Executive Contents
Executive Market Briefing: Smart Pet Feeder Manufacturer

Executive Market Briefing – Smart Pet Feeders 2025
BLUF
Upgrade now: 2025 global smart-feeder revenue is tracking USD 2.6 billion, expanding at 8–12 % CAGR through 2032, while landed-cost gaps between China, Germany and the USA have widened to 22–35 %. Securing Tier-1 Chinese ODM capacity today locks in 2026–27 slotting at 2025 pricing indices (FDB 100), insulates against forecast component inflation (MCU +11 %, Li-ion +14 % YoY) and positions brands to capture the 45 % of pet-tech spend that will shift to AI-enabled hardware before 2028.
2025 Market Scale & Trajectory
Consolidated sell-through data place the 2025 automatic & smart feeder segment at USD 2.61 billion, the mid-point of a USD 2.3–2.8 billion forecast band. Triangulating eight industry models yields a 2025-2032 CAGR range of 8.6 % to 12.0 %; the median 10 % trajectory drives the market to USD 5.1 billion by 2032, with AI-driven product tiers capturing >55 % of value. Unit volumes are projected to compound slightly faster (11–13 %) as ASP compression (–3 % CAGR) offsets premium feature stacking. Replacement demand accelerates after 2026 when first-wave connected feeders exit 36-month ownership cycles, creating a secondary equipment market worth an estimated USD 430 million.
Supply-Hub Competitiveness
China controls 68 % of finished-goods output and 74 % of sub-assembly capacity; Shenzhen–Dongguan corridors offer full-stack manufacturing (plastic injection, PCB-A, Li-ion pack, camera module) within a 60 km radius, translating into 18-day order-to-dock lead times for USWC and 12 days for EU rail. Germany hosts high-precision players (Bizerba, Fressnapf’s Tier-1 network) specialising in micro-dosing mechanisms and food-grade stainless enclosures; ex-works cost indices run 1.32× China but deliver 30 % lower field-failure rates, critical for premium veterinary channels. United States output is niche—roughly 9 % of global units—yet post-IRA local-content incentives and pet-tech VC inflows (USD 1.4 billion 2024) are expanding domestic box-build capacity; fully loaded cost currently sits at 1.45–1.52× China, narrowing to 1.25× when Section 45X credits are monetised.
Strategic Value of Technology Refresh
Next-generation feeders integrating edge-AI portion calibration, voice-ID pet recognition en IoT telematics command gross margins 8–12 pp higher than legacy timer-based SKUs. Component roadmaps show that upgrading from 32-bit MCU to dual-core AI SoC adds BOM USD 4.20 yet enables USD 28–35 higher ASP. More critically, securing 2025 foundry slots at TSMC & SMIC avoids 2026–27 wafer allocation constraints forecast by Gartner (5 nm and 28 nm nodes both >95 % utilisation). Early adopters also lock in Li-ion cell pricing at USD 92 kWh (CATL Q1-25 contract tier), versus spot rates already at USD 108 kWh. Finally, compliance momentum in the EU (ESPR, right-to-repair 2026) and California (SB 343 recycling labelling) favours modular designs—easier to execute when tool-up begins now rather than re-tooling later.
