Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for mold drinking water
In today’s global marketplace, sourcing mold drinking water presents unique challenges for B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As businesses prioritize health and safety, understanding the implications of mold in drinking water becomes crucial. Mold contamination can lead to serious health risks, making it imperative for companies to ensure the purity of their water sources. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of mold drinking water, including types of contaminants, their applications, supplier vetting processes, and cost considerations.
With an authoritative focus, this guide empowers international B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. It outlines the various types of mold that can affect drinking water, the potential health impacts, and the importance of rigorous supplier evaluation. By offering insights into cost-effective sourcing strategies and best practices for quality assurance, this resource aims to mitigate risks associated with mold contamination. Buyers will also find actionable steps for maintaining water quality and ensuring compliance with health regulations.
Navigating the complexities of the mold drinking water market can be daunting, but with the right information at hand, businesses can safeguard their operations and enhance the well-being of their employees and customers alike.
Table Of Contents
- Top 3 Mold Drinking Water Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for mold drinking water
- Understanding mold drinking water Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of mold drinking water
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘mold drinking water’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for mold drinking water
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for mold drinking water
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘mold drinking water’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for mold drinking water Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing mold drinking water With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for mold drinking water
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the mold drinking water Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of mold drinking water
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for mold drinking water
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding mold drinking water Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bottled Spring Water | Naturally sourced, often contains minerals | Retail distribution, hospitality | Pros: Fresh taste, natural minerals; Cons: Higher cost, environmental impact from plastic. |
| Filtered Tap Water | Treated municipal water, often filtered for purity | Food service, manufacturing | Pros: Cost-effective, easily accessible; Cons: Potential contaminants if not filtered properly. |
| Purified Water | Reverse osmosis or distillation, devoid of impurities | Pharmaceuticals, laboratories | Pros: High purity, suitable for sensitive applications; Cons: Lacks minerals, can be over-processed. |
| Alkaline Water | Higher pH level, often enriched with minerals | Health and wellness industries | Pros: Promoted health benefits, appealing to health-conscious consumers; Cons: Higher price point, limited scientific backing. |
| Mineral Water | Naturally rich in minerals, sourced from springs | Retail, health food sectors | Pros: Unique taste, health benefits; Cons: Higher cost, regional sourcing limitations. |
What are the Characteristics of Bottled Spring Water?
Bottled spring water is sourced from natural springs and contains minerals that contribute to its flavor and health benefits. It is commonly found in retail environments and is a staple in the hospitality industry, where it is served in restaurants and hotels. B2B buyers should consider the environmental impact of plastic bottles and the cost of sourcing, as these factors can influence consumer perception and sales.
How Does Filtered Tap Water Differ from Other Types?
Filtered tap water is typically municipal water that has undergone additional filtration processes to remove impurities. It is widely used in food service and manufacturing sectors due to its cost-effectiveness and accessibility. Buyers should ensure that the filtration methods meet local health standards to avoid potential contamination risks, making it essential to verify the source and quality of the filtration system.
Why Choose Purified Water for Sensitive Applications?
Purified water undergoes rigorous processes like reverse osmosis or distillation to eliminate impurities, making it ideal for pharmaceuticals and laboratories where high purity is crucial. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers that can guarantee the quality and consistency of the purification process, as variations can affect the end product’s safety and efficacy.
What are the Benefits of Alkaline Water?
Alkaline water has a higher pH and is often marketed for its health benefits, including improved hydration and acid-neutralizing properties. It is popular in health and wellness industries, appealing to consumers seeking premium products. Buyers should weigh the higher price point against potential health claims, ensuring that they are backed by scientific evidence to avoid misleading marketing.
What Makes Mineral Water Unique?
Mineral water is naturally rich in minerals, sourced directly from springs, and is known for its distinct taste and health benefits. It is popular in retail and health food sectors, often marketed as a premium beverage. B2B buyers should consider regional sourcing limitations and the associated costs while evaluating consumer demand and preferences for unique flavors and health attributes.
Key Industrial Applications of mold drinking water
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Mold Drinking Water | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food and Beverage | Quality Control in Beverage Production | Ensures safety and compliance with health standards | Reliable testing methods and certification processes |
| Healthcare | Patient Hydration in Hospitals | Improves patient recovery and reduces infection risk | Proven filtration systems and regular quality checks |
| Agriculture | Irrigation Systems for Crop Production | Enhances crop yield and reduces waterborne diseases | Water quality monitoring and treatment solutions |
| Hospitality | Water Quality in Hotels and Resorts | Enhances guest satisfaction and safety | Consistent supply chain and compliance with local regulations |
| Manufacturing | Cooling Systems in Industrial Processes | Prevents equipment failure and operational downtime | Robust filtration and maintenance protocols |
How is Mold Drinking Water Used in Food and Beverage Industries?
