of IoT devices is enabling businesses to integrate advanced tracking capabilities into their operations, facilitating better resource allocation and improved customer experiences.
Illustrative image related to tracker mode
Moreover, the rise of mobile applications and cloud-based services allows for seamless data sharing and accessibility, making it easier for businesses to monitor their assets in real-time. The growing emphasis on data analytics is also reshaping how organizations utilize tracking data to inform decision-making processes. Enhanced location tracking, coupled with predictive analytics, enables companies to anticipate logistical challenges and optimize their supply chains accordingly.
Another significant driver is the increasing focus on personal safety and asset security. With more consumers and businesses prioritizing security, tracker modes that offer high-frequency updates and emergency alerts are becoming essential. As a result, suppliers are investing in technology that balances battery efficiency with location accuracy, catering to the diverse needs of B2B buyers across different sectors.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact Tracker Mode Solutions?
In today’s market, sustainability and ethical sourcing are paramount considerations for B2B buyers. The environmental impact of electronic devices, including trackers, cannot be overlooked. As global awareness of climate change and resource depletion rises, buyers are increasingly interested in sourcing from manufacturers that prioritize sustainable practices. This includes the use of recyclable materials, energy-efficient components, and eco-friendly manufacturing processes.
Ethical supply chains are also crucial, particularly in regions where labor practices may vary significantly. B2B buyers are now demanding transparency regarding the sourcing of materials and components, ensuring that their suppliers adhere to ethical labor standards. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and Fair Trade can provide assurance to buyers that their partners prioritize sustainability and ethical practices.
Moreover, integrating sustainable materials into tracker modes can enhance a company’s brand reputation, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers and businesses alike. As the demand for green certifications increases, manufacturers that prioritize sustainability in their tracker mode offerings will likely gain a competitive advantage in the market.
What is the Evolution of Tracker Mode Technology in the B2B Space?
The evolution of tracker mode technology has been rapid, transitioning from basic location tracking to sophisticated systems that integrate multiple functionalities. Initially, tracking devices were limited to simple GPS functionalities, primarily used for personal tracking. However, as technology advanced, the incorporation of IoT and cloud computing transformed these devices into comprehensive solutions for various industries.
Today, tracker modes can operate under different settings—such as ‘Near Home’, ‘Ping’, ‘Active’, and ‘Lost’ modes—allowing users to customize their tracking experience based on specific needs. This flexibility has opened new avenues for B2B applications, particularly in logistics, supply chain management, and personal safety sectors. The focus on battery efficiency and real-time data transmission has further enhanced the usability of these devices, enabling companies to adapt to the ever-changing market demands effectively.
As the tracker mode landscape continues to evolve, it is essential for B2B buyers to stay informed about the latest technological advancements and sourcing trends to leverage these innovations for improved operational effectiveness and competitive advantage.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of tracker mode
-
How do I choose the right tracker mode for my business needs?
Choosing the right tracker mode depends on your specific requirements, such as the frequency of location updates and battery life. For regular monitoring, Active Mode may suffice, offering updates every 7 minutes. If you need real-time tracking during critical situations, opt for Lost Mode, which provides updates every 30 seconds. Assess your operational priorities—whether it’s cost efficiency or immediate responsiveness—to determine the most suitable mode. Additionally, consider the nature of your assets and their movement patterns when making your selection. -
What features should I look for in a tracker mode?
When evaluating tracker modes, focus on features such as location update frequency, battery life, and ease of use. Look for options that allow customizable settings to adapt to various scenarios, such as emergency tracking or standard operations. Also, consider integrations with existing systems or platforms, which can enhance operational efficiency. User-friendly interfaces and mobile app accessibility are essential for real-time monitoring and management. Lastly, ensure robust security features are in place to protect sensitive tracking data. -
What are the payment terms typically offered for tracker mode solutions?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, but common arrangements include upfront payments, installment plans, or subscription-based models. For international transactions, be aware of currency fluctuations and additional fees related to cross-border payments. Always negotiate terms that align with your cash flow requirements and project timelines. Some suppliers may offer discounts for bulk purchases or long-term contracts, so it’s beneficial to inquire about these options to optimize your procurement costs. -
How can I vet suppliers of tracker mode solutions effectively?
To vet suppliers, start by reviewing their industry experience, customer testimonials, and case studies to gauge reliability. Request references from other businesses in your region or sector. Evaluate their compliance with international quality standards and certifications. It’s also advisable to assess their after-sales support and warranty policies. Conducting site visits or requesting product demonstrations can provide further insights into their operational capabilities and product quality. -
What is the Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) for tracker devices?
Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) varies by supplier and can depend on factors such as product type and customization options. While some manufacturers may accept orders as low as 50 units, others may require orders in the hundreds to optimize production costs. It’s crucial to clarify MOQ during your initial discussions with suppliers to ensure your order aligns with their requirements. If your needs are below the MOQ, consider negotiating terms or exploring alternative suppliers who may offer more flexible options. -
How do logistics and shipping impact the procurement of tracker devices?
Logistics and shipping can significantly affect the timely delivery of tracker devices. Factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and regional import duties must be considered. For international orders, choose suppliers with experience in your target markets to navigate these complexities effectively. Assess the supplier’s ability to provide tracking information throughout the shipping process. Additionally, consider lead times for production and shipping to avoid delays in your operations. -
What quality assurance processes should I expect from tracker mode suppliers?