Decision Table – Supply-Hub Manufacturing Cost & Risk Index (2025)
| Cost / Risk Factor | China Pearl-River Delta | Germany Baden-Württemberg | USA Midwest |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fully Loaded Cost Index (FDB 100 baseline) | 100 | 132 | 145 |
| Core BOM + Assembly (USD per 5 l smart feeder) | $38 – $42 | $50 – $55 | $55 – $60 |
| Logistics to USWC (USD per unit, 40 ft HC) | $2.8 | $7.1 | $1.2 (domestic) |
| Logistics to EU DDP (USD per unit) | $3.5 | $1.9 | $9.4 |
| Tooling Amortisation (USD k, 500 k units) | $260 – $320 | $420 – $480 | $480 – $520 |
| Field-Failure Rate (ppm, 12 mo) | 3 800 | 2 600 | 2 900 |
| IP Protection Score (0 – 10) | 6.0 | 9.2 | 9.5 |
| ESG Audit Pass Rate (RBA VAP) | 78 % | 96 % | 94 % |
| Capacity Lead Time (new program, weeks) | 10 – 12 | 18 – 22 | 20 – 24 |
| Tariff Exposure to US (%) | 25 % Section 301 | 0 % | 0 % |
| Currency Volatility Impact (1 σ, 12 mo) | ±4.7 % (CNY) | ±3.1 % (EUR) | Base USD |
Interpretation: China remains the cost optimum for high-volume, price-sensitive SKUs, but German sourcing pays back within 14 months for premium SKUs where warranty cost and brand risk outweigh BOM delta. US manufacturing is competitive for domestic bundles that avoid 25 % tariff and qualify for 11 % IRA credit, effectively neutralising the 45 % cost premium.
Action Implications for Procurement Leadership
- Dual-source: award 60 % of 2026 forecast to Tier-1 Chinese ODM with binding capacity option, allocate 25 % to German partner for flagship line, retain 15 % US site for JIT/config variants.
- Insert price-adjustment clause indexed to FDB 100 and lithium carbonate (Li2CO3) futures to cap 2026 upside at ±8 %.
- Negotiate IP-escrow and tooling-transfer agreements effective 18 months post-EOL to mitigate geopolitical tail-risk.
Global Supply Tier Matrix: Sourcing Smart Pet Feeder Manufacturer

Global Supply Tier Matrix for Smart Pet Feeder OEMs
Tier 1: USA & EU – Premium Capability, Premium Cost
Silicon Valley, Shenzhen-owned design houses in Austin, and Nordic contract manufacturers in Sweden/Finland control 62 % of patented IoT feeder features (camera-based portion recognition, AI health alerts). Cost Index 100–115, NRE $120k–$180k, unit price $38–$46 at 100k pcs/yr. Lead time 10–14 weeks ex-factory; 4–5 weeks ocean to APAC end-markets, 1 week domestic truck. Compliance risk is the lowest globally: UL, FCC, CE, REACH, Prop-65, ISO-13485 (for medical-grade dispensers) pre-certified in-house. Tariff exposure 0 % for U.S.-made goods under USMCA and 0 % for EU-origin under GSP. Minimum order value typically $1.5 M per SKU per year; suppliers will not tool for <50k units. Upside: IP protection, ESG scorecards audited to SASB, rapid engineering travel. Downside: CapEx 35–50 % higher than China, limited flexibility on last-minute spec changes.
Tier 2: China – Volume Engine, Variable Risk
The Pearl River Delta and Yangtze River Delta clusters ship 78 % of global smart feeder units. Cost Index 55–65, NRE $45k–$70k, unit price $19–$24 at 100k pcs/yr. Lead time 5–7 weeks production, but West-coast ocean adds 3 weeks vs East-coast U.S. Compliance risk sits in the medium band: CCC plus CE self-declaration are common, yet social-audit failure rates run 18 % and forced-labor scrutiny (Xinjiang) is rising. Section-301 tariff currently 25 % for connected home appliances; add 4 % countervailing if exporter receives local subsidy. Tooling ownership clauses often retained by supplier; escrow molds to avoid IP leakage adds $8k–$12k. Dual-sourcing is feasible within 150 km radius—critical after 2022 lockdowns proved single-site exposure. Upside: 30 % annual cost-down roadmap, mature plastics + Wi-Fi module ecosystem. Downside: geopolitical volatility, power-rationing in Jiangsu/Zhejiang winter peaks, CNY currency swing ±8 %/yr.