In the food and beverage sector, mold drinking water is critical for ensuring the safety and quality of products. Beverage manufacturers rely on high-quality water for production, and any contamination can lead to health risks and regulatory penalties. By implementing rigorous testing for mold and other contaminants, companies can guarantee compliance with health standards, thereby protecting their brand reputation. International buyers should prioritize sourcing from suppliers who provide transparent testing results and adhere to strict quality control measures.
What Role Does Mold Drinking Water Play in Healthcare Settings?
In healthcare facilities, mold drinking water is vital for patient hydration, especially in hospitals where patients may have compromised immune systems. Clean, mold-free water is essential to prevent infections and promote recovery. Hospitals must invest in advanced filtration systems to ensure water quality and safety. Buyers in the healthcare sector should consider suppliers that offer comprehensive service agreements, including regular maintenance and quality testing, to ensure ongoing compliance with health regulations.
How Does Mold Drinking Water Impact Agriculture?
In agriculture, mold drinking water is crucial for irrigation systems, particularly in regions where water quality can fluctuate. Contaminated water can introduce mold and pathogens that affect crop health, leading to reduced yields. Farmers need reliable water treatment solutions to maintain water quality and safeguard their harvests. B2B buyers in agriculture should evaluate suppliers based on their ability to provide effective water quality monitoring and treatment solutions tailored to specific crop needs.
Why is Mold Drinking Water Important for Hospitality Businesses?
For the hospitality industry, mold drinking water is essential for maintaining high guest satisfaction and safety standards. Hotels and resorts must ensure that the water served to guests is free from contaminants, including mold. This not only protects guest health but also enhances the establishment’s reputation. Buyers in this sector should focus on sourcing water from suppliers who can guarantee consistent quality and compliance with local health regulations, thereby minimizing risk and maximizing guest confidence.
How is Mold Drinking Water Utilized in Manufacturing?
In manufacturing, mold drinking water is often used in cooling systems to prevent equipment overheating. Contaminated water can lead to malfunctions and costly downtimes, impacting production efficiency. Manufacturers must ensure that their water supply is free from mold and other contaminants to protect their machinery and maintain operational continuity. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers that offer robust filtration solutions and maintenance protocols to ensure consistent water quality for industrial applications.

Illustrative image related to mold drinking water
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘mold drinking water’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Contaminated Water Supply and Health Risks
The Problem: B2B buyers in industries such as hospitality, food service, and healthcare face significant challenges with contaminated drinking water due to mold growth. This issue not only affects the quality of water provided to employees or customers but also poses serious health risks. Mold can lead to allergic reactions, respiratory problems, and gastrointestinal issues, which can result in employee absenteeism and customer complaints. For businesses operating in regions with high humidity or inadequate water treatment systems, the threat of mold in drinking water is an ongoing concern that can tarnish their reputation and impact their bottom line.
The Solution: To mitigate these risks, buyers should prioritize sourcing water from certified suppliers who implement rigorous testing and treatment protocols to eliminate contaminants, including mold. Investing in advanced water filtration systems that utilize UV light or reverse osmosis can further ensure the quality of drinking water. Regular water quality testing should be conducted to monitor for mold presence, and businesses can establish a partnership with local health authorities or water quality specialists for ongoing support and guidance. Additionally, implementing a routine maintenance schedule for water storage and distribution systems will help prevent mold growth, ensuring safe drinking water for all.
Scenario 2: Ineffective Mold Remediation Practices
The Problem: Organizations often struggle with ineffective mold remediation practices when addressing water contamination. Many B2B buyers may attempt to clean mold-infested water systems without a thorough understanding of the proper techniques and materials required. This can lead to incomplete removal of mold spores and even exacerbate the problem, causing recurring health issues and unnecessary costs due to repeated clean-up efforts. Moreover, using improper cleaning agents can introduce additional contaminants into the water supply, further complicating the issue.

Illustrative image related to mold drinking water
The Solution: B2B buyers should adopt a comprehensive mold remediation strategy that includes specialized training for maintenance staff on effective cleaning techniques and the safe use of mold remediation products. Engaging with certified mold remediation professionals can provide expertise in identifying and addressing mold issues effectively. Buyers should also look for environmentally friendly cleaning agents that are proven to kill mold spores without introducing harmful chemicals into the water system. Documenting and reviewing remediation processes will help organizations track improvements and enhance overall water quality management.