Reputable suppliers should have comprehensive quality assurance (QA) processes in place, including testing protocols for functionality, durability, and accuracy of location tracking. Inquire about their manufacturing standards and certifications, such as ISO 9001, which indicate a commitment to quality management. Request documentation of QA procedures and any third-party testing results. Regular audits and feedback mechanisms are also important to ensure ongoing product quality and reliability. -
Can tracker modes be customized to suit specific business needs?
Many suppliers offer customization options for tracker modes to meet specific business requirements. This can include adjustments in reporting intervals, battery life optimization, and additional features tailored to your operational needs. Discuss your specific use cases with potential suppliers to explore available customization options. Be clear about your expectations and any unique challenges you face, as this will help suppliers propose solutions that best fit your business context.
Top 9 Tracker Mode Manufacturers & Suppliers List
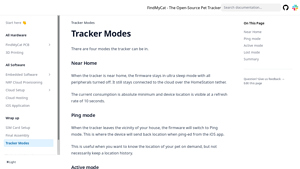
1. FindMyCat – Cat Tracker
Domain: findmycat.io
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: {“tracker_modes”: {“Near_Home”: {“description”: “Firmware stays in ultra sleep mode with all peripherals turned off, connected to the cloud over the HomeStation tether.”, “current_consumption”: “absolute minimum”, “location_refresh_rate”: “10 seconds”}, “Ping_mode”: {“description”: “Device sends back location when ping-ed from the iOS app, useful for on-demand location without history.”, “current_…
2. Jefit – Tracker Mode
Domain: jefit.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Tracker Mode allows users to track workout information from exercise sessions, including weight and repetitions for each set. The app displays upcoming sets and repetitions, and features a smart weight and repetition adjustment option for each exercise set.
3. Tack GPS – Tracking Modes
Domain: support.tackgps.app
Introduction: Tack GPS offers multiple Tracking Modes to balance location update frequency and battery efficiency. The modes include: 1. Emergency Mode: Location updates every 2 minutes, still interval of 15 minutes (Premium Plan: updates every 1 minute, still interval of 8 minutes). 2. Active Mode: Location updates every 10 minutes, still interval of 2 hours (Premium Plan: updates every 5 minutes, still interv…
4. Shift.Tools – MODE Tracker
Domain: shift.tools
Introduction: MODE Tracker is a holistic, transparent, and verified progress tracking tool designed for fashion brands and retailers to enhance their sustainability performance by measuring and communicating year-on-year progress. It has been utilized by six brands: G-Star, Haikure, Just Brands, Ted Baker, VIVOBAREFOOT, and WE Fashion. The tool provides two main outputs: visual scorecards for stakeholder commun…
5. iTrack – Comprehensive GPS Tracking Solutions
Domain: itrack.live
Introduction: iTrack offers a comprehensive GPS tracking solution with features including fleet management, device tracking, mobile apps (X-GPS Tracker), web interface, monitoring tools, geofences, event history, and reporting capabilities. Key functionalities include auto vs manual GPS tracking, route management, driver behavior monitoring (harsh driving, excessive idling), unauthorized movement alerts, and SO…
6. Wialon – Tracker Mode Feature
Domain: help.wialon.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Tracker mode is a feature in the Wialon Logistics application designed for units equipped with the WiaTag device type. It allows for the determination of courier location when personal or vehicle trackers are unavailable. When activated, the application continuously collects and sends location data to the server, or only when movement is detected in the iOS version. It is important to note that ba…
7. Anuko – Time Tracker Tracking Modes
Domain: anuko.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Tracking mode in Time Tracker controls how time is tracked. It is located on the Group settings page and requires a user with manage_basic_settings access rights. There are three tracking mode options: 1) Tracking Time Only – tracks work hours without projects or tasks; 2) Tracking Time by Projects – logs work time against defined projects; 3) Tracking Time by Projects and Tasks – logs time agains…
8. Google – Unknown Tracker Alerts
Domain: support.google.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Unknown tracker alerts feature available on Android devices with Android 6 and up. Trackers are small Bluetooth devices used to locate items like keys or bags, but can be misused for unauthorized tracking. Alerts notify users when an unknown tracker is detected nearby, providing a map and options to play a sound to locate it. Compatible with Find Hub network tags, headphones, and Apple AirTags. Us…
9. Zebra – Live Tracking Mode
Domain: docs.zebra.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Live Tracking Mode allows mobile devices with GPS services to send location information to the server. Key features include: enabling/disabling location services, enabling/disabling Duty mode, and viewing location information on the map. The functionality is dependent on the administrator’s settings; if location services are not enabled by the administrator, the map will not display on the device.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for tracker mode
In the rapidly evolving landscape of tracker technology, strategic sourcing remains a pivotal strategy for international B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding the various tracker modes—ranging from ultra-sleep to lost mode—enables businesses to optimize both battery life and location accuracy based on their unique operational needs.
Investing in advanced tracking solutions not only enhances asset visibility but also fosters greater efficiency in logistics and resource management. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that offer customizable tracking options, ensuring that they can adapt to changing requirements and leverage data insights effectively.
As the demand for real-time tracking solutions continues to grow, international buyers are encouraged to engage with innovative providers and explore partnerships that can deliver cutting-edge technology. The future of tracking is not just about locating assets; it’s about harnessing data to drive strategic decisions. Embrace this opportunity to enhance your operational capabilities and stay ahead of the competition. Take the next step—evaluate your current tracking needs and connect with suppliers who can meet those demands.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.