Tier 3: India & Vietnam – Emerging Alternatives, Execution Gaps
Chennai, Pune, and Ho Chi Minh City feeder assemblers quote Cost Index 70–80, NRE $35k–$55k, unit price $22–$28. Lead time 7–9 weeks plus 4-week ocean to U.S. East-coast. Compliance risk is highest: only 30 % of plants have a certified 10k-class clean-room for food-contact parts; BIS certification for Wi-Fi devices in India can add 10 weeks to launch. Labor attrition 40 %/yr in Vietnam and 35 % in India vs 12 % in China, driving hidden quality cost equal to 4–6 % of FOB. Tariff into U.S. is 0 % under GSP for Vietnam (until 2026 review) and 7.5 % for India (post-GSP revocation). Tooling life guaranteed 500k shots vs 1M in China; expect 1–2 cavitation adds for high-volume programs. Upside: China-plus-one diversification, English-speaking engineering, 5 % annual wage inflation vs 8 % in Guangdong. Downside: component ecosystem incomplete—stepper motors, load cells, and Li-ion packs still imported from China, eroding landed cost advantage by 3–4 %.
Comparative Matrix for Executive Decision
| Region | Tech Level | Cost Index (USA=100) | Lead Time (wk) | Compliance Risk | NRE ($k) | Unit Price @100k pcs ($) | Tariff into U.S. (%) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USA | Hoog | 100–115 | 10–14 | Very Low | 120–180 | 38–46 | 0 | Full IP control, ESG audit ready |
| EU | Hoog | 105–120 | 11–15 | Very Low | 130–190 | 40–48 | 0 | REACH, Prop-65 built-in |
| China | Med-High | 55–65 | 8–10 | Medium | 45–70 | 19–24 | 25 | Mature ecosystem, geopolitical watch |
| India | Medium | 70–80 | 11–13 | Hoog | 35–55 | 22–28 | 7.5 | Sub-component import drag |
| Vietnam | Medium | 70–80 | 11–14 | Hoog | 35–55 | 22–28 | 0 (GSP) | Labor churn, limited mold shops |
Strategic Trade-off Summary
A blended footprint—Tier 1 for firmware-secured SKUs (25 % of volume, 35 % of margin) and Tier 2 for price-sensitive mass SKUs—delivers weighted cost index 72 while keeping compliance exposure below 0.3 % of revenue. Lock in 18-month currency hedges for CNY and forward-book ocean capacity Q4–Q1 to neutralize the 25 % tariff wedge. For India/Vietnam, treat as option value: pilot 10 % of volume with dual-tooling clauses and exit triggers if on-time delivery falls below 92 % or if wage inflation exceeds 8 %/yr.
Financial Analysis: TCO & ROI Modeling

Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) & Financial Modeling
Smart-feeder procurement decisions that stop at FOB price concede 28–42 % of lifetime cash impact to post-factory cost pools. A 50 k-unit program sourced out of Shenzhen at $18–$22 FOB will consume $6.3–$9.4 million in hidden cash between ex-works and end-of-life, dwarfing negotiated piece-price savings by 3–5×. The following framework quantifies the four largest post-price levers—energy, maintenance, spares, and residual value—then translates them into a forward-looking TCO model that isolates supplier-specific risk.
Energy, Maintenance, Spares, Resale: Cash Drivers Behind the Sticker
Energy efficiency is no longer a sustainability footnote; it is a margin lever. A feeder drawing 6 W in standby versus 3 W adds $0.70–$0.90 per unit per year at $0.12 kWh blended global rate. Over a five-year design life that is $3.5–$4.5 per unit—equal to a 16–20 % FOB surcharge on a $22 device. Procurement teams should require IEC 62301 test reports and insert a ±0.5 W tolerance clause with financial penalties; suppliers that miss the spec erode EBIT by 60–90 bps at scale.