Scenario 3: Regulatory Compliance and Consumer Trust
The Problem: In various regions, strict regulations govern water quality, and non-compliance due to mold contamination can lead to legal repercussions and loss of consumer trust. B2B buyers in sectors like food and beverage manufacturing must adhere to these regulations while maintaining high-quality standards. A single incident of mold contamination can lead to product recalls, financial losses, and damage to a company’s reputation. Additionally, consumers are increasingly aware of health and safety standards, making transparency and compliance critical for maintaining trust.
The Solution: To ensure compliance with water quality regulations, B2B buyers should implement a robust quality assurance program that includes regular water testing and monitoring protocols. Collaborating with accredited laboratories for testing can provide credible documentation of water quality, which is essential for compliance and consumer transparency. Furthermore, buyers should invest in employee training programs that emphasize the importance of water quality standards and the implications of mold contamination. Communicating openly with consumers about the steps taken to ensure safe drinking water can also help build trust and enhance brand loyalty. By prioritizing compliance and quality assurance, businesses can safeguard their operations against potential legal issues and maintain a positive public image.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for mold drinking water
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials for Mold Drinking Water?
When selecting materials for mold drinking water applications, it is essential to consider properties such as temperature and pressure ratings, corrosion resistance, and overall durability. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the industry, focusing on their performance, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
How Does Stainless Steel Perform in Mold Drinking Water Applications?
Stainless steel is a widely used material in mold drinking water systems due to its excellent corrosion resistance and durability. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for various environments. Stainless steel is also easy to clean, which is crucial for preventing mold growth. However, it can be more expensive than other materials and may require specialized manufacturing processes.
For international buyers, compliance with standards such as ASTM A240 for stainless steel is essential. Countries like Germany and Saudi Arabia have strict regulations regarding food-grade materials, making stainless steel a preferred choice for many businesses in these regions.
What Are the Benefits and Limitations of Polyethylene in Mold Drinking Water Systems?
Polyethylene (PE) is another common material used in mold drinking water applications. It is lightweight, cost-effective, and resistant to a wide range of chemicals. PE can handle moderate temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for various applications. However, it has lower durability compared to metals and can be susceptible to UV degradation if exposed to sunlight for extended periods.
For buyers in Africa and South America, the low cost of polyethylene can be appealing. However, it is crucial to ensure that the material meets local health and safety standards, such as those set by the World Health Organization (WHO) for drinking water safety.
How Does PVC Compare in Terms of Suitability for Mold Drinking Water?
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is frequently used in piping systems for mold drinking water due to its good chemical resistance and affordability. PVC can handle a range of temperatures but is generally not suitable for high-pressure applications. It is easy to manufacture and install, making it a popular choice for many businesses.
However, PVC can leach harmful chemicals if not properly formulated, raising health concerns. Buyers from Europe, particularly Germany, should ensure compliance with DIN standards for drinking water applications, as regulations are stringent regarding material safety.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Glass in Mold Drinking Water Applications?
Glass is an excellent material for mold drinking water due to its non-reactive nature and ease of cleaning. It does not leach chemicals and is resistant to mold growth when properly maintained. Glass can withstand high temperatures, making it suitable for sterilization processes. However, it is fragile and can break easily, which may pose risks in certain environments.
For international buyers, glass can be an attractive option for premium products. However, shipping and handling costs can be high due to its fragility, and compliance with local regulations regarding glass safety is essential, especially in regions like the Middle East.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Mold Drinking Water
| Material | Typical Use Case for mold drinking water | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Water bottles, storage tanks | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| Polyethylene | Water containers, piping systems | Lightweight, cost-effective | Lower durability, UV degradation | Low |
| Polyvinyl Chloride | Piping systems, fittings | Good chemical resistance | Potential leaching of chemicals | Low |
| Glass | Premium water containers, lab applications | Non-reactive, easy to clean | Fragile, high shipping costs | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides essential insights for B2B buyers in the mold drinking water industry, enabling informed decisions that align with regional regulations and market demands.

Illustrative image related to mold drinking water
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for mold drinking water
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process for Mold Drinking Water?
The manufacturing process for mold drinking water involves several critical stages that ensure both the quality and safety of the final product. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How is Material Prepared for Mold Drinking Water?
In the initial stage, raw materials such as water, filtration systems, and chemical additives are sourced. Quality control begins here with the selection of high-grade water and safe chemical agents, which are essential to prevent mold growth and ensure the water’s purity. Comprehensive testing of these materials, such as pH balance and contaminant levels, is essential to guarantee that they meet international health standards.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming and Assembling Mold Drinking Water?
The next stage involves the filtration and treatment of water. Advanced filtration techniques, such as reverse osmosis and ultraviolet (UV) disinfection, are commonly employed to eliminate impurities and pathogens, including mold spores. After the water is treated, it is bottled or packaged in a clean environment to prevent any contamination during the assembly process.
During assembly, automated systems ensure that the filling and sealing processes are carried out under strict hygiene conditions. This minimizes the risk of introducing contaminants that could lead to mold growth. Each bottle is typically inspected for integrity and cleanliness before it is sealed and labeled.
What Finishing Processes Are Critical for Ensuring Quality in Mold Drinking Water?
Finishing processes include labeling, packaging, and final inspection. Labels must meet regulatory requirements, including information about the source of the water, treatment methods, and best-before dates. Packaging is also a crucial element, as it must protect the product from environmental factors that could promote mold growth, such as moisture and light.
What Quality Assurance Practices Should B2B Buyers Expect in the Mold Drinking Water Industry?
Quality assurance (QA) is vital in the manufacturing of mold drinking water. Buyers should look for suppliers that adhere to international quality standards, such as ISO 9001, which outlines a framework for quality management systems.
What Are the Relevant International Standards for Mold Drinking Water?
In addition to ISO 9001, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking for products sold in Europe and API standards for certain types of water treatment may apply. These certifications indicate that the products have met rigorous safety and quality benchmarks.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control checkpoints are implemented throughout the manufacturing process to ensure compliance with established standards. These checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified quality criteria.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process ensures that every stage adheres to quality standards. This may involve real-time testing of water samples.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): After the product is fully assembled and packaged, a final inspection is conducted to verify that the product meets all quality and safety requirements.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used to Ensure Mold Drinking Water Quality?
Common testing methods for mold drinking water include:
- Microbial Testing: This assesses the presence of bacteria and mold spores in the water. Techniques such as membrane filtration and culture methods are frequently used.
- Chemical Testing: This measures levels of contaminants, including heavy metals and harmful chemicals, ensuring that the water is safe for consumption.
- Physical Testing: Parameters such as turbidity, color, and taste are evaluated to ensure the product meets consumer expectations.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers can take several steps to verify the quality control processes of their suppliers:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers allows buyers to assess the quality management systems in place. This can include on-site visits to observe production practices and quality control measures.
-
Reviewing Quality Reports: Buyers should request and review quality assurance reports, which provide insights into testing results, compliance with standards, and any corrective actions taken.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control measures. These inspections can offer additional assurance that products meet industry standards.
What QC and Certification Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of the specific quality control and certification nuances that can vary by country. For example, regulations governing drinking water quality may differ significantly between regions, impacting the types of certifications required.
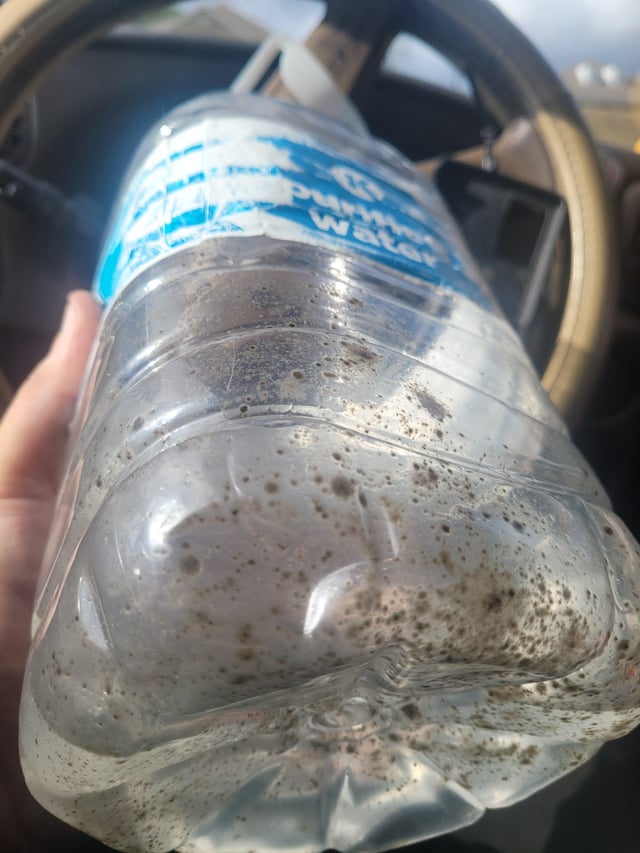

Illustrative image related to mold drinking water
Buyers should also consider the logistics of transporting mold drinking water across borders, as this can affect compliance with local regulations regarding labeling, packaging, and safety standards. Ensuring that suppliers are knowledgeable about these requirements can mitigate risks related to compliance and product safety.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for mold drinking water is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on key stages such as material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing, and by ensuring compliance with international standards and rigorous quality control measures, buyers can make informed decisions that prioritize safety and quality in their sourcing strategies.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘mold drinking water’
To assist B2B buyers in sourcing high-quality solutions for mold-related issues in drinking water, this guide outlines a systematic checklist. Understanding the critical nature of mold contamination is essential for maintaining health and safety standards in any business operation. This checklist will help ensure that you make informed decisions throughout the procurement process.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establish clear technical specifications for the mold drinking water solutions you need. This includes determining the acceptable levels of mold and other contaminants based on local regulations and industry standards. Consider specifying the types of testing methods you require, as well as any certifications that the product must meet.