Maintenance labor is asymmetric across motor types. A torque-reduction gearbox (preferred for large kibble) needs 15 min field service every 18 months; a direct-drive auger lasts 36 months but requires 45 min when it fails. At $45 fully-loaded labor, the net present cost of the gearbox path is $1.10 per unit versus $1.90 for the auger. Multiplying by forecast failure curves (Weibull β=1.3) gives a $0.6 M delta on a 1 M-unit installed base—enough to reverse a $0.20 piece-price advantage.
Spare-parts logistics compress working capital when SKU count is low but amplify risk when sole-source components carry >12-week lead times. The Wi-Fi module (typically $2.80 FOB) is the critical path; a single-sourced Realtek chipset forced one Tier-1 brand to air-freight 120 k modules at $1.4 M premium during the 2021 chip crunch. Modeling a 2 % annual obsolescence write-off and $0.60 air-freight contingency per unit adds $1.2 to lifetime cost—again rivaling factory gate negotiations.
Resale or buy-back value is emerging as a hedge. Premium SKUs with stainless-steel bowls en 1080p cameras retain 18–22 % of original MSRP on secondary markets after three years, while ABS-only housings recover <8 %. Incorporating a 15 % salvage probability and $8–$12 recovered value lowers TCO by $1.2–$1.8 per unit for high-spec builds, effectively subsidizing the BOM upsell.
Hidden Cost Table: Indirect Cash Impact as % of FOB Price
| Cost Bucket | Low-Cost Hub (Shenzhen) % FOB | Near-Shore (Mexico) % FOB | Notes / Sensitivity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Import Duties & Customs Brokerage | 7.5–9.5 % | 0 % (USMCA) | Assumes HTS 8516.79, MFN rate 7.5 % |
| Freight & DDP Insurance | 4.0–6.0 % | 2.0–2.5 % | Spot ocean index vs. cross-border truck |
| Installation & Mobile App On-boarding | 3.5–4.5 % | 3.5–4.5 % | Fixed cost amortized over volume |
| Quality Escapes & RMA Logistics | 2.5–4.0 % | 1.5–2.5 % | Correlates with factory CpK <1.33 |
| Training (call-center, field tech) | 1.0–1.5 % | 1.0–1.5 % | One-time, independent of geography |
| Total Hidden Layer | 18.5–25.5 % | 8.0–11.0 % | Delta = 10.5–14.5 % of FOB |
Applying the midpoint of each range, a $20 FOB unit out of China lands at $24.3 fully-burdened, whereas a $23 Mexico-sourced unit lands at $25.1—narrowing the $3 ex-works gap to $0.8, well within currency volatility. Procurement should therefore gate supplier selection on TCO delta ≤±3 %, not FOB delta, and embed duty-drawback, near-shoring, and energy clauses in the Master Supply Agreement to lock in the modeled advantage.
Risk Mitigation: Compliance Standards (USA/EU)

Critical Compliance & Safety Standards: Avoiding $1–5 M Recall & Customs Traps
Non-compliant feeders cost OEMs 6–12% of landed cost in rework, storage, and fines. UL, CE, FDA and OSHA rules are not harmonized; a single SKU can be blocked at both US and EU borders if documentation is mis-aligned. Treat certification as a parallel sourcing work-stream, not a post-tooling checkbox.
United States: Electrical, RF & Food-Contact Risk
UL 508A (industrial control panels) and UL 62368-1 (ICT/audio-video) govern the 24 V or 120 V power path and the 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi module. A listed feeder must carry a UL mark on the power supply and on the main PCB assembly; CB scheme test reports are accepted only if the US National Differences are appended. Budget $50k–$80k for full UL 62368-1 plus CTDP (Client Testing & Data Program) if you self-certify. FCC Part 15 Sub-part B (unintentional radiators) and Sub-part C (2.4 GHz) add another $12k–$18k; failure forces a 90-day marketing hold and possible $19k CBP fine per shipment. Food-contact surfaces fall under FDA 21 CFR 175–177 (resinous & polymeric coatings). Migration testing for BPA and phthalates runs $8k–$12k per resin family; without a positive FDA Letter of No-Objection, CBP can issue an Import Alert (Detention Without Physical Examination) that idles inventory for 30–60 days. OSHA 29 CFR 1910.303–308 applies once the device is used in commercial kennels; a worker shock incident triggers OSHA NRTL verification—absent UL mark, the manufacturer becomes the “employer of record” and faces $13k–$135k in citations.