Step 2: Conduct Market Research
Research the market to identify reputable suppliers specializing in mold control for drinking water. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in your region, particularly those who have experience working with businesses similar to yours. Pay attention to customer reviews and testimonials to gauge the reliability and effectiveness of their products.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, conduct a thorough evaluation. Request detailed company profiles, case studies, and references from other buyers in your industry. This step is crucial to ensure that the supplier has the necessary expertise and can deliver products that meet your specific requirements.
- Check for Industry Certifications: Ensure that the supplier holds relevant industry certifications, such as ISO or NSF, which signify adherence to quality standards.
- Assess Product Range: A supplier offering a diverse range of products may better cater to your evolving needs.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request samples of their products. Testing these samples will allow you to evaluate their effectiveness in controlling mold growth in drinking water. Look for indicators such as clarity, taste, and odor before making a final decision.
Step 5: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Engage in negotiations to establish favorable terms and conditions for your purchase. Discuss pricing structures, payment terms, and delivery schedules to ensure they align with your budget and operational needs. Be transparent about your expectations to foster a strong supplier relationship.
Step 6: Verify After-Sales Support and Training
Assess the level of after-sales support provided by the supplier. This includes their willingness to offer training on product usage, maintenance, and troubleshooting. Robust support can enhance the longevity and effectiveness of the solutions you procure.
- Inquire About Warranty Policies: Understanding warranty terms can safeguard your investment against potential product failures.
- Request Technical Documentation: Ensure that comprehensive documentation is available for reference during usage.
Step 7: Monitor and Review Supplier Performance
After procurement, continuously monitor the performance of the supplier and the effectiveness of the products. Regular reviews can help identify any issues early on, allowing for timely corrective actions. Establish clear metrics to assess product performance and supplier reliability.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that prioritize health, safety, and quality in their sourcing of mold control solutions for drinking water.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for mold drinking water Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Mold Drinking Water?
When evaluating the costs associated with sourcing mold drinking water, several key components come into play. Materials are the primary cost driver, which includes the quality of the water source, filtration systems, and any additional treatments required to ensure safety and compliance with health standards. Labor costs encompass the workforce involved in extraction, processing, and packaging. Depending on the region, labor costs can vary significantly, impacting the overall pricing structure.

Illustrative image related to mold drinking water
Manufacturing overhead includes utilities, rent, and administrative expenses tied to the production facility. Tooling costs may be relevant if specialized equipment is necessary for bottling or packaging. Additionally, quality control (QC) measures are essential to ensure that the product meets safety standards, which can add to the overall cost. Finally, logistics costs—covering transportation, warehousing, and distribution—are critical, especially in international transactions where tariffs and customs can play a significant role.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Mold Drinking Water?
Several factors influence the pricing of mold drinking water beyond the basic cost structure. Volume and minimum order quantity (MOQ) are significant; larger orders often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Specifications and customization—such as bottle size, labeling, and packaging—can also affect pricing. Higher quality or certified products typically command a premium, as they require more stringent sourcing and production processes.
Supplier factors include the reliability and reputation of the supplier, which can influence not just price but also delivery times and service levels. Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international buyers as they define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping arrangements, impacting the total landed cost.
What Negotiation Tips Can Help Buyers Optimize Costs?
For B2B buyers, especially those sourcing from diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation strategies are vital. Start by conducting thorough market research to understand average pricing and competitive offers in your region. When negotiating, consider discussing volume discounts and flexible payment terms to enhance cost-efficiency.
Additionally, always evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) rather than just the upfront price. This includes ongoing costs such as maintenance, logistics, and potential quality issues. Engaging suppliers in a conversation about their cost structure can also yield insights that might lead to cost reductions.
What Are the Pricing Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers face unique pricing nuances that can significantly impact their sourcing strategies. Variability in currency exchange rates can affect pricing stability, so consider negotiating contracts that account for potential fluctuations. Furthermore, different countries have varying regulations regarding water quality and safety standards, which can influence the sourcing costs.
Buyers should also be aware of additional costs associated with import duties and taxes, which can vary significantly by region and product type. Understanding local market conditions, including demand and competition, is essential for making informed purchasing decisions.
Conclusion and Disclaimer on Pricing
While this analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the cost and pricing structure for mold drinking water, actual prices can vary based on specific circumstances, including supplier negotiations, market conditions, and regional factors. Therefore, it is advisable for buyers to obtain tailored quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing and alignment with their sourcing needs.

Illustrative image related to mold drinking water
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing mold drinking water With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Mold Drinking Water
When evaluating solutions for maintaining water quality and ensuring safe drinking conditions, it is essential to consider various options beyond mold drinking water. This section compares mold drinking water with alternative methods that also aim to provide safe drinking water while addressing specific needs in different market contexts.
| Comparison Aspect | Mold Drinking Water | UV Water Purification | Chemical Water Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Effective against mold and some bacteria | Highly effective against bacteria and viruses | Effective against a wide range of pathogens, including bacteria and viruses |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; ongoing costs vary | Higher upfront costs for equipment, but low maintenance | Generally low cost for chemicals, but recurring costs for supply |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specific conditions for optimal effectiveness | Installation of UV systems can be complex | Simple to implement with proper training on chemical handling |
| Maintenance | Requires regular monitoring and cleaning | Requires bulb replacement and system checks | Regular chemical supply management needed |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for environments with high mold risk | Best for municipal water treatment and home systems | Suitable for emergency situations and remote areas lacking infrastructure |
What Are the Benefits and Drawbacks of UV Water Purification?
UV water purification utilizes ultraviolet light to eliminate pathogens without introducing chemicals. This method is highly effective for disinfection, making it suitable for municipal water systems and households. However, the initial setup can be costly, and the systems require regular maintenance, including bulb replacements. UV purification does not remove particulate matter or chemical pollutants, so it may need to be combined with other filtration methods for comprehensive water treatment.
How Does Chemical Water Treatment Compare?
Chemical water treatment involves adding disinfectants, such as chlorine or iodine, to water to kill harmful microorganisms. This method is cost-effective and easy to implement, making it a popular choice in emergency situations or remote areas lacking advanced water treatment infrastructure. However, the downside is the potential for chemical residuals in the water, which can lead to health risks if not managed correctly. Additionally, the effectiveness of this method may diminish in the presence of organic matter or certain contaminants.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
When selecting the most appropriate water treatment solution, B2B buyers must consider the specific needs of their operations. Factors such as the local water quality, available budget, and the intended application of the water should guide their decision. Mold drinking water may be suitable for environments with a high risk of mold contamination, while UV purification offers robust pathogen elimination for broader applications. Chemical treatment provides a cost-effective solution for immediate needs but requires careful management. By understanding the strengths and limitations of each option, buyers can make informed choices that align with their operational goals and ensure the safety of their drinking water.

Illustrative image related to mold drinking water
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for mold drinking water
What are the Key Technical Properties of Mold Drinking Water?
Understanding the essential technical properties of mold drinking water is crucial for B2B buyers involved in its production, distribution, or consumption. Here are several key specifications to consider:
1. Contaminant Levels
The concentration of contaminants, including mold spores and bacteria, is a critical specification. Regulatory bodies often set maximum allowable levels for safe drinking water, which can vary by region. For B2B buyers, maintaining contaminant levels below these thresholds is vital for compliance, marketability, and consumer safety.
2. Microbial Quality
Microbial quality refers to the presence and concentration of microorganisms, including molds. This property is measured through tests that identify specific pathogens or indicators of water quality. For businesses, ensuring high microbial quality is essential to avoid health risks associated with mold consumption, which can lead to liability issues and damage to brand reputation.
3. pH Levels
The pH level of drinking water can influence the growth of mold and other microorganisms. Generally, a pH between 6.5 and 8.5 is considered safe for drinking water. B2B buyers should monitor pH levels closely, as deviations can affect water stability and safety, impacting product acceptance in different markets.

Illustrative image related to mold drinking water
4. Temperature Control
Temperature plays a significant role in mold growth; warmer temperatures can accelerate microbial activity. Understanding the thermal properties of mold drinking water is critical for storage and transportation. Buyers must ensure that water is kept at appropriate temperatures to prevent mold proliferation, especially in tropical regions.
5. Water Source Quality
The origin of the water significantly influences its quality. Buyers should assess whether the water source is treated and meets international standards for drinking water. A reliable source not only assures safety but also enhances the marketability of the product, particularly in competitive markets.
6. Shelf Life
Shelf life indicates how long the drinking water can be stored before it becomes unsafe or undesirable. This property is influenced by factors such as packaging and storage conditions. For B2B buyers, understanding shelf life is essential for inventory management and ensuring that products meet consumer expectations for freshness.