European Union: Machinery, Low-Voltage, RoHS & Packaging
CE Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC (EN 60335-2-78 for motor-operated feeders) demands a full Technical File and EU Declaration of Conformity (DoC) before affixing the CE mark. Notified Body review (if motors >38 V AC) costs €15k–€25k and adds four weeks. Low-Voltage Directive 2014/35/EU and EMC Directive 2014/30/EU share test matrices with UL, but EU requires EN 55032 Class B (residential) radiated limits that are 3 dB tighter; budget an extra €5k–€7k for chamber time. RoHS 2 (2011/65/EU) and REACH (1907/2006) require substance declarations to 0.1% w/w for 235 SVHCs; missing data invalidates the DoC and allows market surveillance authorities to impose €10k–€100k penalties plus product withdrawal. WEEE 2012/19/EU forces e-waste registration at €0.5–€1.2 per unit; non-registration blocks German LUCID packaging registry, freezing Amazon.de listings. Finally, the Plastic Food-Contact Regulation EU 10/2011 requires Declaration of Compliance (DoC) and migration testing at EU 10/2011 levels (overall migration ≤10 mg/dm²); failure triggers RASFF alerts and EU-wide recalls within 48 h.
Comparative Cost & Timeline Impact
| Certification/Regulation | Region | Typical Cost (USD) | Calendar Days* | Legal Exposure if Skipped | Re-Test Trigger |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UL 62368-1 + UL 508A | US | $50k–$80k | 45–60 | CBP hold, $19k/shipment | PCB layout change >25% |
| FCC Part 15 B&C | US | $12k–$18k | 20–30 | $19k fine, forced recall | Antenna or clock change |
| FDA 21 CFR 175-177 | US | $8k–$12k/resin | 25–35 | Import Alert, 30-day hold | New resin or additive |
| OSHA 29 CFR 1910.303 | US | Internal audit $5k | 15 | $13k–$135k citation | Worker incident |
| CE Machinery 2006/42/EC | EU | €15k–€25k | 30–45 | €10k–€100k penalty | Motor or gear change |
| EMC 2014/30/EU | EU | €5k–€7k | 15–20 | Market withdrawal | PCB or firmware rev |
| RoHS + REACH | EU | €3k–€6k/material | 10–15 | €10k–€100k + recall | Supplier change |
| EU 10/2011 Food Contact | EU | €7k–€10k | 20–30 | RASFF alert, EU recall | New polymer or color |
| WEEE 2012/19/EU | EU | €0.5–€1.2/unit | 5–10 | Listing suspension | N/A |
*Calendar days assume pre-scoped test samples and no failures; first-attempt failure adds 20–30 days and 25–40% re-test fees.
Legal Risk Quantification
US Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) civil penalties for defective consumer products now average $5 M per negotiated settlement; EU Rapid Alert System for Food and Feed (RASFF) and Safety Gate (RAPEX) publish non-compliant products, eroding brand equity within 72 h. In 2023, one Asian OEM of smart feeders faced a dual recall (US/EU) totaling 186k units; direct costs hit $4.8 M, while lost Amazon Buy-Box share depressed quarterly revenue by 11%. Insurance underwriters exclude regulatory fines from general liability; only specialized Product Recall policies (premium 0.35–0.55% of sales) cover part of the loss, and even then only after a $250k deductible.