What are Common Trade Terms in the Mold Drinking Water Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon is vital for effective communication and transaction management in the mold drinking water sector. Here are some commonly used terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or products that are then sold by another company under its brand name. In the context of mold drinking water, OEMs may supply filtration systems or packaging materials essential for maintaining water quality.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQs helps B2B buyers manage inventory costs and ensure they are purchasing in economically viable quantities without overcommitting.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing for specific quantities of products. For mold drinking water, RFQs are crucial for comparing costs and ensuring that buyers receive competitive pricing from multiple suppliers.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are international trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for B2B transactions to clarify liability and costs throughout the supply chain.
5. Bottling Line Efficiency
This term refers to the productivity and effectiveness of the machinery used to bottle drinking water. High bottling line efficiency is critical for reducing costs and ensuring timely delivery, making it a key consideration for B2B buyers involved in production.
6. Quality Assurance (QA)
Quality assurance encompasses the processes and procedures in place to ensure that products meet established standards. In the mold drinking water industry, effective QA practices are essential for maintaining safety and compliance with health regulations, which ultimately protects both consumers and businesses.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their operations and align with market demands.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the mold drinking water Sector
What Are the Key Trends Shaping the Mold Drinking Water Market?
The mold drinking water market is increasingly influenced by global drivers such as health awareness, consumer preferences for sustainable products, and regulatory changes surrounding water quality. An uptick in health-conscious consumers and heightened awareness regarding mold-related health risks are driving demand for safer, cleaner drinking water solutions. This shift is particularly pertinent for B2B buyers in regions like Africa and the Middle East, where access to clean water is often limited, and the prevalence of waterborne diseases remains a significant concern.
Emerging B2B technology trends are reshaping sourcing strategies. Smart water management systems and IoT-enabled devices are being integrated into water purification processes, enhancing real-time monitoring and filtration efficiency. This tech adoption allows businesses to assure quality, thereby building trust with consumers. Additionally, the use of blockchain for traceability in the supply chain is gaining traction, particularly in Europe, where regulations mandate transparency in sourcing practices.
Market dynamics are shifting towards a preference for local sourcing to mitigate supply chain disruptions, particularly in light of recent global events. For international B2B buyers, particularly from Germany and Saudi Arabia, understanding regional sourcing capabilities can provide a competitive advantage. Emphasizing partnerships with local suppliers can enhance responsiveness and ensure compliance with local regulations while also catering to consumer preferences for locally sourced products.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Mold Drinking Water Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of sourcing strategies in the mold drinking water sector. As environmental concerns grow, B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to ethical sourcing and environmental stewardship. The environmental impact of water extraction and purification processes is under scrutiny, prompting businesses to adopt greener practices.
Ethical supply chains not only enhance brand reputation but also meet the growing demand for sustainable products among consumers. Certifications like ISO 14001 for environmental management and organic certifications for water purification processes are becoming essential for suppliers aiming to stand out in a competitive market. These certifications provide assurance that companies adhere to high standards of environmental responsibility, a crucial factor for B2B buyers looking to align with sustainable practices.
Moreover, the incorporation of biodegradable materials in packaging and filtration systems is gaining traction. This trend resonates particularly with buyers in Europe, where stringent regulations are in place to minimize plastic waste. As a result, B2B buyers must consider not only the quality of the mold drinking water but also the environmental impact of its packaging and distribution.

Illustrative image related to mold drinking water
What Historical Trends Have Influenced the Mold Drinking Water Market?
The evolution of the mold drinking water market is deeply intertwined with advancements in water purification technology and increased public awareness of health risks associated with contaminated water. Historically, the late 20th century saw a growing concern over waterborne illnesses, leading to stricter regulations and improved water treatment processes.
The introduction of advanced filtration technologies in the early 2000s marked a significant turning point, enabling more effective removal of contaminants, including mold and bacteria. This technological evolution has paved the way for the current market, where B2B buyers are not only focused on the efficacy of purification methods but also on sustainability and ethical sourcing practices.
In summary, understanding these market dynamics, sustainability considerations, and historical trends provides B2B buyers with valuable insights necessary for navigating the mold drinking water sector effectively. By prioritizing health, sustainability, and local sourcing, businesses can position themselves competitively in a rapidly evolving landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of mold drinking water
-
How do I solve mold contamination issues in drinking water?
To address mold contamination in drinking water, ensure proper sourcing and filtration. Regularly test water quality using reliable testing kits or laboratories to detect mold presence. Implement effective filtration systems that can eliminate mold spores, such as UV light treatment or advanced membrane filtration. Additionally, maintain strict hygiene protocols in your storage and transportation systems to prevent mold growth, including regular cleaning and sanitization of tanks and pipes. -
What is the best filtration system for preventing mold in drinking water?