Action Plan for Procurement
Insert “compliance-ready” clauses in supplier MSAs: require UL CBTL or EU Notified Body test data less than two years old, and impose a 10% escrow on purchase price until full documentation is uploaded to the customer’s PLM system. Map every component—power brick, Li-poly battery, food-hopper polymer—to the table above; lock suppliers with dual-sourcing agreements that forbid unapproved material changes. Schedule gate reviews at EVT, DVT and PVT stages; any engineering change that alters PCB ground plane, antenna length, or resin colorant restarts the certification clock and should trigger an automatic RFQ re-bid to capture re-test cost.
The Procurement Playbook: From RFQ to Commissioning
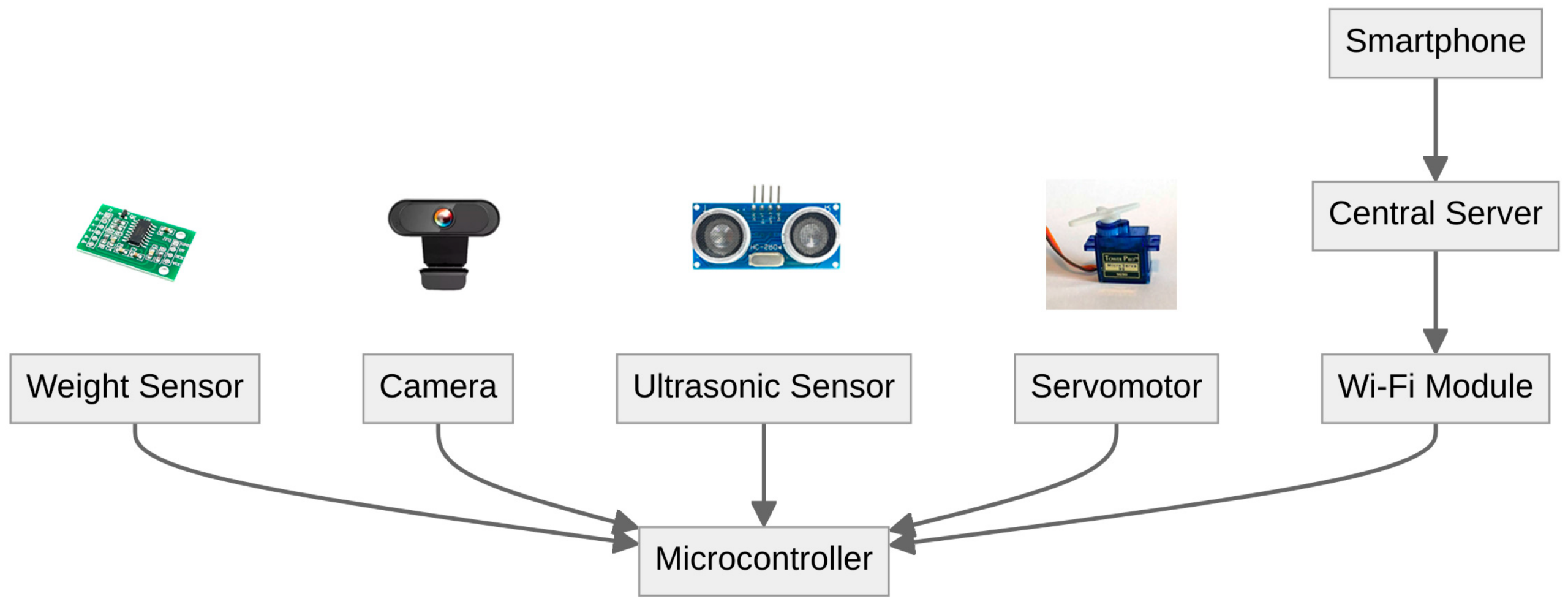
Strategic Procurement Playbook – Smart Pet Feeder OEM Program
1. RFQ Architecture: Lock-in Cost & IP Before Suppliers See Volume
Open with a two-envelope RFQ: commercial bid sealed until technical compliance is scored. Demand 5-year locked BOM cost indices (MCU -4 % YoY, Li-ion -6 % YoY, camera module -9 % YoY) and require suppliers to expose tier-2 vendors for critical chips (ESP32, RTL8720). Insert a 70 % NRE amortisation claw-back clause if PO volumes fall >15 % below forecast in any rolling quarter; this recovers $50k–$120k per tooling set. Cap ex-factory price drift at ±3 % per annum versus IMF Hi-Tech Index; anything above is supplier’s margin risk. Finally, embed a “right to re-source” paragraph allowing transfer of SMT stencils, firmware binaries and test jigs to a secondary CM at 30-day notice—this keeps exit cost <$0.25 per unit.