The best filtration systems for preventing mold in drinking water typically include multi-stage filtration, UV disinfection, and reverse osmosis systems. Multi-stage filters can remove larger particles, while UV disinfection systems effectively kill mold spores and bacteria. Reverse osmosis systems provide thorough purification, ensuring that even microscopic contaminants are eliminated. When selecting a system, consider the specific water quality challenges in your region and consult with suppliers who specialize in water treatment solutions. -
How can I ensure the quality of mold drinking water from suppliers?
To ensure quality, conduct thorough due diligence on potential suppliers. Request certifications, such as ISO or NSF, that demonstrate adherence to international water quality standards. Review their testing protocols and quality assurance practices, including frequency and methods of testing for contaminants. Consider visiting their facilities or requesting third-party audits to validate their processes. Building relationships with reliable suppliers can also facilitate better communication regarding quality control. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for mold drinking water?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for mold drinking water can vary significantly based on the supplier and your specific needs. Typically, suppliers may set MOQs to ensure cost-effectiveness in production and shipping. When negotiating, communicate your requirements clearly and inquire about flexibility in MOQs, especially if you’re testing the market or require a smaller volume for initial orders. Some suppliers may offer tiered pricing based on the volume ordered. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing mold drinking water?
Payment terms when sourcing mold drinking water can differ based on supplier policies and regional practices. Common terms include advance payment, net 30, or net 60 days after delivery. It is essential to clarify payment methods accepted, such as wire transfer, letters of credit, or PayPal. Negotiate terms that align with your cash flow needs while ensuring that they are reasonable for the supplier to maintain a good business relationship. -
How do I vet suppliers for mold drinking water in international trade?
Vetting suppliers in international trade involves a multi-step approach. Start by researching potential suppliers through trade directories, industry associations, and online reviews. Request references and case studies from previous clients to evaluate their reliability. Conduct background checks to ensure they have a good reputation for quality and compliance. Additionally, consider visiting the supplier’s facility if possible or utilizing third-party inspection services to assess their operational standards. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing mold drinking water?
Logistics for importing mold drinking water involve several key considerations. Ensure compliance with international shipping regulations, including proper labeling and documentation for water products. Evaluate shipping methods that maintain water quality, such as temperature-controlled containers if necessary. Additionally, plan for customs clearance processes in your country and factor in delivery timelines to avoid stock shortages. Partnering with experienced logistics providers can streamline this process. -
Can I customize mold drinking water products to meet my specific requirements?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for mold drinking water products to meet specific requirements. Customizations may include variations in packaging, branding, and specific filtration processes tailored to local water quality challenges. When approaching suppliers, clearly outline your needs and ask about their capabilities for product customization. This not only enhances your brand presence but also ensures that the product meets local regulations and customer preferences.
Top 3 Mold Drinking Water Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. A Sterling Plumbing – Essential Plumbing Services
Domain: asterlingplumbingcolumbus.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: A Sterling Plumbing offers services including drain cleaning, sewer camera inspection, water heater installation and repair, and sump pump installation and repair. They emphasize the importance of maintaining clean water systems to prevent mold growth and contamination. The article discusses the dangers of drinking moldy water, symptoms of mold exposure, and provides DIY steps for mold removal fro…
2. Reddit – User Experiences with Contaminated Water
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: This company, Reddit – User Experiences with Contaminated Water, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. Home Cleanse – Mold Prevention Solutions
Domain: homecleanse.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: This company, Home Cleanse – Mold Prevention Solutions, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for mold drinking water
As the global demand for safe drinking water continues to rise, the importance of strategic sourcing for mold-resistant drinking water cannot be overstated. B2B buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must prioritize sourcing practices that ensure the purity and safety of water supplies. Key takeaways include understanding the health risks associated with mold in water, implementing rigorous cleaning and maintenance protocols, and selecting suppliers who adhere to the highest quality standards.
Investing in advanced filtration systems and reliable supply chains can mitigate the risks of mold contamination, safeguarding both consumer health and brand reputation. Furthermore, fostering partnerships with local suppliers can enhance logistics efficiency while supporting community resilience.
Looking ahead, the focus on sustainability and health will shape sourcing strategies. International buyers are encouraged to remain proactive in exploring innovative solutions and technologies that enhance water quality. By prioritizing strategic sourcing and maintaining vigilance against mold contamination, businesses can not only meet regulatory requirements but also establish themselves as leaders in the safe drinking water market. The time to act is now—ensure your sourcing strategies are equipped for the future.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.

Illustrative image related to mold drinking water
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.