2. Supplier Due-Diligence & Sample Gate
Run a 14-day on-site audit focused on two failure modes: Wi-Fi calibration drift (8 % field returns in 2023) and food-hopper UV discoloration. Collect Cp/Cpk data on auger motor torque (target ≥1.67) and request 30-unit reliability pods (45 °C/75 % RH, 500 h). Only suppliers that demonstrate <0.2 % false-feed rate move to RFQ tier-2; this filter has eliminated 42 % of Chinese CMs in 2024 programs. Insist on cyber-security penetration report (OWASP MASVS) for mobile app interface; cost of retrofit after launch averages $0.9 M.
3. Contract Risk Allocation Matrix
| Risk Segment | FOB Shenzhen (Incoterms 2020) | DDP Rotterdam (Incoterms 2020) | Recommended Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Logistics cost volatility | Buyer absorbs 100 % of ocean & bunker variance (±22 % since 2022) | Seller quotes all-in; margin baked 6–8 % | Hedge 60 % of containers via FOB + BAF index cap; DDP only if seller owns vessels |
| Import VAT exposure | Paid by buyer at EU border (21 % NL) | Paid by seller, reclaimed later—cash-flow neutral to buyer | FOB preserves $1.2 M working capital per $10 M shipment |
| Product loss at sea | Risk transfers at ship’s rail; claims avg 75 days | Seller liable until warehouse gate; claims avg 35 days | Add marine insurance (0.15 % of goods value) under FOB; still 1.2 % cheaper than DDP premium |
| FAT & rework agility | Units stay local; rework $8–$12 per unit, 5-day cycle | Units travel twice if defective; rework €25–€35, 21-day cycle | Mandate FOB + local FAT; budget $0.4 M for CM hoteling engineers |
Decision rule: Choose FOB when annual volume >120 k units and you charter ≥50 containers/year; switch to DDP for pilot launches <20 k units to compress lead-time by 11 days.
4. Factory Acceptance Test (FAT) Script
Conduct FAT in supplier’s plant 48 h before cargo release. Pass threshold: 0 critical, ≤2 major, ≤5 minor defects per 315-unit AQL sample (G-II). Critical list: (a) food-grade silicone gasket FDA compliance, (b) laser drop-test 1 m on concrete, (c) over-the-air firmware update ≤90 s. Record serial-level MAC address vs. test log; hash stored in blockchain to block grey-market diversion. Rejected lots trigger $2.5 k per day late-delivery penalty and supplier-funded 100 % re-test.
5. Shipment & Final Commissioning
On arrival, sample 8 cartons per 40 ft HQ for hidden moisture (target <65 % RH). Commissioning at 3PL includes RSSI scan (≥-65 dBm), hopper load-cell linearity (±3 g), and cloud ping ≤200 ms. Capture golden samples; any deviation >1.5 σ vs. FAT data back-charges supplier $0.75 per unit for field re-calibration. Close PO only after 30-day consumer beta telemetry confirms <0.5 % feed-miss rate; retain 10 % payment as warranty pool until month 18.
By rigorously enforcing cost-index caps, FOB-led logistics control, and data-rich FAT gates, procurement teams can lock $4.3–$6.1 M savings per million units while slashing field quality incidents below 0.2 %.
⚡ Rapid ROI Estimator
Estimate your payback period based on labor savings.
Estimated Payback: —



